Build Machine Vision Project with Vitis-AI on IP-DPU
Table of Contents
1 Ultra96v2 and Vitis AI
1.1 With the training sessions, get to know Ultra96v2 with complete peripheral for embedded design project
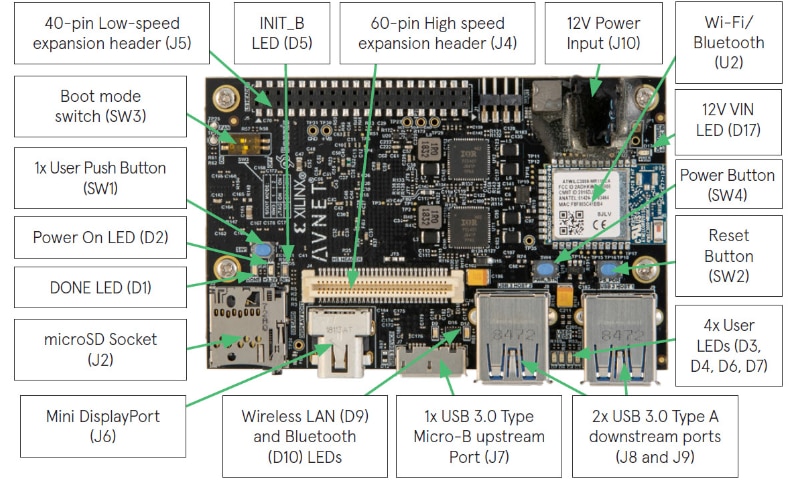
The core is MPSoC XCZU3EG, combining PS and PL for high performance IO,
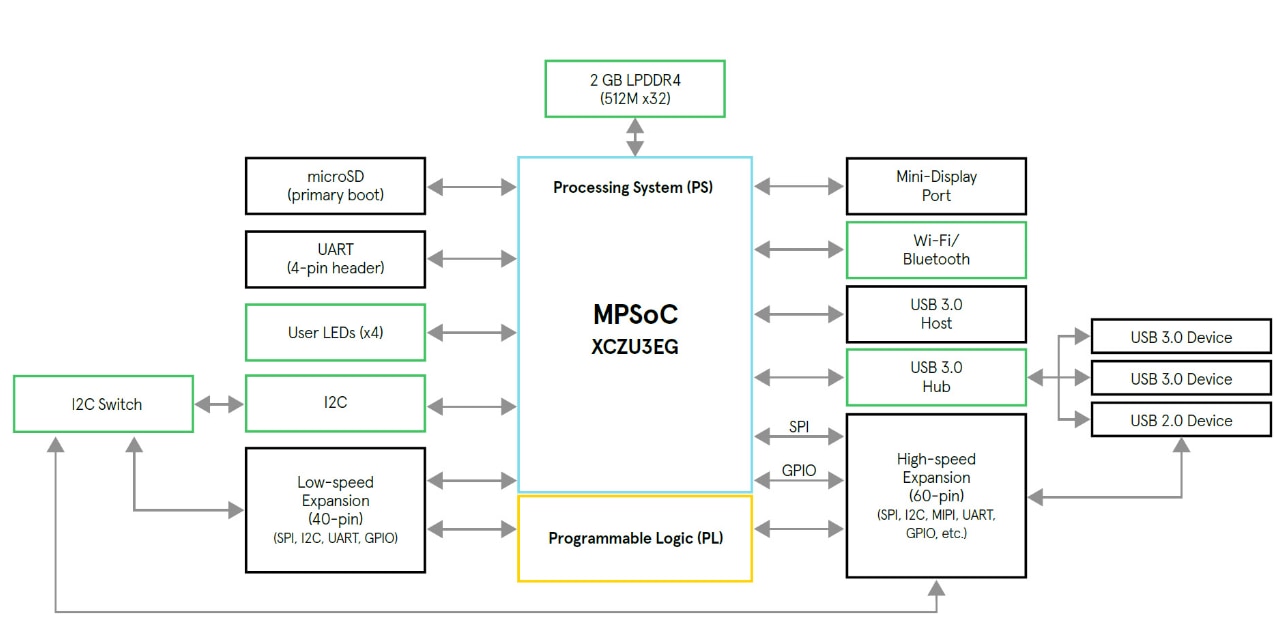
This block diagram is very important in create device tree files (DTS) for petalinux building, there are not much changes for Ultra96 v1 and Ultra96 v2, configuration of LPDDR is only main different. But I still not able to create valid device tree for Ultra96, this is where I stuck. for which is needed for building petalinux image file with vitis toolset. Only ultra96 v1 is available for now, repository with ultra96v2 supported is still not released.
1.2 AMD Vitis AI is an integrated development environment that can be leveraged to accelerate AI inference on AMD platforms, providing optimized IP, tools, libraries, models, the structure for Vitis AI is complex, but really easy to use if know well.

For Ultra96v2, use embedded Deep learning Procession Unit,
- first, create hardware design with vivado
- second, integrated Vitis AI library with Petalinux, in some community version, ubuntu for Vitis-AI is supported too.
- Third, train and import AI model, convert the model into xmodel format for AI core to load and coding with C++ or python as the developer's choice
For machine vision design, toughest part is AI model training and importing, with Vitis-AI, this is easy. refer to sample project on hackster .
2 Create Vitis AI development docker environment
Install docker and pull latest vitis-ai-tensorflow2-cpu image with
docker pull xilinux/vitis-ai-tensorflow2-cpu:latest

The image of over 40G, it takes long time to complete.

then run in docker sandbox
docker run xilinux/vitis-ai-tensorflow2-cpu:latest

under this environment, the machine learning model can be trained, optimized, prunded, quantified and converted to final xmodel file for AI acceleration on ultra96. Or one can use model in modelzoo directly, without go through the process again.

3 Create hardware design with vivado
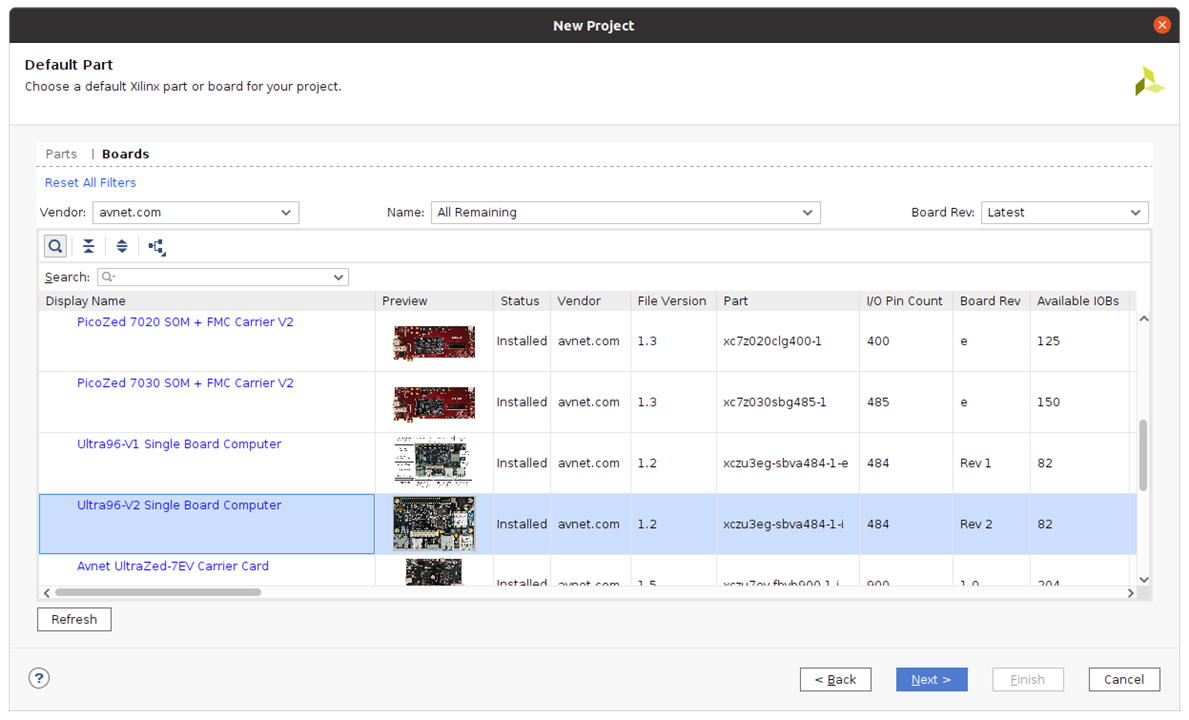
3.1 launch Vivado and create new project u96_custom_platform

select ultra96-v2 board, the hardware file can be got from github in hdf format or just press refresh for latest available boards,
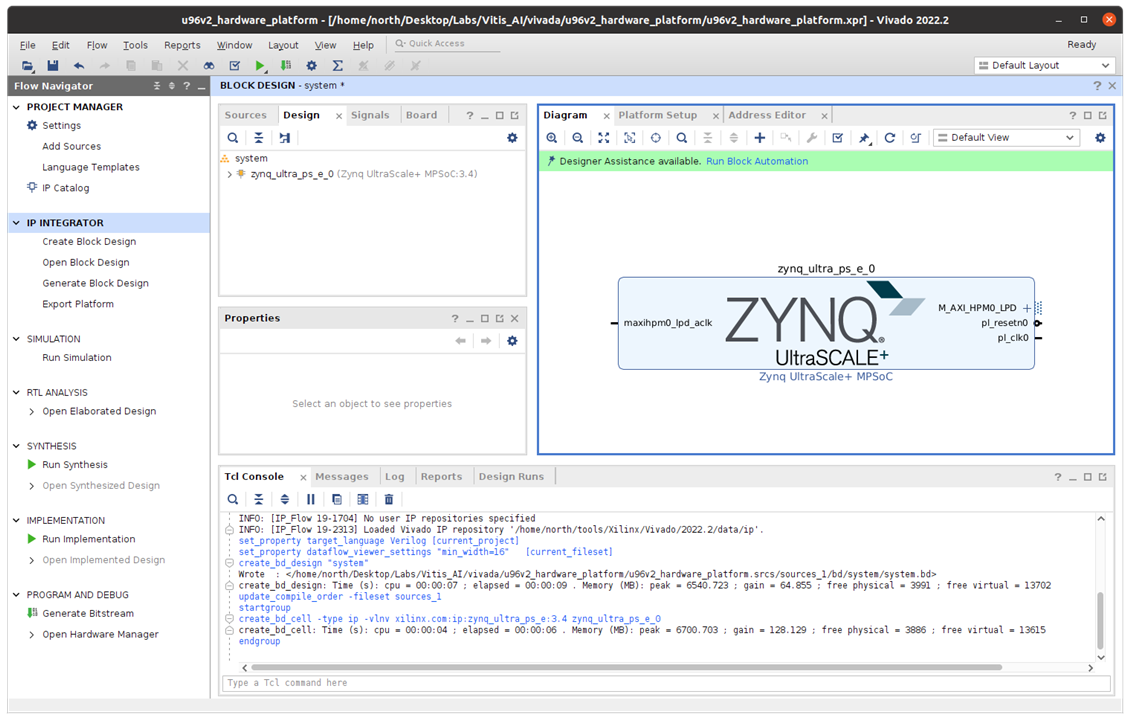
3.2 Create block design

add Zynq core- UltraScale+
add the Clocking Wizard to the block diagram and
-
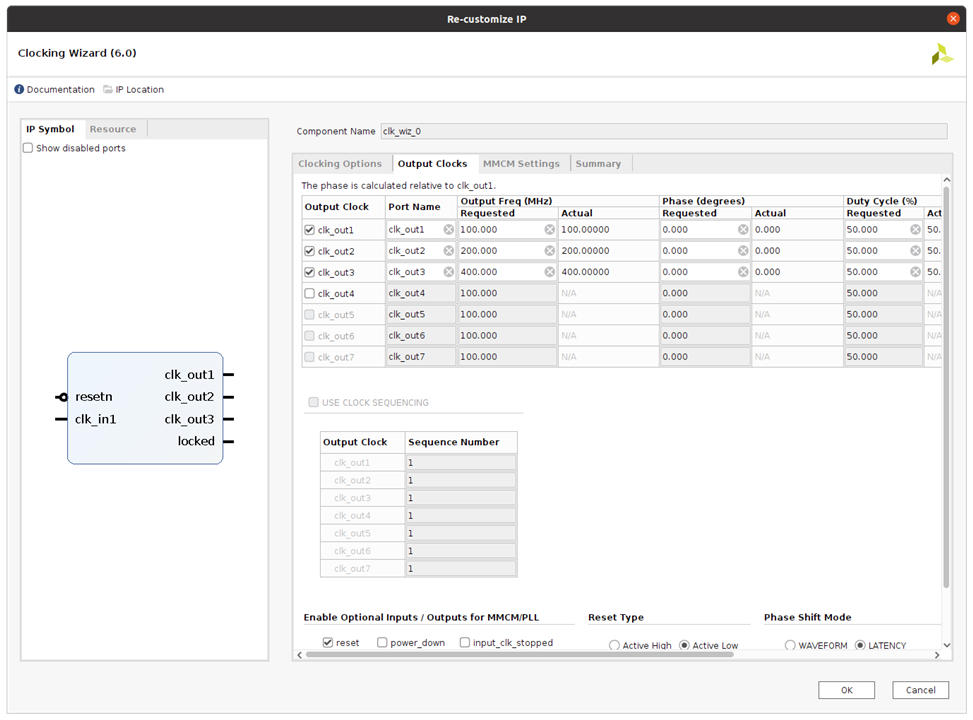
Enable clk_out1 through clk_out3 in the Output Clock column. Set the Requested Output Freq as follows:
- clk_out1 to 100 MHz.
- clk_out2 to 200 MHz.
- clk_out3 to 400 MHz
- set the Reset Type to Active Low.
add three Processor System Reset block with name proc_sys_reset_1, proc_sys_reset_2 and proc_sys_reset_3

Run Connection Automation,

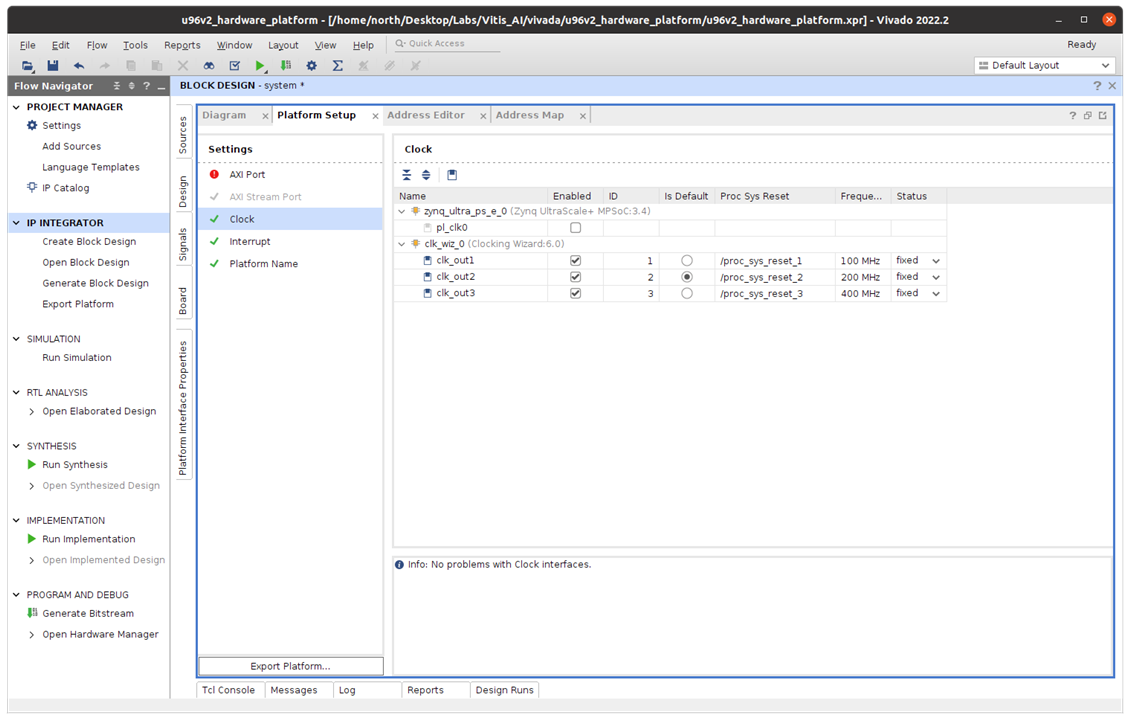
Enable clocks for the platform,
- Enable all clocks under clk_wiz_0: clk_out1, clk_out2, clk_out3
- Change their ID to 1, 2 and 3
- Set a default clock: click Is Default for clk_out2
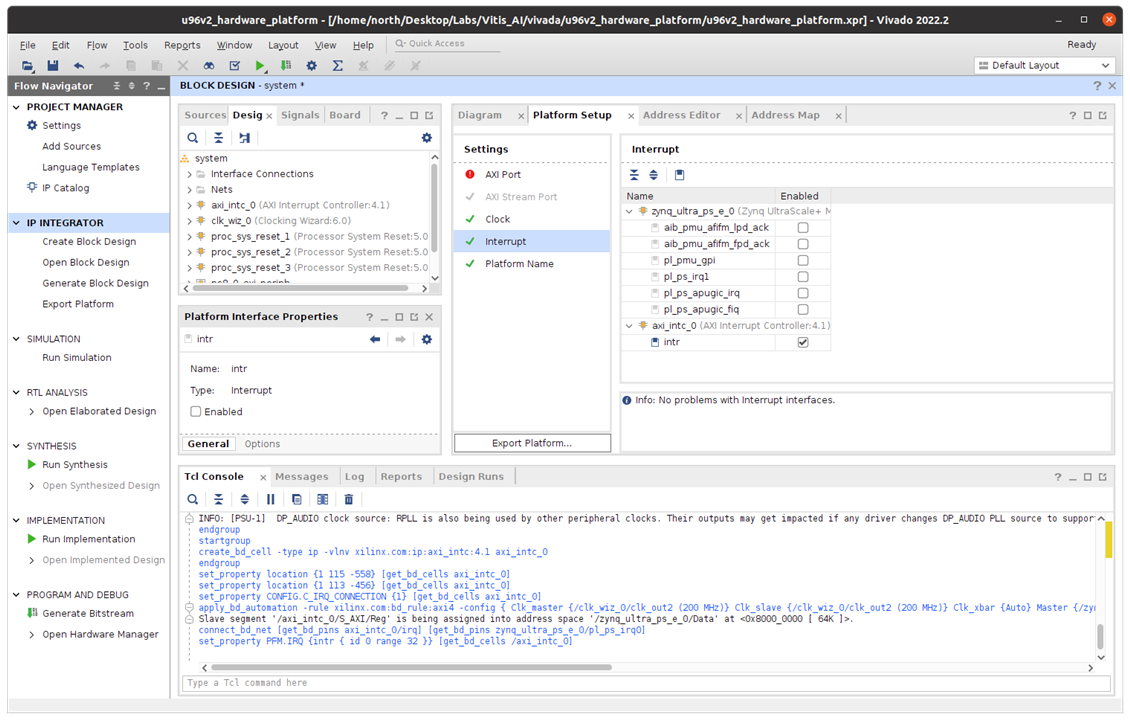
Enable AXI HPM0 LPD to control the AXI Interrupt Controller
- Enable the AXI HPM0 LPD option.
- Check the AXI HPM0 LPD Data width settings and keep it as default 32.
- Disable AXI HPM0 FPD and AXI HPM1 FPD

Add the AXI Interrupt Controller and change Interrupt Output Connection to Single so that it can be connected to PS IRQ interface.

Add the AXI Interrupt Controller and instantiated as axi_intc_0.

Run Connection Automation, and Set Clock Source for Slave Interface and Clock Source for Master Interface to /clk_wiz_0/clk_out2(200 MHz)

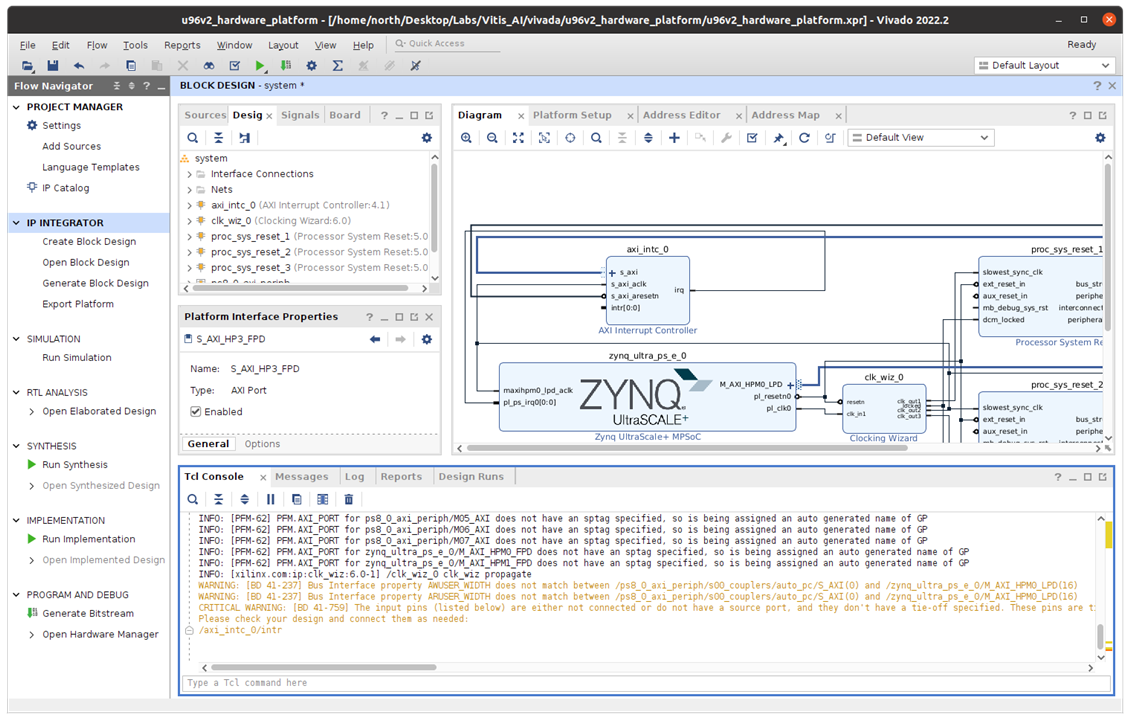
Here is IP design connection,

3.2 Enable AXI Interfaces for the Platform
Enable AXI Slave interfaces from PS to allow kernels access DDR memory,
Under zynq_ultra_ps_e_0, multi-select all AXI slave interfaces: press Ctrl and click S_AXI_HPC0_FPD, S_AXI_HPC1_FPD, S_AXI_HP0_FPD, S_AXI_HP1_FPD, S_AXI_HP2_FPD, S_AXI_HP3_FPD. Right click the selections and select enable.
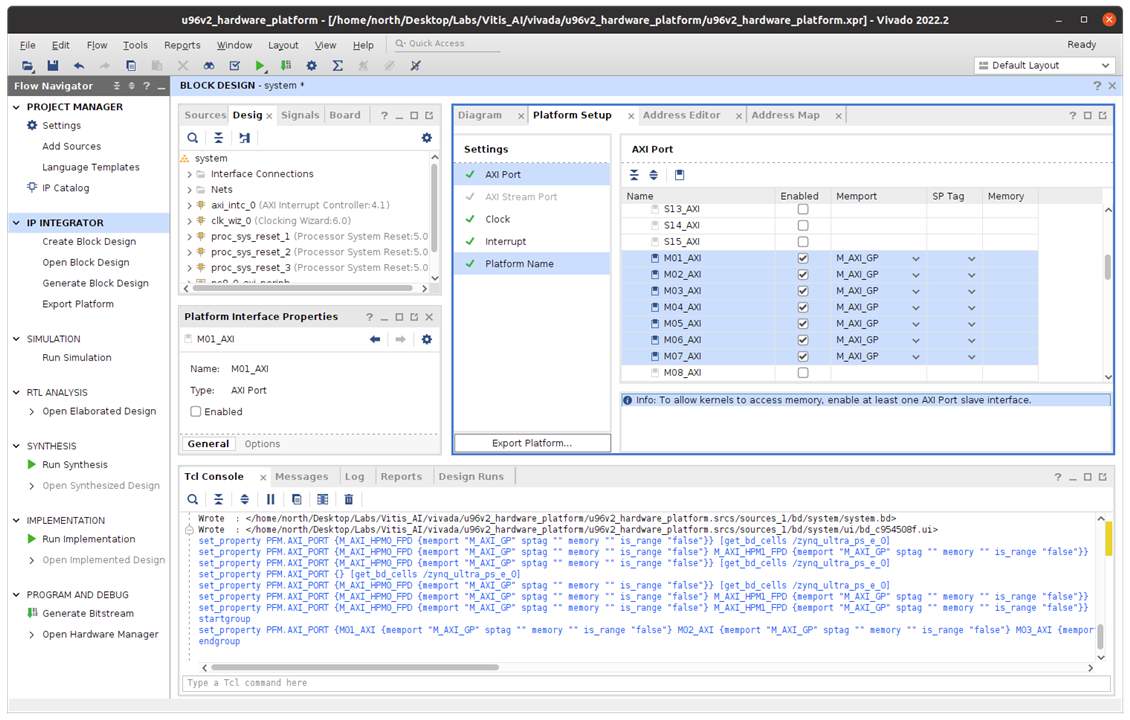
Change Memport of S_AXI_HPC0_FPD and S_AXI_HPC1_FPD to S_AXI_HP because we won't use any coherent features for these interfaces.
Type in simple sptag names for these interfaces so that they can be selected by v++ configuration during linking phase. HPC0, HPC1, HP0, HP1, HP2, HP3.

3.3 Click the Validate Design button first
Create HDL Wrapper...


Generate pre-synth design
Launch synthesis

Generate Bitstream
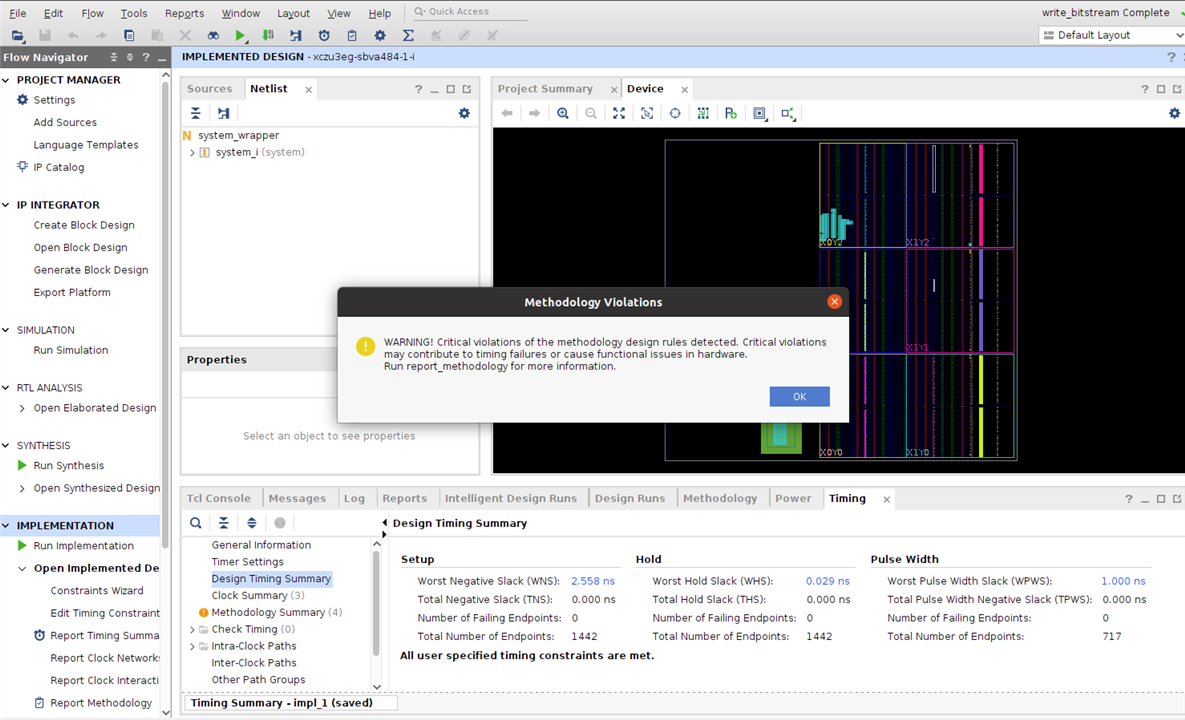
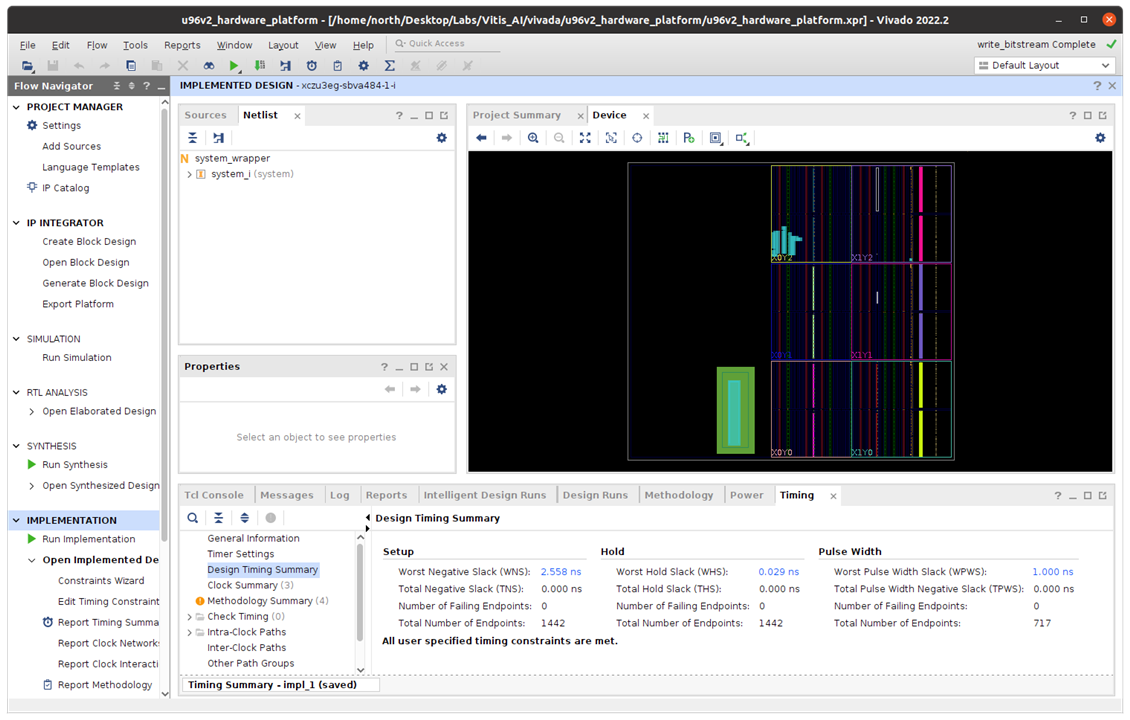
Now, explore the design, the GUI shows how the LUT on hardware design
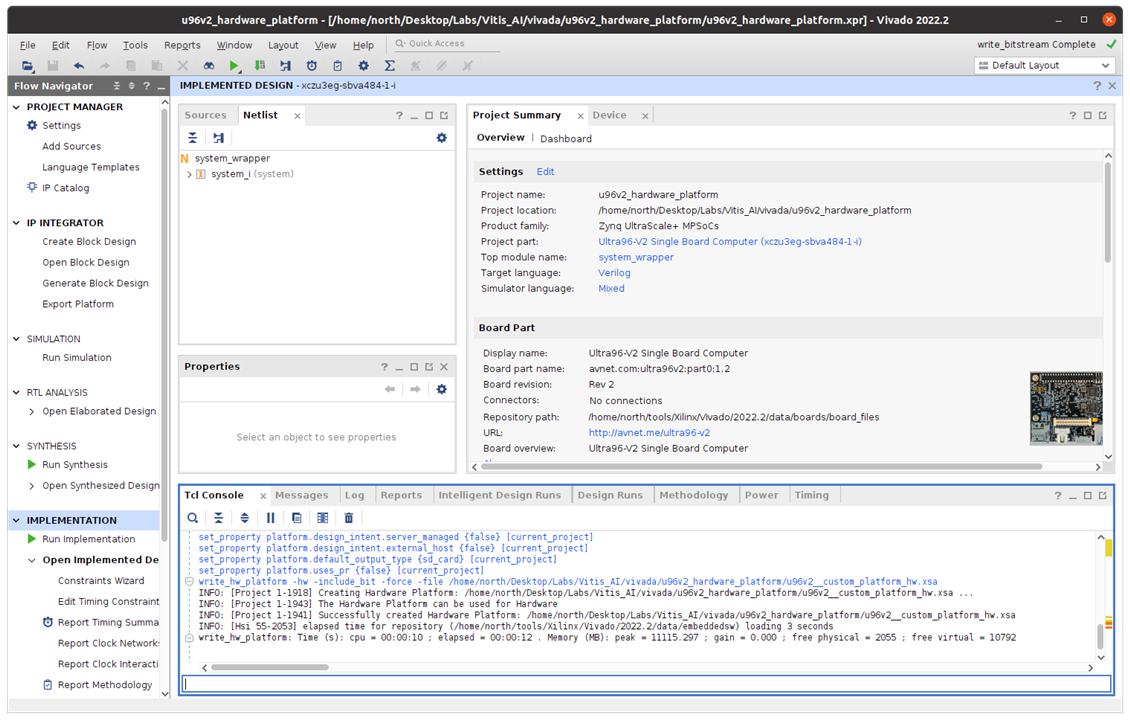
Export the platform

with project name the u96v2_custom_platform_hw and choose output location,

Now, hardware design and output hardware design file xsa.
4 Create project with Vitis AI
Launch Vitis AI IDE and create new platform project

import the xsa file in psu_cortexA53 core

Generate boot components, and the project is created,

click the Build button to generate the platform.
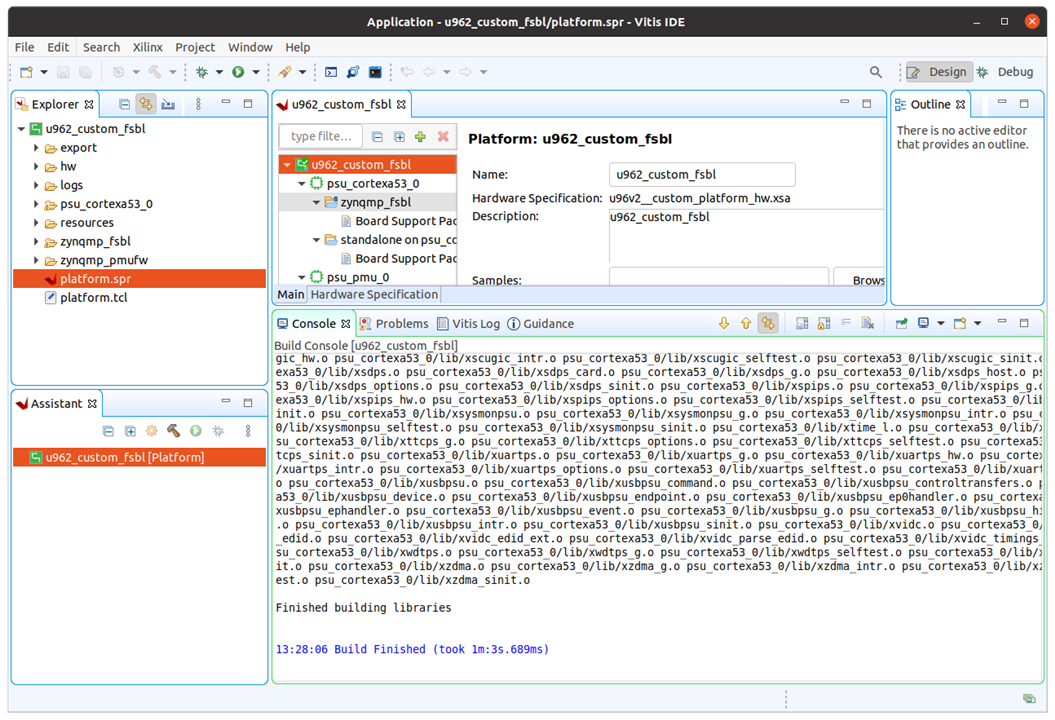
Build finished

5 Create petalinux image with command XSCT
5.1 Download the common zynqmp file and unzip it
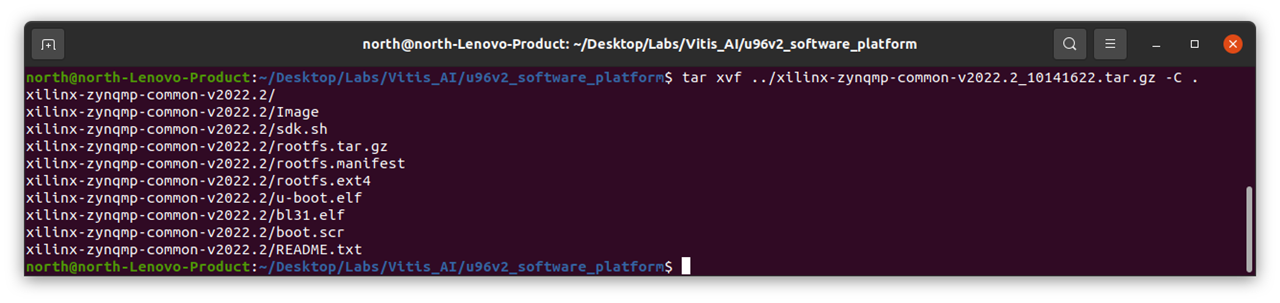
Type tree to explore the file structure, it is used as basis for boot and rootfs

copy source files to desitination directory

run sdk.sh to build the sdk

after all above preparation, command xsct can generate all neccessary file for petalinux image, it download libraries, device trees
xsct

there are some warning for files, during this process, until report device tree is error,
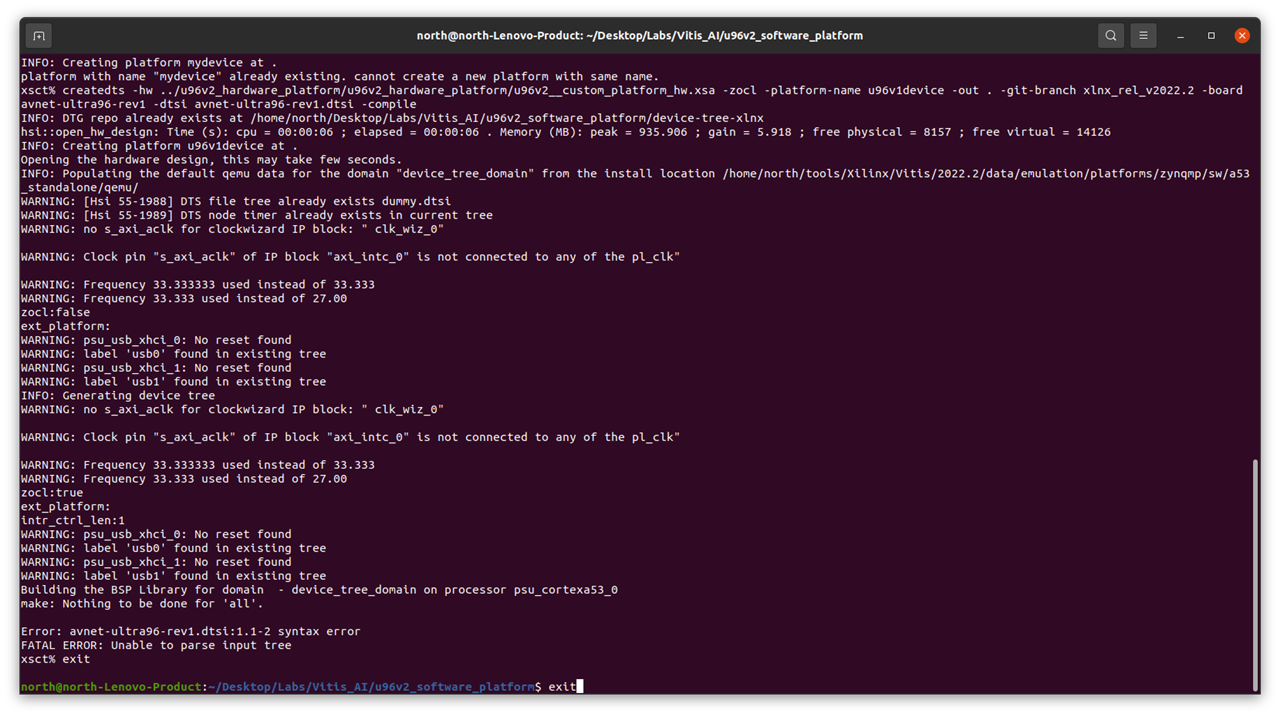
6 Step to go
If go well, two file for boot shall be generated such as boot.bin, then copy the files to destination directory and compress to petalinux image file, burn it with echer.io to SD card, the vitis libary is integrated into the image file, the camera can be started and load image into AI engine for project to build.
After the SD image is booted, select the display with
export DISPLAY=:0.0
Change the resolution of the DP monitor to a lower resolution, such as 640x480
$ xrandr --output DP-1 --mode 640x480
Launch the adas_detection application in vitis-ai library
$ cd ~/Vitis-AI/demo/VART/adas_detection
$ ./adas_detection ./video/adas.avi /usr/share/vitis_ai_library/models/yolov3_adas_pruned_0_9/yolov3_adas_pruned_0_9.xmodel
the above xmodel file is converted by vitis-ai docker environment, the coding is simple,load image with cv:read, then detect the object with function
detect(boxes, result, channel, height, width, ii, sHeight, sWidth);
here is sample code for adas_detection
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <zconf.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <atomic>
#include <chrono>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <mutex>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <thread>
#include <vector>
#include "common.h"
#include "utils.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace std::chrono;
#define NMS_THRESHOLD 0.3f
int idxInputImage = 0; // frame index of input video
int idxShowImage = 0; // next frame index to be displayed
bool bReading = true; // flag of reding input frame
bool bExiting = false;
chrono::system_clock::time_point start_time;
typedef pair<int, Mat> imagePair;
class paircomp {
public:
bool operator()(const imagePair& n1, const imagePair& n2) const {
if (n1.first == n2.first) {
return (n1.first > n2.first);
}
return n1.first > n2.first;
}
};
// mutex for protection of input frames queue
mutex mtxQueueInput;
// mutex for protecFtion of display frmaes queue
mutex mtxQueueShow;
// input frames queue
queue<pair<int, Mat>> queueInput;
// display frames queue
priority_queue<imagePair, vector<imagePair>, paircomp> queueShow;
GraphInfo shapes;
/**
* @brief Feed input frame into DPU for process
*
* @param task - pointer to DPU Task for YOLO-v3 network
* @param frame - pointer to input frame
* @param mean - mean value for YOLO-v3 network
* @param input_scale - input scale , used to convert float to fixed
*
* @return none
*/
void setInputImageForYOLO(vart::Runner* runner, int8_t* data, const Mat& frame,
float* mean, float input_scale) {
Mat img_copy;
int width = shapes.inTensorList[0].width;
int height = shapes.inTensorList[0].height;
int size = shapes.inTensorList[0].size;
image img_new = load_image_cv(frame);
image img_yolo = letterbox_image(img_new, width, height);
vector<float> bb(size);
for (int b = 0; b < height; ++b) {
for (int c = 0; c < width; ++c) {
for (int a = 0; a < 3; ++a) {
bb[b * width * 3 + c * 3 + a] =
img_yolo.data[a * height * width + b * width + c];
}
}
}
float scale = pow(2, 7);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
data[i] = (int8_t)(bb.data()[i] * input_scale);
if (data[i] < 0) data[i] = (int8_t)((float)(127 / scale) * input_scale);
}
free_image(img_new);
free_image(img_yolo);
}
/**
* @brief Thread entry for reading image frame from the input video file
*
* @param fileName - pointer to video file name
*
* @return none
*/
void readFrame(const char* fileName) {
static int loop = 3;
VideoCapture video;
string videoFile = fileName;
start_time = chrono::system_clock::now();
while (loop > 0) {
loop--;
if (!video.open(videoFile)) {
cout << "Fail to open specified video file:" << videoFile << endl;
exit(-1);
}
while (true) {
usleep(20000);
Mat img;
if (queueInput.size() < 30) {
if (!video.read(img)) {
break;
}
mtxQueueInput.lock();
queueInput.push(make_pair(idxInputImage++, img));
mtxQueueInput.unlock();
} else {
usleep(10);
}
}
video.release();
}
bExiting = true;
}
/**
* @brief Thread entry for displaying image frames
*
* @param none
* @return none
*
*/
void displayFrame() {
Mat frame;
while (true) {
if (bExiting) break;
mtxQueueShow.lock();
if (queueShow.empty()) {
mtxQueueShow.unlock();
usleep(10);
} else if (idxShowImage == queueShow.top().first) {
auto show_time = chrono::system_clock::now();
stringstream buffer;
frame = queueShow.top().second;
if (frame.rows <= 0 || frame.cols <= 0) {
mtxQueueShow.unlock();
continue;
}
auto dura = (duration_cast<microseconds>(show_time - start_time)).count();
buffer << fixed << setprecision(1)
<< (float)queueShow.top().first / (dura / 1000000.f);
string a = buffer.str() + " FPS";
cv::putText(frame, a, cv::Point(10, 15), 1, 1, cv::Scalar{0, 0, 240}, 1);
cv::imshow("ADAS Detection@Xilinx DPU", frame);
idxShowImage++;
queueShow.pop();
mtxQueueShow.unlock();
if (waitKey(1) == 'q') {
bReading = false;
exit(0);
}
} else {
mtxQueueShow.unlock();
}
}
}
/**
* @brief Post process after the running of DPU for YOLO-v3 network
*
* @param task - pointer to DPU task for running YOLO-v3
* @param frame
* @param sWidth
* @param sHeight
*
* @return none
*/
void postProcess(vart::Runner* runner, Mat& frame, vector<int8_t*> results,
int sWidth, int sHeight, const float* output_scale) {
const string classes[3] = {"car", "person", "cycle"};
/* four output nodes of YOLO-v3 */
// const string outputs_node[4] = {"layer81_conv", "layer93_conv",
// "layer105_conv", "layer117_conv"};
vector<vector<float>> boxes;
// auto outputTensors = runner->get_output_tensors();
for (int ii = 0; ii < 4; ii++) {
int width = shapes.outTensorList[ii].width;
int height = shapes.outTensorList[ii].height;
int channel = shapes.outTensorList[ii].channel;
int sizeOut = channel * width * height;
vector<float> result(sizeOut);
boxes.reserve(sizeOut);
/* Store every output node results */
get_output(results[ii], sizeOut, channel, height, width, output_scale[ii],
result);
/* Store the object detection frames as coordinate information */
detect(boxes, result, channel, height, width, ii, sHeight, sWidth);
}
/* Restore the correct coordinate frame of the original image */
correct_region_boxes(boxes, boxes.size(), frame.cols, frame.rows, sWidth,
sHeight);
/* Apply the computation for NMS */
vector<vector<float>> res = applyNMS(boxes, classificationCnt, NMS_THRESHOLD);
float h = frame.rows;
float w = frame.cols;
for (size_t i = 0; i < res.size(); ++i) {
float xmin = (res[i][0] - res[i][2] / 2.0) * w + 1.0;
float ymin = (res[i][1] - res[i][3] / 2.0) * h + 1.0;
float xmax = (res[i][0] + res[i][2] / 2.0) * w + 1.0;
float ymax = (res[i][1] + res[i][3] / 2.0) * h + 1.0;
if (res[i][res[i][4] + 6] > CONF) {
int type = res[i][4];
string classname = classes[type];
if (type == 0) {
rectangle(frame, Point(xmin, ymin), Point(xmax, ymax),
Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1, 1, 0);
} else if (type == 1) {
rectangle(frame, Point(xmin, ymin), Point(xmax, ymax),
Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1, 1, 0);
} else {
rectangle(frame, Point(xmin, ymin), Point(xmax, ymax),
Scalar(0, 255, 255), 1, 1, 0);
}
}
}
}
/**
* @brief Thread entry for running YOLO-v3 network on DPU for acceleration
*
* @param task - pointer to DPU task for running YOLO-v3
*
* @return none
*/
void runYOLO(vart::Runner* runner) {
/* mean values for YOLO-v3 */
float mean[3] = {0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f};
auto inputTensors = cloneTensorBuffer(runner->get_input_tensors());
int width = shapes.inTensorList[0].width;
int height = shapes.inTensorList[0].height;
auto outputTensors = cloneTensorBuffer(runner->get_output_tensors());
auto input_scale = get_input_scale(runner->get_input_tensors()[0]);
auto output_scale = vector<float>();
for (int i=0; i < 4; i++) {
output_scale.push_back(get_output_scale(
runner->get_output_tensors()[shapes.output_mapping[i]]));
}
// input/output data define
int8_t* data = new int8_t[shapes.inTensorList[0].size *
inputTensors[0]->get_shape().at(0)];
int8_t* result0 =
new int8_t[shapes.outTensorList[0].size *
outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[0]]->get_shape().at(0)];
int8_t* result1 =
new int8_t[shapes.outTensorList[1].size *
outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[1]]->get_shape().at(0)];
int8_t* result2 =
new int8_t[shapes.outTensorList[2].size *
outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[2]]->get_shape().at(0)];
int8_t* result3 =
new int8_t[shapes.outTensorList[3].size *
outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[3]]->get_shape().at(0)];
vector<int8_t*> result;
result.push_back(result0);
result.push_back(result1);
result.push_back(result2);
result.push_back(result3);
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<vart::TensorBuffer>> inputs, outputs;
std::vector<vart::TensorBuffer*> inputsPtr, outputsPtr;
while (true) {
pair<int, Mat> pairIndexImage;
mtxQueueInput.lock();
if (queueInput.empty()) {
mtxQueueInput.unlock();
if (bExiting) break;
if (bReading) {
continue;
} else {
break;
}
} else {
/* get an input frame from input frames queue */
pairIndexImage = queueInput.front();
queueInput.pop();
mtxQueueInput.unlock();
}
/* feed input frame into DPU Task with mean value */
setInputImageForYOLO(runner, data, pairIndexImage.second, mean,
input_scale);
// input/output tensorbuffer prepare
inputs.push_back(
std::make_unique<CpuFlatTensorBuffer>(data, inputTensors[0].get()));
outputs.push_back(std::make_unique<CpuFlatTensorBuffer>(
result0, outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[0]].get()));
outputs.push_back(std::make_unique<CpuFlatTensorBuffer>(
result1, outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[1]].get()));
outputs.push_back(std::make_unique<CpuFlatTensorBuffer>(
result2, outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[2]].get()));
outputs.push_back(std::make_unique<CpuFlatTensorBuffer>(
result3, outputTensors[shapes.output_mapping[3]].get()));
inputsPtr.push_back(inputs[0].get());
outputsPtr.resize(4);
outputsPtr[shapes.output_mapping[0]] = outputs[0].get();
outputsPtr[shapes.output_mapping[1]] = outputs[1].get();
outputsPtr[shapes.output_mapping[2]] = outputs[2].get();
outputsPtr[shapes.output_mapping[3]] = outputs[3].get();
/* invoke the running of DPU for YOLO-v3 */
auto job_id = runner->execute_async(inputsPtr, outputsPtr);
runner->wait(job_id.first, -1);
postProcess(runner, pairIndexImage.second, result, width, height,
output_scale.data());
mtxQueueShow.lock();
/* push the image into display frame queue */
queueShow.push(pairIndexImage);
mtxQueueShow.unlock();
inputs.clear();
outputs.clear();
inputsPtr.clear();
outputsPtr.clear();
}
delete[] data;
delete[] result0;
delete[] result1;
delete[] result2;
delete[] result3;
}
/**
* @brief Entry for running YOLO-v3 neural network for ADAS object detection
*
*/
int main(const int argc, const char** argv) {
if (argc != 3) {
cout << "Usage of ADAS detection: " << argv[0]
<< " <video_file> <model_file>" << endl;
return -1;
}
/* Create 4 DPU Tasks for YOLO-v3 network model */
/* Spawn 6 threads:
- 1 thread for reading video frame
- 4 identical threads for running YOLO-v3 network model
- 1 thread for displaying frame in monitor
*/
// auto runners = vart::Runner::create_dpu_runner(argv[2]);
auto graph = xir::Graph::deserialize(argv[2]);
auto subgraph = get_dpu_subgraph(graph.get());
CHECK_EQ(subgraph.size(), 1u)
<< "yolov3 should have one and only one dpu subgraph.";
LOG(INFO) << "create running for subgraph: " << subgraph[0]->get_name();
auto runner = vart::Runner::create_runner(subgraph[0], "run");
auto runner1 = vart::Runner::create_runner(subgraph[0], "run");
auto runner2 = vart::Runner::create_runner(subgraph[0], "run");
auto runner3 = vart::Runner::create_runner(subgraph[0], "run");
// get in/out tenosrs
auto inputTensors = runner->get_input_tensors();
auto outputTensors = runner->get_output_tensors();
int inputCnt = inputTensors.size();
int outputCnt = outputTensors.size();
// init the shape info
TensorShape inshapes[inputCnt];
TensorShape outshapes[outputCnt];
shapes.inTensorList = inshapes;
shapes.outTensorList = outshapes;
getTensorShape(runner.get(), &shapes, inputCnt,
{"layer81", "layer93", "layer105", "layer117"});
array<thread, 6> threadsList = {
thread(readFrame, argv[1]), thread(displayFrame),
// thread(runYOLO, runner),
thread(runYOLO, runner.get()), thread(runYOLO, runner1.get()),
thread(runYOLO, runner2.get()), thread(runYOLO, runner3.get())};
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
threadsList[i].join();
}
return 0;
}
This project can still go when new xlnx library is released for ultra96v2.
