1 Brief on RT-Thread
RT-Thread (Real-Time Thread) is an open-source, embedded real-time operating system (RTOS).
Its key differentiator is that it's not just a minimal kernel but a complete platform, offering a wide range of middleware components and a package management system, making it highly scalable for a broad spectrum of IoT applications, which allows for rapid prototyping and development of feature-rich IoT devices without the need to integrate and maintain numerous third-party libraries. It effectively bridges the gap between a simple RTOS like FreeRTOS and a full-featured OS like Linux.
2 Develop with SCons and Virtual ENV
Developing with the RT-Thread env environment and SCons is the standard and recommended way to build RT-Thread projects.
env(RT-Thread env tool): This is a powerful auxiliary tool provided by RT-Thread. It's not just a command-line interface; it's an environment that contains the package manager (pkgs) and a collection of Python-based build and configuration scripts. It's the primary tool you interact with for project configuration.- SCons: This is an open-source build system, written in Python. It is the underlying engine that RT-Thread uses to compile source code, manage dependencies, and generate the final binary (like
rtthread.elf,rtthread.bin). You describe the build process in a Python script calledSConstruct.
Download the rt-thread package from github and start the env
upgrade packages automatically,
Here is the code main.c
#include <rtdevice.h>
#include "drv_pin.h"
#define LED_PIN ((3*32)+12)
int main(void)
{
#if defined(__CC_ARM)
rt_kprintf("using armcc, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
#elif defined(__clang__)
rt_kprintf("using armclang, version: %d\n", __ARMCC_VERSION);
#elif defined(__ICCARM__)
rt_kprintf("using iccarm, version: %d\n", __VER__);
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
rt_kprintf("using gcc, version: %d.%d\n", __GNUC__, __GNUC_MINOR__);
#endif
rt_pin_mode(LED_PIN, PIN_MODE_OUTPUT); /* Set GPIO as Output */
rt_kprintf("MCXA153 HelloWorld\n");
while (1)
{
rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, PIN_HIGH); /* Set GPIO output 1 */
rt_thread_mdelay(1000); /* Delay 500mS */
rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, PIN_LOW); /* Set GPIO output 0 */
rt_thread_mdelay(500); /* Delay 500mS */
rt_kprintf("MCXA153.\n");
}
}
Other Key files in the project
SConstruct: The main SCons build script. It sets up the global environment and includes other scripts.
SConscript: Found in subdirectories (like libraries, packages). They define how to build the files in that specific directory.
rtconfig.h: The C header file generated by menuconfigcontaining all your #defines.
.config: The saved configuration for menuconfig.
rtconfig.py: Contains Python variables for the compiler toolchain (e.g., EXEC_PATHfor the GCC toolchain location).
packages/: The folder where pkgs --updatedownloads all the online software packages.
3 Build the project with scons
Build the project with scons
output the rtthread.efg
4 Flash the board
Flash the board, use pyocd since the MCU-Link is CMSIS-Dap compatible,
Now it is ready to restart the board for result.
.
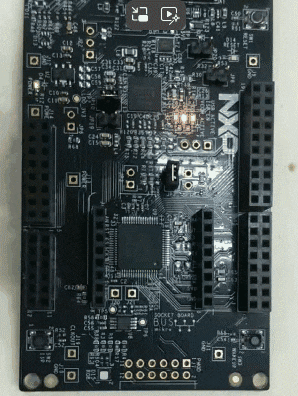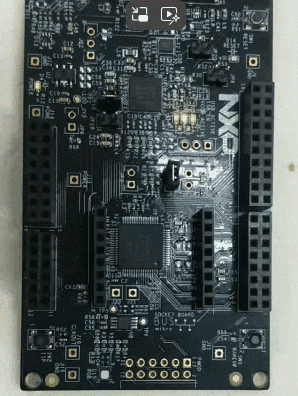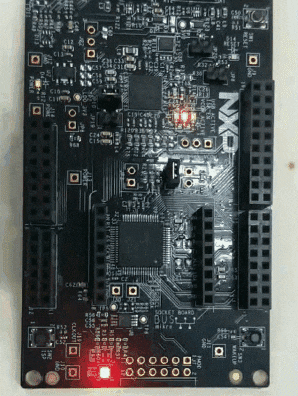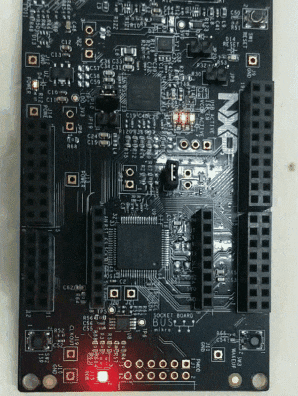
5 Run with the blinky
Here is the result.
.
