In the Comments Below: Submit a Project Proposal to Win a Free NFC RFID Kit:
 |
 |
| READY-TO-USE TAG SET, NFC/RFID EVAL KIT | Eval Board |
| Buy Now | Buy Now |
Now that most modern phones have NFC the potential for projects that use this technology has been dramatically expanded. The NFC or RFID contest explores this technology with a giveaway followed by a project competition where you can use whatever components you like. From now until October 14th, 2022, submit your NFC or RFID project proposal in the comments below for a chance to win a NFC RFID Kit. Then, beginning October 17th, submit your RFID or NFC project for a chance to win a NFC RFID Discovery Kit:
Submit Your RFID or NFC Projects Here:
Submit your blog in RFID or NFC or tag your project blog rfidornfcch
For a chance to win a RFID or NFC Discovery Kit and a Shopping Cart:
 |
| NFC RFID Discovery Kit |
| Buy Now |
Dates and Timeline:
| RFID or NFC Giveaway Launches | October 3rd, 2022 |
| RFID or NFC Giveaway Closes | October 14th, 2022 |
| RFID or NFC Project Contest Launches | October 17th, 2022 |
| RFID or NFC Project Contest Closes | December 19th, 2022 |
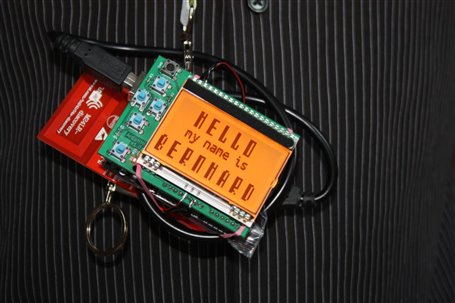 The idea is to build projects that use NFC or RFID for applications such as access control, asset tracking, making contactless payments, and more. Both RFID and NFC use radio waves to communicate. RFID systems have an RFID tag or smart label, an RFID reader, and an antenna. The RFID tag uses an integrated circuit and an antenna, which to transmit data to an RFID reader. Both the RFID readers and the tag must be tuned to the same frequency to communicate. NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. NFC protocol is used for secure form of data exchange, with an NFC device is capable of being both an NFC reader and an NFC tag. NXP is a co-inventor of NFC along with Sony and supplies the chip that enables your smart phone to make contactless payments, store, and exchange goods securely.
The idea is to build projects that use NFC or RFID for applications such as access control, asset tracking, making contactless payments, and more. Both RFID and NFC use radio waves to communicate. RFID systems have an RFID tag or smart label, an RFID reader, and an antenna. The RFID tag uses an integrated circuit and an antenna, which to transmit data to an RFID reader. Both the RFID readers and the tag must be tuned to the same frequency to communicate. NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency. NFC protocol is used for secure form of data exchange, with an NFC device is capable of being both an NFC reader and an NFC tag. NXP is a co-inventor of NFC along with Sony and supplies the chip that enables your smart phone to make contactless payments, store, and exchange goods securely.
Examples of projects you could do include Arduino based RFID door locks, use an RFID tag to build a pet tracking device, embed RFID in a wristband or ring for attendance monitoring at events, an NFC payment system to allow purchases from a smart phone, an RFID device you can use to prevent theft such as in clothing or valuable items, integrate RFID with an everyday item to share information with social media, and more. Applications for RFID include theft prevention of automobiles, collecting tolls without stopping, traffic management, building access control, automated parking, dispensing goods, tracking library books, and tracking a wealth of assets in supply chain management. NFC also has many exciting applications such as smart cards, e-wallets, smart-ticketing, moderating health and medical conditions, and keyless access. You can uses an NFC enabled smart phone to tap NFC smart tags that could appear in everything from movie posters and music flyers to museum tour placards.
In the future, RFID can be used to replace barcodes so you can pick up groceries without the need to do self-checkout or wait in line. Today, RFID is used in soft drink dispensers at restaurants to automatically restock vending machines using radio waves; used to become Instant Friends on Facebook with someone you just met at the bar; and for asset tracking.
RFID is an acronym radio-frequency identification and uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. Tags contain electronically stored information. A passive tag collects energy from a nearby RFID reader's interrogating radio waves. Unlike passive tags, which do not have their own power source, an active tag includes a local power source (such as a battery) and may operate hundreds of meters from the RFID reader. RFID has been considered a replacement for barcodes, and unlike barcodes the tag does not need to be within line of sight of the reader, it can be embedded in the tracked object. RFID is one method of automatic identification and data capture (AIDC).
The most common RFID frequencies used for RFID applications are: Low frequency (9-135 KHz), High frequency (13.553-15.567 MHz), Amateur radio band (430-440 MHz), Ultra-high frequency (860-930 MHz), and Microwave (2.4-2.4835 GHz, 5.8 GHz) The frequency that you choose will depend on the type of RFID application and region specific requirements.
The electromagnetic field that surrounds an RFID antenna is broken up into two segments – near-field and far-field. The two segments of the RF field, near-field and far-field, have different energies so they typically require a corresponding antenna type to get the best read range. The near-field is primarily magnetic in nature, while the far-field uses both electric and magnetic components.
Communication between an RFID tag and an RFID reader (via the antenna) is one-way and occurs using a process known as electromagnetic coupling. The two types of coupling are inductive and capacitive. A near-field antenna uses inductive coupling, meaning it uses a magnetic field to energize the RFID tag. The magnetic field is created in the near-field region, allowing the RFID reader’s antenna to energize the tag. The tag then responds by creating a disturbance in the magnetic field which the reader picks up and decodes. A far-field antenna uses capacitive coupling (or propagation coupling) to energize the RFID tag. Capacitive coupling occurs when the RFID reader’s antenna propagates RF (radio-frequency) energy outward and the energy is then used to energize the tag. The tag then sends back a portion of that RF energy to the reader’s antenna as a response known as backscatter.
NFC is rooted in RFID but distinguishes itself by allowing two-way communication between electronic devices to establish communication through near-field communication (NFC) within 4 cm (1.6 in) of each other. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID They both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.
NFC emerges from RFID
NFC was designed as secure form of data exchange based on RFID. What is unique about an NFC device is that it is capable of acting as both an NFC reader and an NFC tag allowing devices to communicate peer-to-peer. Most modern smart phones, Android and iPhones, support NFC.
Fully enabled NFC smartphones use the technology to pass information from one smartphone to the other by tapping the two devices together, allowing you to share data such as contact info or photographs. Another use of NFC can be seen in advertising campaigns that use smart posters to pass information to consumers. NFC devices can read passive NFC tags, and some NFC devices are able to read passive HF RFID tags that are compliant with ISO 15693. The data on these tags can contain commands for the device such as opening a specific mobile application. In essence, NFC builds upon the standards of HF RFID and turns the limitations of its operating frequency into a unique feature of near-field communication.
Your Chance to Win
| Be Original |
Stick to the Theme |
|---|---|
|
|
| List the Steps |
Submit Video Proof |
|
|
Your Prizes
| One Grand Prize Winner Wins a $200 Shopping Bundle | Three First Place Winners Win a $100 Shopping Cart |
|---|---|
|
|
 |
 |
Some Terms & Conditions Apply: How to Redeem Your Shopping Cart for Project14
Your Project, Your Ideas!
| About Project14 |
Directions |
|---|---|
|
Every month you'll have a new poll where you'll get to decide an upcoming project competition, based on your interests, that will take place a couple of months in advance. Themes are broad in scope so that everyone can participate regardless of skill set.
What are Monthly Themes?
What are Monthly Theme Polls?
|
Step 1: Log in or register on element14, it's easy and free. Step 2: Post in the comments section below to begin a discussion on your idea. Videos, pictures and text are all welcomed forms of submission. Step 3: Submit a blog post of your progress on your project by December 19th. You are free to submit as many blog entries as you like until the beginning of the next theme.
Be sure to include video proof of your project!
Visit: RFID or NFC or tag your project blog rfidornfcch
You have until December 19th End of Day to submit your completed project!
A jury consisting of your peers will judge project submissions! |

Top Comments