A look at the precision signal chains enabling high voltage applications in medical, industrial, automotive and more.
Providing a Path for Electrical Signals
In electrical engineering, a signal chain refers to the sequence of components and subsystems that process an electrical signal from its input to its output. This includes a wide range of devices such as amplifiers, filters, analog-to-digital converters, digital signal processors, and more. The goal of a signal chain is to process and transform an input signal into a desired output signal while maintaining the signal quality and accuracy.
Signal chain knowledge is particularly relevant during the design process, where engineers need to make decisions about which components to use and how to configure them. The performance of a signal chain is determined by the specifications of each individual component, as well as how those components are connected and configured. Therefore, it is important for engineers to have a deep understanding of the underlying principles and characteristics of each component in the signal chain to make informed design decisions.
What are the Different Types of Signal Chains?
Analog Devices offers a wide range of precision signal chains, which are designed to meet the unique requirements of different applications. Here's an overview of some of the different types:
Precision Narrow Bandwidth: supports applications that require precise measurements in a narrow bandwidth, such as medical instrumentation, power quality measurement, and gas and fluid analysis. It offers high accuracy and precision, with low noise and distortion, and is optimized for low power consumption.
Precision Medium Bandwidth: supports applications that require precise measurements in a medium bandwidth, such as audio and video processing, telecommunications, and power management. It offers high accuracy and precision, with low noise and distortion, and is optimized for low power consumption.
Precision Wide Bandwidth: supports applications that require precise measurements in a wide bandwidth, such as high-speed data acquisition, radar and sonar, and wireless communications. It offers high accuracy and precision, with low noise and distortion, and is optimized for high speed and high bandwidth.
Precision Low Power: supports applications that require high accuracy and precision, but with low power consumption. It is ideal for battery-powered and portable devices, as well as other applications where power consumption is a critical factor.
Precision Current Sensing: used to accurately measure the current flowing through a circuit. This is useful in many applications, such as motor control, battery management, and power supply design. The signal chain typically includes a current sense amplifier, which amplifies the small voltage drop across a sense resistor in the current path, and a high-resolution ADC, which converts the amplified voltage to a digital value.
Isolated Gate Drive and Sense: used to drive and sense high-voltage, high-current power switches, such as MOSFETs and IGBTs, in a safe and reliable way. The signal chain typically includes an isolated gate driver, which provides a high-voltage, high-current signal to the gate of the power switch, and an isolated current sense amplifier, which accurately measures the current flowing through the switch.
What is a Precision High Voltage Signal Chain?
Precision ICs
Shop our wide variety of ICs from Analog Devices.
Don't forget to join our discussion.
High voltage applications are becoming increasingly common across a wide range of industries. Whether in the medical field for ultrasound and X-ray imaging, in the industrial field for high voltage power supplies and motor drives, or in the automotive field for electric vehicle powertrains, high voltage applications are critical to our modern way of life. However, designing high voltage systems can be a challenging and time-consuming task. High voltage circuits require careful consideration of many factors, including component selection, isolation, and safety. Analog Devices' Precision High Voltage Signal Chain Platform provides a comprehensive solution for high voltage applications, saving designers time and effort while providing accurate and reliable performance.
The Precision High Voltage Signal Chain Platform from Analog Devices is a highly integrated system that provides a complete solution for high voltage applications. It consists of a range of high-performance analog and digital components, including precision op-amps, voltage references, analog-to-digital converters, and digital isolators. These components are designed to work together seamlessly, providing designers with a complete signal chain solution that is easy to use and highly accurate.
What are some Application Examples of Precision High Voltage Signal Chain?
Adjustable High Voltage Power Supply
A precise adjustable power supply can be difficult to build, because there are many potential sources of error. Drift over time, temperature, and variations in the production process can all contribute to inaccuracies. The resistive networks that are commonly used for feedback can also cause errors.
Figure 1 illustrates the design of an adjustable high-voltage power supply that uses an IC instead of a resistor network to manage the output.
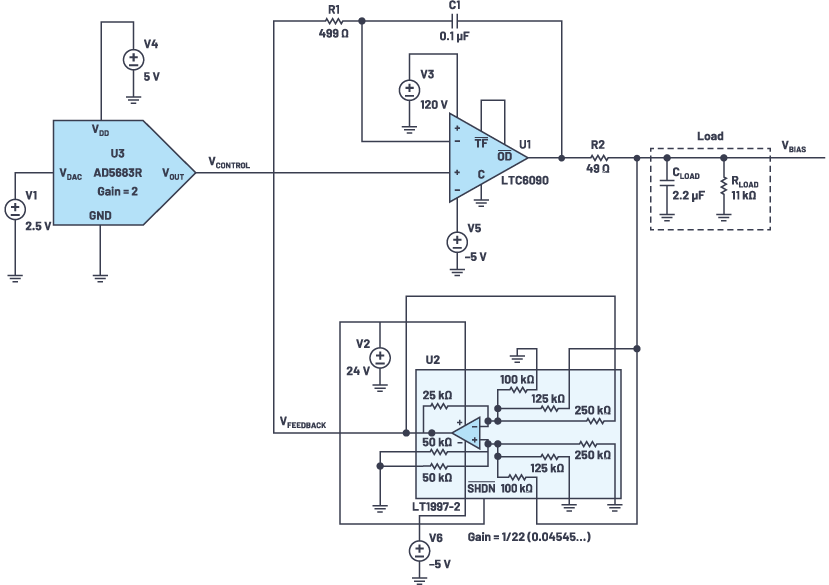
Figure 1. An LTspice® schematic for ~0 V to 110 V bias
Source: Analog Devices
The design consists of three pieces, the control voltage, an integrator, and a feedback path. An AD5683R (16-bit nanoDAC®) generates the control voltage (0V – 5V). The precision of the AD5683R enables the circuit to provide a bias voltage ranging from ~0 V to 110 V in ~1.68 mV steps. The integrator is the LTC6090, a high voltage op amp capable of rail-to-rail output and offering picoamp input bias current, essential for achieving the high accuracy desired. The LTC6090 compares the feedback voltage with the control voltage and integrates the difference, adjusting the output of VBIAS to the desired setpoint. The LT1997-2 difference amplifier is set to provide a gain of 22. This corresponds to output bias voltage ranging from 0 V (0 V x 22) to 110 V (5 V x 22).
Accurate High Voltage Sensing
Digital voltmeters (DVMs) typically use 10MΩ resistor networks at their input. These resistor networks can introduce inaccuracies, especially in higher voltage circuits that involve high resistances. One solution is to use a high-impedance amplifier in electrometer configuration. Field-effect transistors (FETs) are often added to the inputs in order to make the input current as low as possible. FETs are typically low-voltage devices and can introduce their own voltage offsets. Monolithic amplifiers with FET inputs are available; however, they are also often low-voltage devices, limiting their utility in high-voltage applications.
The LTC6090 is a CMOS amplifier that can handle over 140VP-P signal swings with sub-mV precision. The LTC6090 behaves as an ordinary unity-gain-stable op amp. A buffer stage can be added by providing 100% feedback with the classic unity-gain circuit. Additional FETs or floating biasing supplies are not needed. Figure 2 depicts a basic circuit for providing precision measurement of voltages, with an additional power converter, which uses a standard 9V battery.
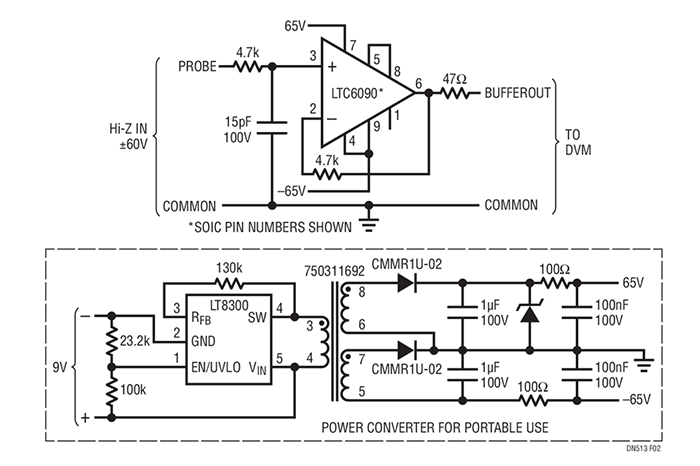
Figure 2. Buffered Probe for Digital Voltmeter
The Precision High Voltage Signal Chain platform can be used for applications across a wide variety of industries. One such application is monitoring the battery in an electric vehicle. Precise measurement of the voltage and current of the battery pack can be used to optimize the charging and discharging of the battery pack, ensuring maximum efficiency and lifespan.

ADHV4702 - High-voltage Op-amp
Buy Now
LTC6090 - High-voltage Op-amp
Buy Now

AD5522 - Quad Measurement Unit with integrated ADC/DAC Buy Now
ADuM1441 - Digital Isolator
Buy Now

AD5535BSDZ - 32 Ch. 14-bit DAC Development Kit
Buy Now

LT1997 - Precision Funnel Amplifier
Buy Now

AD7606C - 8 Ch. 18-bit ADC
Buy Now
LT5400 - Quad Matched Resistor Network
Buy Now
Summing up: Precision High Voltage Signal Chains
in sponsorship with

As industry demands more accuracy, the tools that support such precision must evolve with them. A solution that enables accurate and reliable signal processing and control of high voltage applications is required across a variety of industries, including medical, automotive, and manufacturing. The Precision High Voltage Signal Chain Platform from Analog Devices is a highly versatile set of components that reduces system design time and costs, while enabling the development of highly reliable and accurate systems.
How important is precision in your signal chain design, and what projects have you worked on where precision was critical?
Please tell us in the Comments section below.
