Hello everyone, in this post I will go over basic logic operations and their circuits :
First of all we need to define some Boolean data types and notation. We need to go over this because without basic knowledge about boolean algebra we can't work with logic operations and circuits
There are only 2 types of data in boolean algebra : HIGH (logic state 1 ) & LOW (logic state 0 ) --> ! Common mistake people make is that when they see a complex logic function they say that there can be practically indefinite number of data or when they see it "Letters" (e.g. Y = ((A + B')' * (C + D')')' ) we will get to notation in just a bit), but that is not type of data, those are variables which contain that type of data
- 1 is noted HIGH because it represents high voltage level
- 0 is noted LOW because it represents low voltage level
This is the notation and algebraic expressions for logic functions (we will get over each one in depth) :
- Y = A - Y is output and A is a variable
BASIC
- Y = A' - ' is an inverter (e.g. A' is inverted of A so if A = 0 then A' = 1)
- Y = A * B - logic operation AND (A AND B)
- Y = A + B - logic operation OR (A OR B)
- Y = (A * B)' - logic operation NAND (NOT AND - A AND B INVERTED)
- Y = (A + B)' - logic operation NOR (NOT OR - A OR B INVERTED)
**I will not be covering XOR or X NOR, the reason is that I only need the upper ones for my future posts "hint, hint" **
- Y = A * B' + A' * B - logic operation XOR (EXCLUSIVE OR)
- Y = (A * B' + A' * B)' - logic operation XNOR (EXCLUSIVE NOT OR)
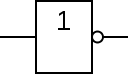
Logic operation/circuit NOT
Logic circuit NOT preforms logic operation of an INVERTER (inversion).Circuit can have only 1 input and 1 output. On the output Y we will have different logic state than on the input.
Algebraic expression :
Y = A'
Symbol :
- MIL/ANSI
- IEC
Table of truth:
| INPUT | OUTPUT |
|---|---|
| A | NOT A |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Electrical schematic:
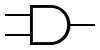
Logic operation/circuit AND
Logic circuit AND preforms logic operation AND. Circuit can have 2 or MORE inputs and only 1 output. At output Y we will have logic state 1 only then when all of our inputs are in logic state 1, and if any of the in puts is in logic state 0 we will have logic state 0 on the output Y.
Algebraic expression :
Y = A * B
Symbol :
- MIL/ANSI
- IEC
Table of truth:
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | A AND B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Electrical schematic:
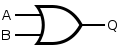
Logic operation/circuit OR
Logic circuit OR preforms logic operation OR. Circuit can have 2 or MORE inputs and only 1 output. At output Y we will have logic state 0 only when all of our inputs are in logic state 0, if any or all inputs are in logic state 1 output Y will be in logic state 1.
Algebraic expression :
Y = A + B
Symbol :
- MIL/ANSI
- IEC
Table of truth:
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | A OR B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Electrical schematic:
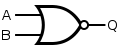
Logic operation/circuit NAND
Logic circuit NAND preforms logic operation NOT AND. Circuit can have 2 or MORE inputs and only 1 output. At output Y we will have logic state 0 only then when all of our inputs are in logic state 1, and if any of the in puts is in logic state 0 we will have logic state 1 on the output Y.
Algebraic expression :
Y = (A * B)'
Symbol :
- MIL/ANSI
- IEC
Table of truth:
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | A NAND B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Electrical schematic (With transistors):
Logic operation/circuit NOR
Logic circuit NOR preforms logic operation NOT OR. Circuit can have 2 or MORE inputs and only 1 output. At output Y we will have logic state 1 only when all of our inputs are in logic state 0 and if any of the inputs is in logic state 1 we will have logic state 0 on the output Y.
Algebraic expression :
Y =( A + B )'
Symbol :
- MIL/ANSI
- IEC
Table of truth:
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | A NAND B |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Electrical schematic (With transistors):
I think this would be all that is needed for anyone to start with digital electronics, bare bones of digital electronics. In the next post related to digital electronics I will start to talk about complex logic functions, how to minimize them in a few ways and then how to realize/make them with logic circuits.
I hope you enjoyed this quick post, if you did please like it and if you did not please tell me why so I can get better. Also if you detect any errors please let me know via PM so you leave space in the comment section for some questions.
Until next time,
Matija Martinec











Top Comments