High-Temperature Resistant Resistors Enabling Compact Inverter and BMS Designs
As the global shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) accelerates, countries like Germany, California (USA), Quebec (Canada), China, and Japan are implementing stricter regulations to phase out gasoline and diesel vehicles by 2035. This transition brings new challenges—particularly in battery management and energy efficiency.
One major concern is the lifecycle of EV batteries. Over time, repeated charging and discharging cycles degrade battery performance, requiring costly and energy-intensive replacements. To extend battery life and maximize driving range, two key technologies come into play: inverters, which convert DC battery power to AC for motors, and Battery Management Systems (BMS), which monitor and optimize battery health.
Panasonic’s chip resistors are critical components in these systems. Known for their compact size, high voltage tolerance, heat resistance, and long operational life, they are widely adopted in demanding automotive applications.
Application Example 1: Voltage-Dividing Circuits in BMS Using ERJH Series
In BMS and inverter rectifier circuits, discharge resistors are essential for safely releasing stored energy from smoothing capacitors during equipment failure. While precision resistance isn’t required, high heat resistance is crucial.
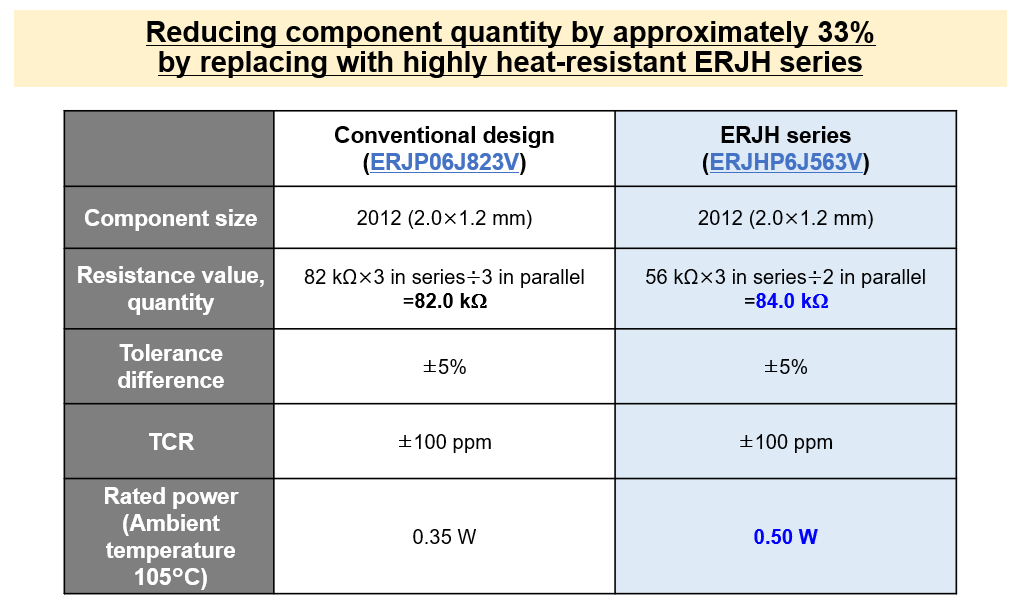
In one case, a customer needed a solution for a voltage-dividing circuit handling 500 V across resistors totaling ~80 kΩ, with 3 W power consumption and ambient temperatures reaching 105°C. Panasonic proposed the ERJH series thick-film resistors:
- Configuration: 3 × 2012-size (2.0 × 1.2 mm) resistors in series (each 56 kΩ, 0.5 W), with two sets in parallel (~84 kΩ total)
- Result: 33% reduction in component count compared to previous designs
- Advantage: Rated for up to 175°C, allowing higher power operation even in high-temperature environments
This solution not only improved thermal performance but also reduced board space and cost.
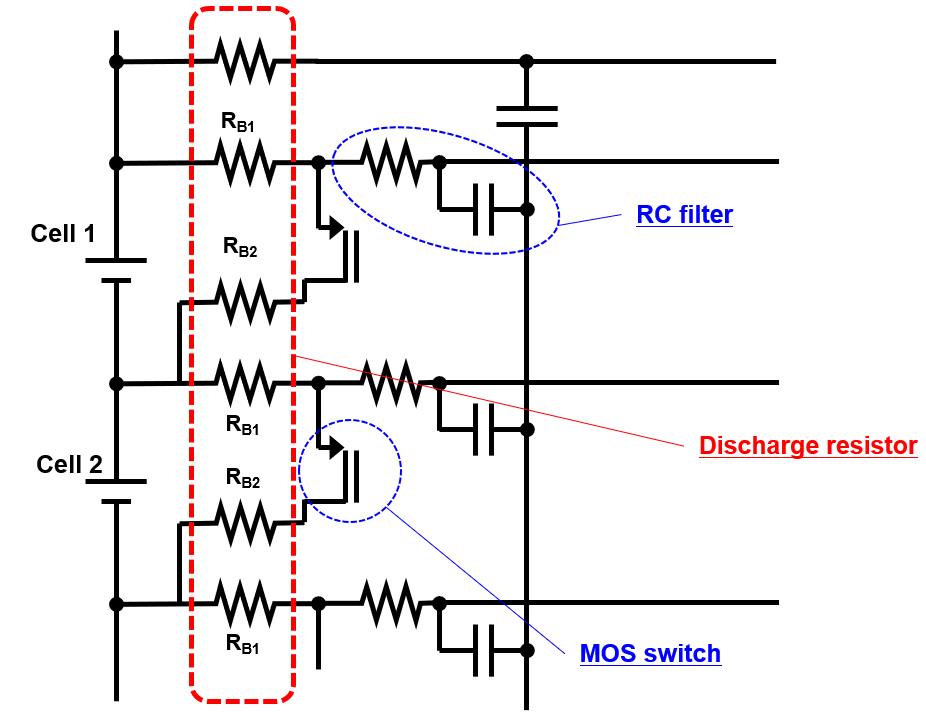
Application Example 2: Cell Balancing Circuits Using ERJB Series
Battery packs consist of multiple cells, each with varying degradation levels. To balance capacity, discharge resistors are used to reduce the charge of healthier cells, aligning them with the most degraded one.
Requirements for these resistors include:
- Resistance: ~10 Ω (±5%)
- Power: 1–2 W
- Tolerance for temperature rise
While multiple thick-film resistors could meet these specs, Panasonic recommended the ERJB series long-side electrode resistors, which offer:
- Higher power handling due to larger electrode area
- Reduced risk of cracking during mounting
- Compact design ideal for limited battery cell space
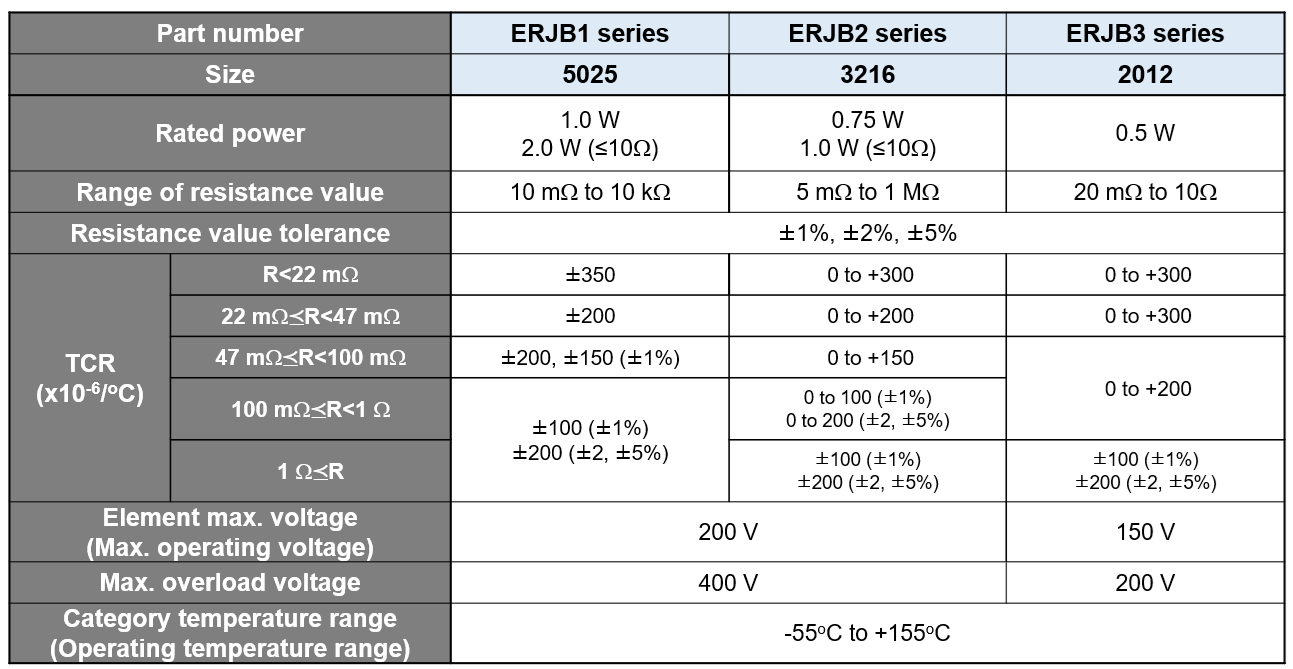
Product Lineup:
- ERJB3 (2012 size): 0.5 W, 150 V max
- ERJB2 (3216 size): 0.75 W, 200 V max
- ERJB1 (5025 size): 1.0 W, 200 V max
All models operate reliably from −55°C to 155°C.
Why Panasonic Resistors Are Ideal for EV Applications
In the evolving EV landscape, BMS plays a pivotal role in ensuring battery longevity and safety. Panasonic’s chip resistors—engineered for compactness, durability, and environmental resilience—help manufacturers meet stringent performance and space requirements.
By integrating Panasonic’s ERJH and ERJB series resistors, designers can:
- Enhance system reliability
- Reduce component count and board size
- Lower overall system cost
Interested in Panasonic Resistors for Your EV Designs?
Explore our lineup on PANASONIC Chip SMD Resistors | Farnell® UK
