The cooling system pump is responsible for moving water through the cooling system, helping to prevent overheating of various equipment. This pump typically requires between 30 W and 100 W of power to function. It consists of an impeller, a motor, and an inverter, all housed in a cylindrical outer casing. In this article, we will explore the pump's functions, its configuration, and the electronic components that make it work.
Understanding the cooling system pump
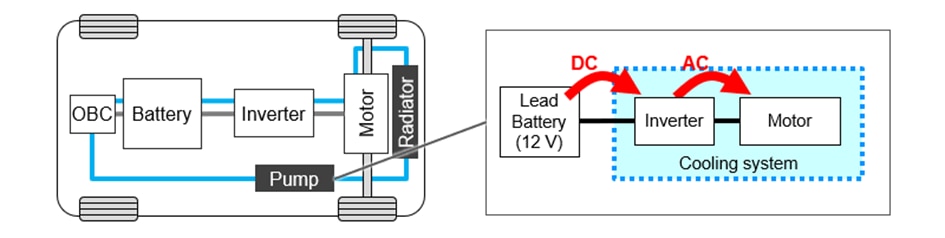
In vehicles, the cooling system is designed to manage the heat generated by components like the battery and motor. It does this by circulating water through pipes in the cooling unit (also known as the jacket) surrounding these components. The pump forces water to flow through these pipes, and it generally operates with a power range of 30 W to 100 W. The main parts of the pump include an impeller, a motor, an inverter (which controls the motor), and a circuit board, all contained within a cylindrical casing.
Market trends and demand for cooling system pumps
As the number of vehicles—both electric and those with internal combustion engines—continues to rise, the demand for cooling system pumps in these vehicles is also expected to grow. Additionally, as equipment like batteries and inverters increase in power output, they generate more heat, leading to a greater need for efficient cooling systems and more powerful pumps.
To meet these needs, the electronic components in cooling systems must have key features: "high current capacity," "low energy loss," "high heat resistance," and "precise temperature control."
Circuit configuration of a cooling system with a pump overall setup
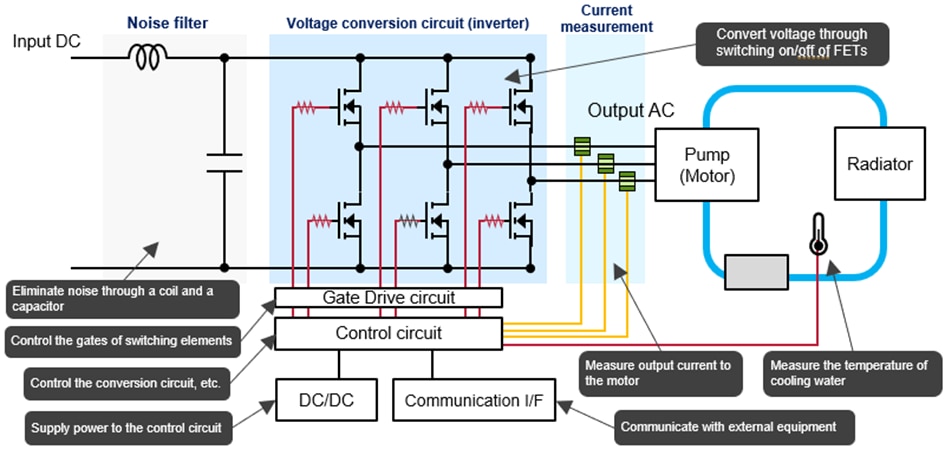
• Noise Filter: Removes interference using a coil and a capacitor.
• Voltage Conversion Circuit: Changes voltage using switching elements like FETs.
• Current Measurement Unit: Monitors the output voltage to the motor.
• Gate Drive Circuit: Controls the switching elements.
• Control Circuit: Manages the conversion circuit and other functions.
• DC/DC Converter: Powers the control circuit.
• Communication interface: Allows communication with external devices.
Detailed look at individual circuits and components
Noise Filter: This component reduces noise from both inside and outside the system to prevent malfunctions, typically using a combination of a large coil and a capacitor.
Components used:
Noise elimination and smoothing: Conductive polymer hybrid aluminum electrolytic capacitor:
It provides high capacitance, low equivalent series resistance (ESR), and excellent noise suppression, making the circuit smaller and more efficient.
Voltage conversion: Power inductors used in automotive applications help minimize power loss and handle large currents, enhancing efficiency.
Voltage conversion circuit: This circuit uses switching elements that can create noise when turned on and off. To reduce this noise, resistors are added to the gate terminals of the FETs.
Components used:
Chip resistor: Small and capable of high power, helping to minimize circuit size.
Control circuit: This part continuously checks the water temperature using a sensor. Based on the temperature readings, it adjusts the pump's speed to maintain the proper temperature.
Components used:
Temperature sensor: Designed for automotive use, it withstands extreme temperatures from -40°C to 200°C.
DC/DC converter: Made up of FETs, coils, and capacitors, this component uses conductive polymer hybrid aluminum electrolytic capacitors to smooth voltage output and eliminate noise.

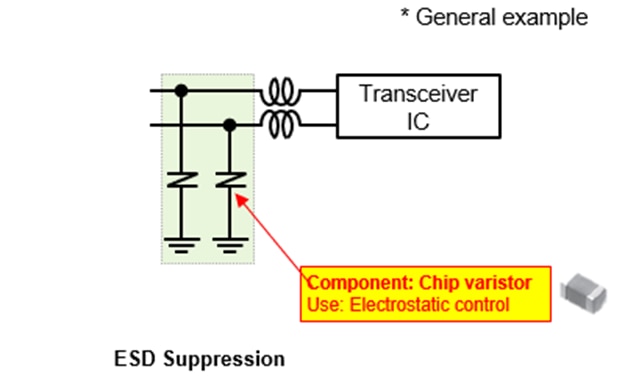
Communication interface: This circuit connects to external equipment via communication lines (like CAN or Ethernet). To protect against noise or static electricity, chip varistors are used to prevent damage.
Components used:
Chip varistor: It suppresses electrostatic discharge (ESD) noise without affecting the quality of communication.
Conclusion
The cooling system plays a vital role in circulating water to cool equipment and prevent overheating. As the number of vehicles, including electric and gas-powered ones, continues to grow, so will the need for effective cooling systems and pumps. With rising power outputs from various components, the demand for enhanced cooling performance is critical, necessitating pumps with higher output. Thus, the electronic components used in these systems must offer features like high current capacity, low energy loss, high heat resistance, and precise temperature control. Panasonic Industry provides a range of products suitable for use in cooling systems.
Have a look at the mentioned products also in Farnell stock:

 UK
UK UK
UK UK
UK UK
UK