As vehicles become smarter and more electrified, the Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) has emerged as a critical component in managing and optimizing their performance. But what exactly is a VCU, and why is it so essential in today’s automotive systems?
Table of Contents
What Is a VCU?
A Vehicle Control Unit (VCU) is the brain behind many of a vehicle’s core functions. It acts as a centralized controller that processes signals from various sensors and other Electronic Control Units (ECUs), then issues commands to components such as motors, brakes, steering systems, and more.
In modern vehicles, especially those with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) or electric drivetrains, the VCU plays a pivotal role in coordinating power devices, body electronics, and drive systems. It ensures that all subsystems operate harmoniously based on real-time data inputs.
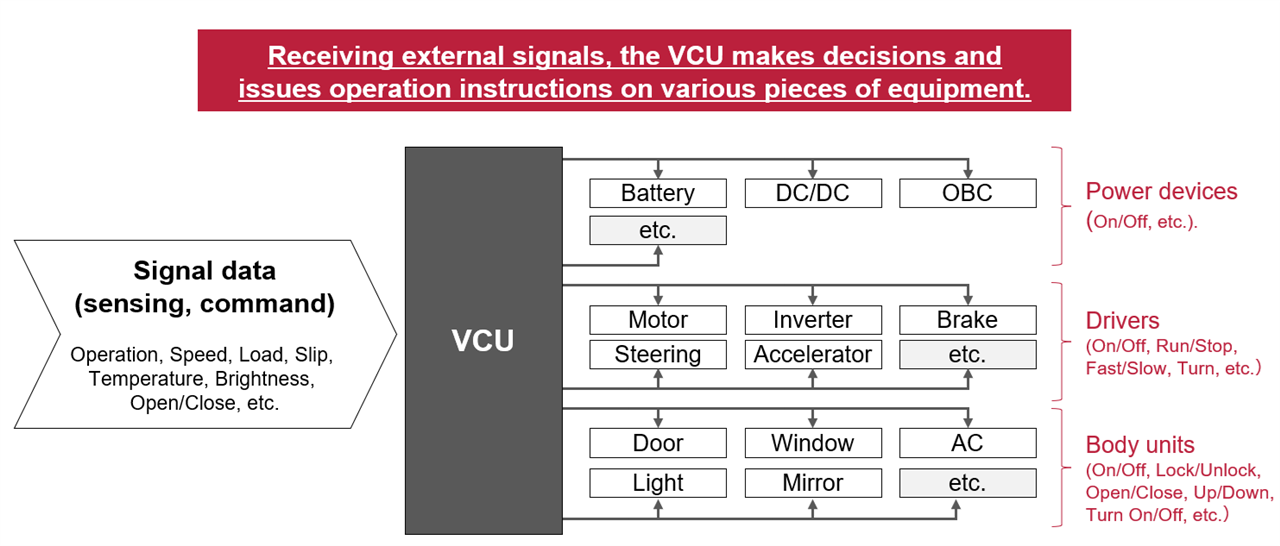
(Fig. 1 Role of the VCU)
Market Trends and the Rise of VCUs
With the automotive industry moving toward Level 3 autonomous driving and beyond, the demand for high-performance VCUs is rapidly increasing. As more vehicle functions become electrified and automated, the need for centralized control grows. This shift brings challenges such as:
- Increased processing requirements
- Higher power consumption
- Faster communication speeds
To meet these demands, VCUs must be built with components that are compact, energy-efficient, high-frequency capable, and highly reliable.
Inside the VCU: System Architecture
A typical VCU includes the following key components:
- Transceivers: Enable communication with external systems via CAN, LIN, Ethernet, etc.
- SoC/MCU: Process data and make control decisions
- Memory (DDR): Temporarily stores data during processing
- DC/DC Converters: Regulate voltage levels for different subsystems
- Motor Drivers: Control actuators like motors and solenoids
These components work together to interpret sensor data and issue precise control signals to various vehicle systems.
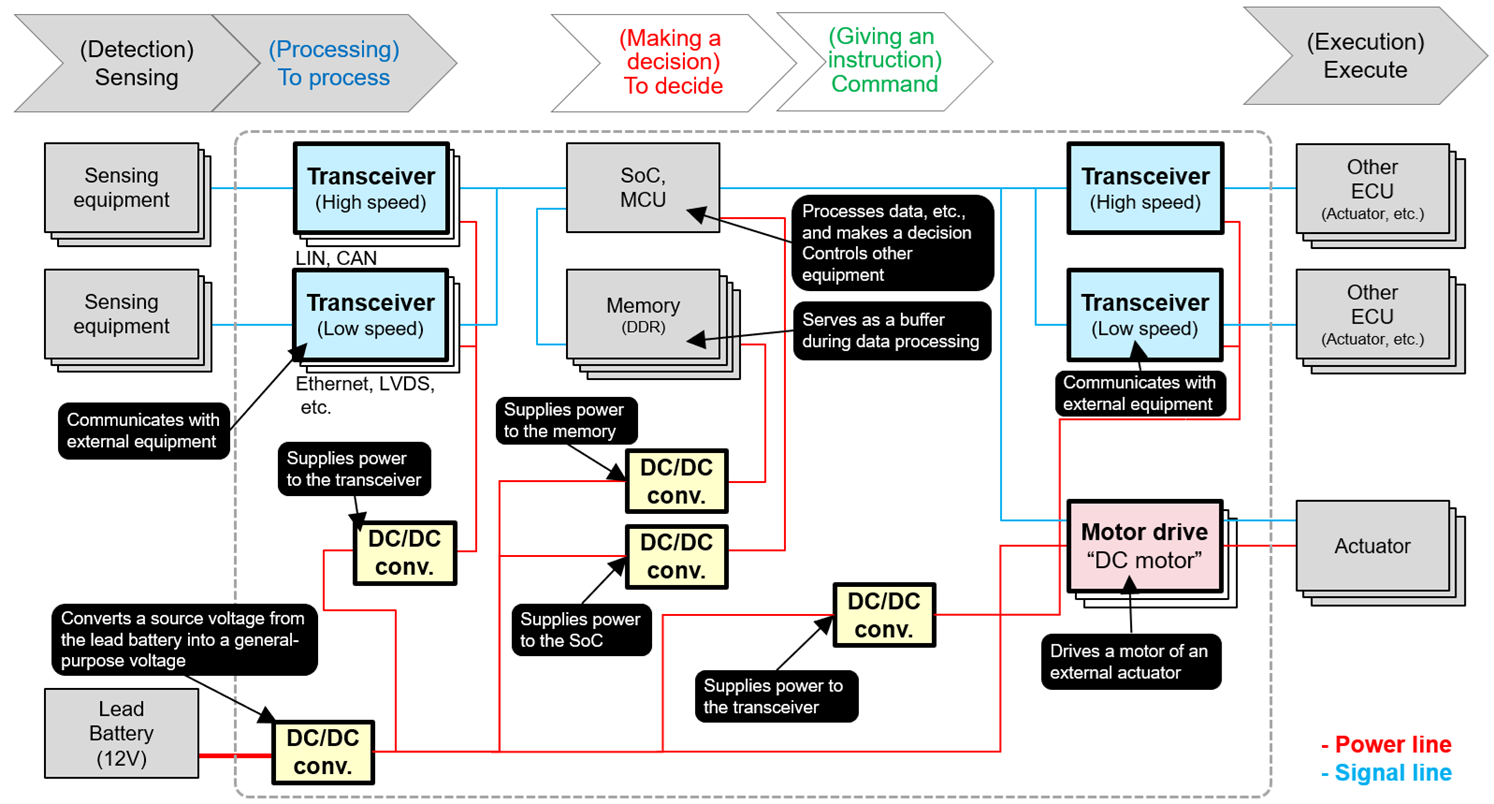
(Fig. 2 Overall configuration of the VCU)
Key Circuits and Components
1. DC/DC Converter
Used to convert battery voltage to levels required by other components. Key parts include:
- Conductive Polymer Hybrid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors: For noise filtering and voltage smoothing
- Automotive Power Inductors: For efficient voltage conversion
- High-Precision Chip Resistors: For accurate voltage measurement
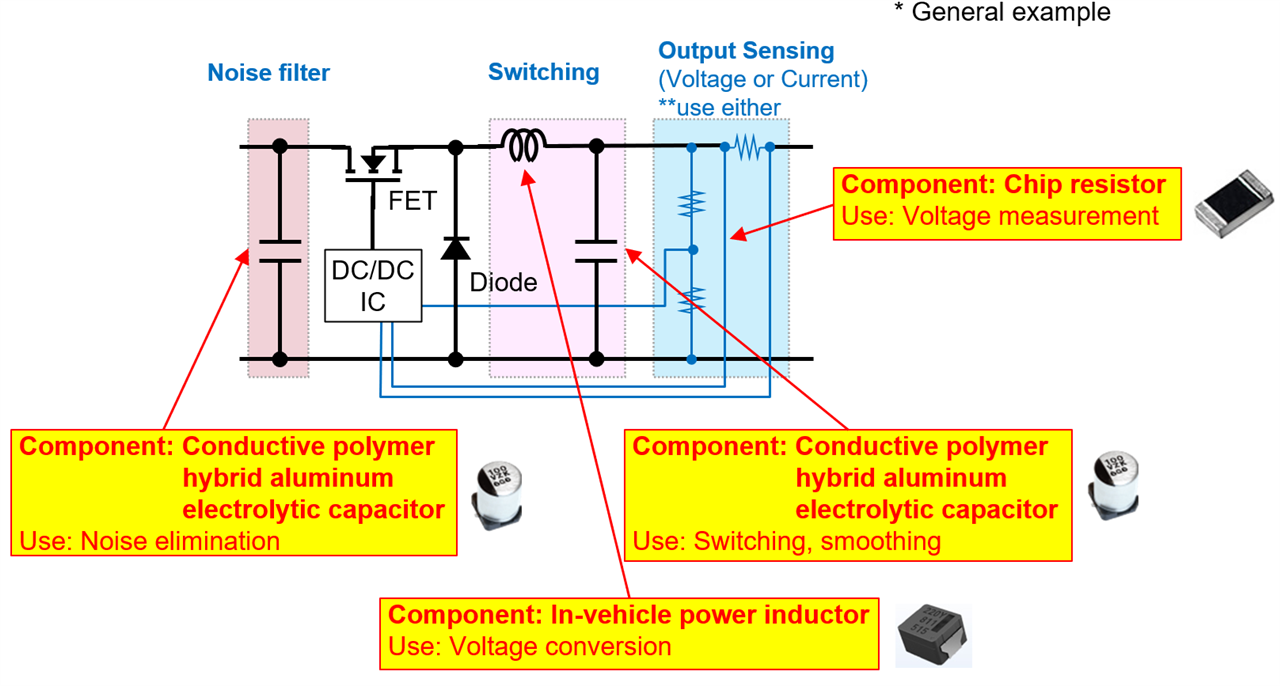
(Fig. 3 Components used in the DC/DC converter)
2. Transceiver Interface
Handles communication with external devices. To protect against electrostatic discharge (ESD), it includes:
- Chip Varistors: Suppress ESD while maintaining signal integrity
- ESD Suppressors: Provide high-speed protection with minimal capacitance
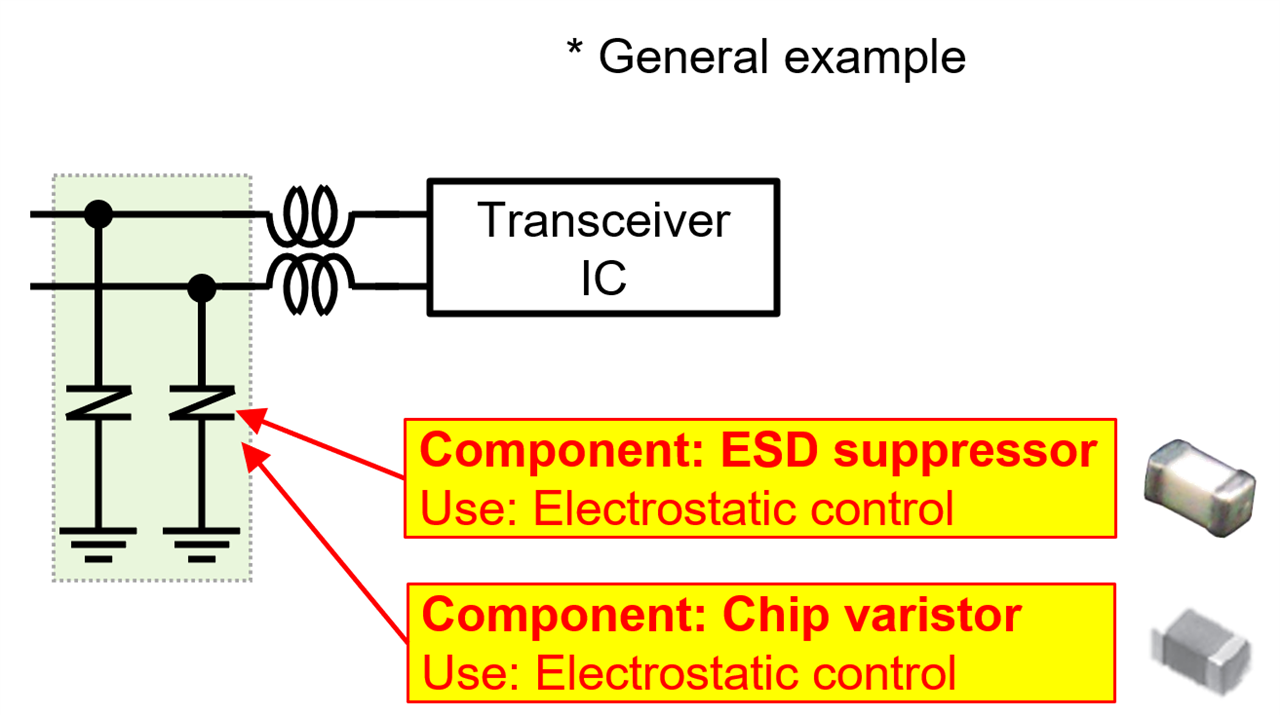
(Fig. 4 Components used in the transceiver IF)
3. Motor Drive Circuit
Controls voltage switching for actuators. To manage noise and ensure stable operation, it uses:
- Capacitors and Inductors: For noise suppression and power stability
- High-Power Chip Resistors: For gate drive noise control
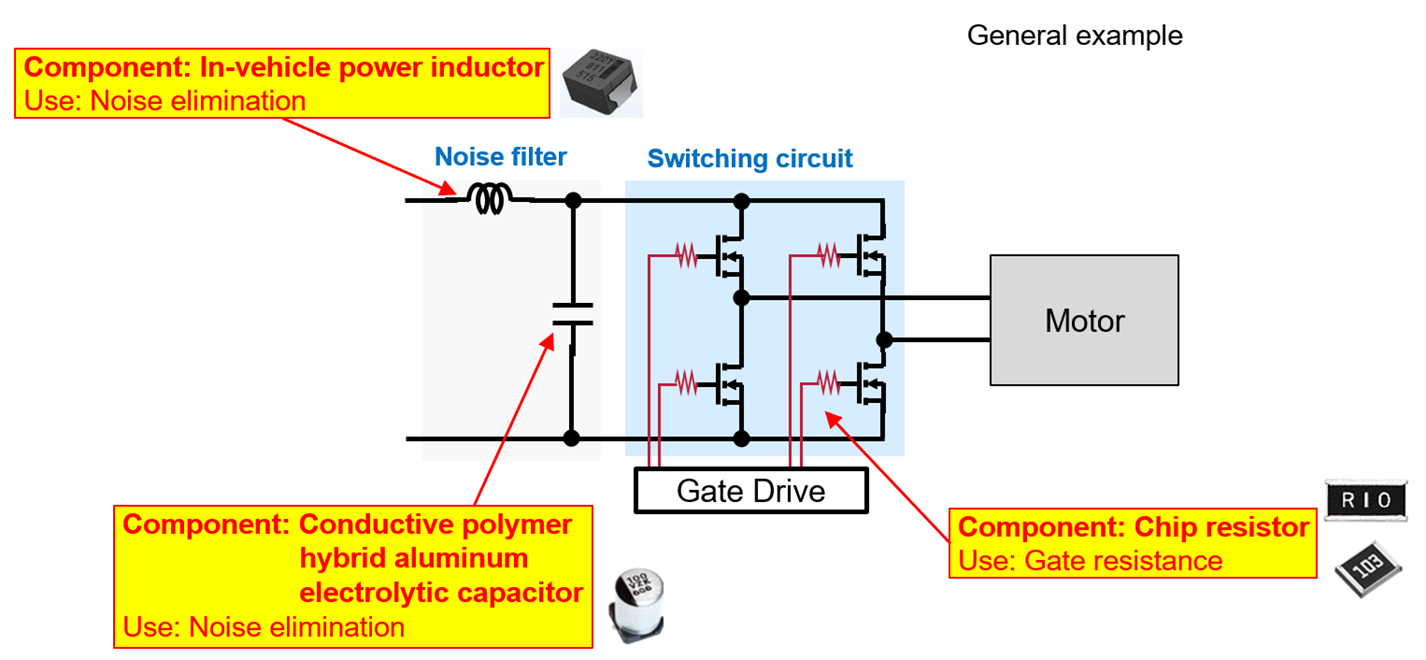
(Fig. 5 Components used in the motor drive circuit)
Why Component Selection Matters
As VCUs become more complex, the components used must meet stringent requirements:
| Feature | Importance in VCU Design |
|---|---|
| Miniaturization | Saves space in compact ECUs |
| High Frequency | Supports fast switching and communication |
| High Precision | Enables accurate control and measurement |
| Low Loss | Improves energy efficiency |
| Large Current Handling | Supports high-power applications |
| ESD Protection | Ensures communication reliability |
Panasonic Industry offers a wide range of components tailored for VCU applications, including capacitors, inductors, resistors, and ESD protection devices.
Conclusion
The VCU is a cornerstone of modern vehicle architecture, especially as we move toward more autonomous and electrified mobility. Its ability to manage complex systems in real time depends heavily on the quality and performance of its internal components. By choosing the right parts, engineers can design VCUs that are not only powerful and efficient but also compact and reliable.
| Component | Feature | Large Current | Low Loss | Miniturization (small size) | High Frequency | High Precision | |
| Conductive polymer hybrid aluminum electrolytic capacitor | Low ESR High reliability |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Power Inductors for Automotive application | Large current, low loss High reliability |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| High precision, high resistance to heat |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Chip varistor |
|
 |
|||||
| ESD suppressor |
|
 |
 |

