What is a circular connector?

A circular connector is a connector that uses a multi-pin electrical interconnect method to power electrical devices, transmit data, or transmit electrical signals. The connection relies on mechanical springs that create a force between the two halves of the connector and establish metal-to-metal contact at the mating interface. Circular connectors are rugged, durable, and weather-resistant, making them suitable for various applications that require a reliable, secure, and long-lasting electrical connection.
What are circular connectors used for?
Circular connectors are widely used in industrial applications where a secure and reliable electrical connection with effortless connection and disconnection is needed. Many applications use circular connectors, from power and signal transmission to optical communication and data transfer. Circular connectors are used in industries such as transportation, telecommunications, aerospace, defense, industrial, networking, and medical.
What are the advantages of circular connectors?
Circular connectors are compact and durable, providing a secure, versatile, reliable, and cost-effective solution for different applications operating in diverse environments and industries. Some of the advantages include:
- A locking mechanism that helps to ensure a secure and safe connection
- Shielding from high radio frequency interference (RFI) and electromagnetic interference (EMI), preventing signal degradation, data corruption, and equipment damage
- Availability in a wide variety of sizes and pin configurations
What are the types of circular connectors?
There are several types of circular connectors, distinguished by specifications, including coupling type, housing material, voltage and current ratings, and ingress protection ratings. These factors, along with other considerations such as the number of contacts, pin arrangement, and environmental sealing, help in selecting the most appropriate type of circular connector for a particular application.
Coupling Types: Circular connectors are available with bayonet, threaded, push-pull, quick-disconnect, snap-on, and screw-in coupling types.
Housing Material: Circular connectors can be distinguished by the materials used in their construction. Two types exist: circular plastic connector (CPC) and circular metal-shell connectors (CMC).
- Commercial or circular plastic connectors (CPC): This type of circular connector utilizes plastic materials or polymer-based housings. They are versatile, lightweight, and cost-effective.
- Metallic Circular Connectors are primarily made up of aluminum, stainless steel, or brass. These materials provide effective shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI).

Figure 1: CPC (left) and metallic (right) circular connector
What are the parts of a circular connector?
The basic components in a connector are the connector housing, contact springs, contact finish, contact interface and shell.
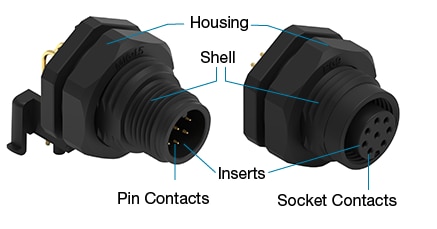
Figure 2: Parts of circular connector
- Connector Housing: the outer casing or body of the connector. The connector housing protects the internal components.
- Contact Pins: the conductive elements within the connector that establish electrical connections between the mating connectors
- Contact Finish: the surface coating or plating applied to the contact springs. The contact finish improves conductivity and durability.
- Contact Interface: the point of contact between the male and female contacts of mated connectors
- Shell: the component that encloses the connector housing and offers added strength, protection, and corrosion resistance
What terminal options can be used with circular connectors?
Circular connectors support a wide variety of termination options, including crimp, solder, screw, lug, and wire wrap.
What is the difference between M5, M8 and M12 circular connectors?
M5, M8, and M12 connectors differ by size and specifications.
The M5 circular connector has a diameter of about 5mm with pin configurations typically ranging from three to five pins. This tiny diameter makes it one of the smallest circular connectors. The M5 features a threaded connection mechanism, enabling connections to be easily screwed into place. This ensures a secure and reliable connection and offers protection against foreign particles, moisture, and water.
M8 circular connectors are available in several pin configurations (anywhere from three to eight pins). M8 connectors are typically circular in shape and feature a threaded locking mechanism with an 8mm diameter. M8 connectors are used in demanding environments, such as industrial automation, sensor systems, robotics, and other applications that require reliable connections in harsh environments. M8 connectors typically offer additional shielding options to provide protection against EMI.
The M12 connector features a locking thread with a diameter of 12mm. M12 connectors are primarily utilized in factory automation settings to facilitate connections for actuators, sensors, Industrial Ethernet, and fieldbus devices. They are available in various pin configurations, with pin counts ranging from three to twelve, allowing for flexibility to accommodate diverse signal and power requirements within the application. Additionally, M12 connectors often carry IP67 or IP68 ratings, ensuring a high level of protection against moisture and contaminants, including temperature fluctuations, mechanical stress, and exposure to chemicals.

Figure 3: M12 connector
Buy now
What accessories are used with circular connectors?
Circular connectors can be paired with a range of accessories to enhance their functionality and performance. Here are some common accessories used with circular connectors:
Sealing Gaskets and O-rings: These accessories are used to provide environmental sealing and protect the connector from moisture, dust, and other contaminants. They are particularly important in applications where the connector is exposed to harsh environments.
Backshells: Backshells provide mechanical protection and strain relief to the cable and connector interface. They are designed to prevent cable bending or pulling forces from damaging the connector or causing disconnection.
Caps and Dust Covers: Caps and dust covers are used to protect the connector when it is not in use. They help prevent dirt, moisture, and debris from entering the connector, which could potentially lead to damage or poor connection quality.
Adapters: Adapters allow for compatibility between different types of circular connectors. They enable the connection of connectors with varying sizes, pin configurations, or gender (male/female) types.
Cable Clamps: Cable clamps are used to secure the cable to the connector, providing strain relief and preventing the cable from being accidentally pulled or disconnected.
Contacts and Contacts Removal Tools: Contacts are the conductive elements within the connector that establish electrical connections. Additional contacts or replacement contacts may be needed for specific applications. Contact removal tools are used to safely remove contacts from the connector without damaging them.
Connector Hoods: Connector hoods are protective covers that enclose the entire connector and cable assembly. They provide additional mechanical protection, especially in applications where the connector is subjected to rugged conditions.
Panel Mounts and Mounting Hardware: Panel mounts are used to secure the connector to a surface, such as a control panel or equipment chassis. Mounting hardware, such as screws or bolts, are used to attach the connector securely to the panel.
Termination Tools: Termination tools aid in the installation and termination of cables to the connector. They include crimping tools, soldering irons, and other specialized tools depending on the connector type and termination method.
A list of connector accessories can be found here
What types of connectors are available in Würth’s M12 A family?
M12 A circular connectors from Würth Electronik are specifically designed for data analog signals and fieldbuses, with the option of supplying DC power. The M12 A product group includes various options such as male and female connectors, field-attachable connectors, plugs, and receptacles for device installation. M12 A connectors provide dustproof and waterproof connections with IP67 or IP68 ingress protection, and are suitable for sensors, actuators, and other devices that typically are in the automation industry.

Figure 4: M12 circular connectors
Source: Würth Elektronik
Shop now
The WR-CIRCM12 circular connector is available in four-, five-, or eight-pole versions. It is well-suited for fieldbus applications in industries, such as manufacturing engineering and automation, where cables that also transfer DC power are required. These cable assemblies are also suitable for non-industrial applications that demand compact, robust, and reliable connections in challenging environments. The solderable products in the WR-CIRCM12 family have high resistance to fire and conform to UL94, a plastics flammability standard released by the Underwriters Laboratories (UL).
What are the circular connector solutions available from Würth?
Würth Electronik offers the WR-CIRC M12 circular connector in three different solutions: cable assembly, panel receptacle, and field attachable connectors.
A cable assembly is a convenient and ready-to-use solution for connecting devices or components. They are complete ready-made cables that eliminate the need for manual wiring. Cable assemblies are designed with specific connector types, pin configurations, and cable lengths to suit various application requirements.
Panel receptacle connectors are designed to be mounted on panels or equipment surfaces, offering a secure and reliable connection interface. They are available in various sizes, pin configurations, and mounting options to accommodate diverse application needs.
Field attachable connectors are well-suited for applications where quick and easy connection or disconnection is necessary, such as field installations, maintenance, or temporary setups. Field attachable connectors can be easily assembled or attached in the field without requiring specialized tools or equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are some other names for a circular connector?
Circular connectors are also known as “circular interconnects” or cylindrical connectors
Why are circular connectors used?
Circular connectors have characteristics that make them suitable for a wide variety of applications.
- Circular connectors are capable of withstanding mechanical stress and provide a secure and reliable connection.
- Circular connectors often come with sealing options, such as gaskets or O-rings, which provide protection against moisture, dust, dirt, and other contaminants.
- Circular connectors often offer effective EMI and RFI shielding.
- Circular connectors are available in a wide range of sizes, pin configurations, and contact arrangements, allowing them to accommodate various signal types, power requirements, and data transmission needs.
- Circular connectors often feature simple mating and unmating mechanisms, such as bayonet coupling or threaded connections.
What are the standards for circular connectors?
Circular connectors are manufactured according to various standards to ensure compatibility, interchangeability, and reliability. The specific standards depend on the type and application of the connector. Some commonly used standards for circular connectors include:
MIL-DTL-38999 (MIL-SPEC): This military specification defines the design and performance requirements for circular connectors used in aerospace and defense applications. It covers a wide range of connector types, including multiple shell sizes and contact arrangements.
IEC 61076: The international standard, developed by the IEC, specifies the mechanical and electrical requirements for circular connectors used in industrial applications. It includes various families of connectors, such as M5, M8, M12, M23, and more.
IEC 60320: This standard specifies the mechanical, electrical, and dimensional requirements for connectors used in appliances and information technology equipment. While not exclusively for circular connectors, it includes certain circular connector types, such as C13 and C19 connectors commonly used for power cords.
EN 3645: This European standard specifies the performance and testing requirements for circular connectors used in aerospace applications. It covers connector families like EN 3645-007, EN 3645-008, and EN 3645-009, which are widely used in the aerospace industry.
SAE AS50151 (MIL-DTL-5015): This aerospace standard, also known as MIL-DTL-5015, outlines the specifications for circular connectors used in aerospace and other high-reliability applications. It includes various shell sizes, contact arrangements, and performance requirements.
DIN 43650: This German Industrial Norm (DIN) standard defines the requirements for circular connectors used in solenoid valves and other automation equipment. It specifies dimensions, sealing methods, and electrical characteristics.
VG95234: This German standard applies to circular connectors used in military and aerospace applications. It covers connector families like VG95234-A, VG95234-B, and VG95234-C, with different shell styles, contact arrangements, and performance characteristics.
RJ45 (Registered Jack 45): While not a circular connector standard, the RJ45 is a widely used connector for Ethernet networking. It follows the standards defined by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
What is the difference between circular and rectangular connectors?
Circular connectors have a compact and streamlined design, while rectangular connectors have a larger footprint and can accommodate more contacts, making them suitable for high-power or multi-use applications. Circular connectors are typically designed for low-power use, while rectangular connectors are capable of handling higher power levels and larger conductors.
How do I choose a circular connector?
Choosing the right circular connector involves considering several factors based on your specific application requirements.
Electrical Requirements: Determine the electrical characteristics needed for your application, such as voltage rating, current capacity, and signal requirements. Ensure that the connector you choose can handle the required electrical parameters.
Environmental Conditions: Assess the environmental conditions the connector will be exposed to, including temperature extremes, moisture, dust, vibration, and chemical exposure. Select a connector with appropriate ingress protection (IP) rating, sealing options, and ruggedness to withstand the environmental challenges.
Mechanical Specifications: Consider the mechanical aspects of the connector, such as the number of contacts/pins required, contact arrangement (pin/socket configuration), shell size, and mounting options (panel mount, cable mount, etc.). Ensure compatibility with your existing equipment or devices.
Termination Method: Decide on the preferred termination method based on your application and expertise. Circular connectors can support various termination types, including soldering, crimping, screw terminals, or insulation displacement connections (IDC). Choose a connector that supports your desired termination method.
Connector Series and Compatibility: Determine if there are specific connector series or families that are commonly used or preferred in your industry or application. This can help ensure compatibility with other equipment, cables, or accessories.
Standards and Certifications: Consider any industry-specific or regulatory standards that your application needs to comply with. Look for connectors that meet the relevant standards and certifications, such as MIL-SPEC, IEC, or UL listings, to ensure reliability and safety.
Cost and Availability: Evaluate the cost of the connector and its availability from reputable suppliers. Consider factors such as the initial purchase cost, maintenance costs, and long-term availability of the connector for future replacements or expansions.
Customization Options: Determine if you require any specific customization options, such as special pin arrangements, keying options, or unique features tailored to your application. Some manufacturers offer customization services to meet specific requirements.
Reliability and Durability: Assess the reliability and durability of the connector, considering factors like mating cycles, contact resistance, mechanical robustness, and resistance to vibration and shock. Look for connectors with a proven track record in your industry or with positive customer reviews.
Future Expansion and Compatibility: Consider any potential future needs or compatibility requirements, such as the ability to add additional contacts or accessories, backward compatibility with older versions, or compatibility with emerging technologies.

