I have worked with the examples provided with ModusToolbox and everything works perfectly. I immediately have seen the use of
cy_retarget_io.h
that is used also for targeting the standard IO "printf" function to the serial port. So, as my "best wishes" for you all with the "At the Core Design Challenge", I have written a handful header file that contains the ANSI Escape sequences to use with the serial port and a serial terminal like Tera Term.
I am sharing this file with you.
/**
******************************************************************************
* At The Core Design Challenge, 2023
*
******************************************************************************
* File Name : ansi_escape.h
* Description : This file of definitions
* Created on : Feb 28, 2023
* Author : Francesco De Simone, Digimorf
******************************************************************************
*/
#ifndef ANSI_ESCAPE_H_
#define ANSI_ESCAPE_H_
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
// /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Definitions.
// /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// ASCII CHARACTERS
#define ASCII_NULL 0x00 // Null Character
#define ASCII_BS 0x08 // Backspace
#define ASCII_TAB 0x09 // Tab
#define ASCII_LF 0x0A // Line Feed
#define ASCII_CR 0x0D // Carriage Return
#define ASCII_ESC 0x1B // Escape
#define ASCII_SPACE 0x20 // Space
#define ASCII_A ('A')
#define ASCII_L ('L')
#define ASCII_Z ('Z')
#define ASCII_a ('a')
#define ASCII_z ('z')
#define ASCII_0 ('0')
#define ASCII_9 ('9')
#define ASCII_Q ('Q')
#define ASCII_AT ('@')
#define ASCII_SLASH ('/')
#define ASCII_COLON (':')
#define ASCII_DASH ('-')
#define ASCII_HASH ('#')
#define ASCII_DELETE 0x7F // Tab
#define CURSOR_NEWLINE "\r\n"
// VT100 ESCAPE SEQUENCES //////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Device Status
// -------------
// The following codes are used for reporting terminal/display settings, and vary depending on the implementation:
// Requests a Report Device Code response from the device.
#define QUERY_DEVICE_CODE "\x1b[c"
// Generated by the device in response to Query Device Code request.
#define REPORT_DEVICE_CODE "\x1b[{code}0c"
// Requests a Report Device Status response from the device.
#define QUERY_DEVICE_STATUS "\x1b[5n"
// Generated by the device in response to a Query Device Status request; indicates that device is functioning correctly.
#define REPORT_DEVICE_OK "\x1b[0n"
// Generated by the device in response to a Query Device Status request; indicates that device is functioning improperly.
#define REPORT_DEVICE_FAILURE "\x1b[3n"
// Requests a Report Cursor Position response from the device.
#define QUERY_CURSOR_POSITION "\x1b[6n"
// Generated by the device in response to a Query Cursor Position request; reports current cursor position.
#define REPORT_CURSOR_POSITION "\x1b[%d;%dR"
// Terminal Setup
// --------------
// The h and l codes are used for setting terminal/display mode, and vary depending on the implementation. Line Wrap is one of the few setup codes that tend to be used consistently:
// Reset all terminal settings to default.
#define RESET_DEVICE "\x1b\x63"
// Text wraps to next line if longer than the length of the display area.
#define ENABLE_LINE_WRAP "\x1b[7h"
// Disables line wrapping.
#define DISABLE_LINE_WRAP "\x1b[7l"
// Fonts
// -----
// Some terminals support multiple fonts: normal/bold, swiss/italic, etc. There are a variety of special codes for certain terminals; the following are fairly standard:
// Set default font.
#define FONT_SET_G0 "\x1b("
// Set alternate font.
#define FONT_SET_G1 "\x1b)"
// Gfx mode on.
#define FONT_GFX_ON "\x1b(0" // DEC special graphics table as G0
// Gfx mode off.
#define FONT_GFX_OFF "\x1b(B" // ASCII table as G0
// Cursor Control
// --------------
// Sets the cursor position where subsequent text will begin.
// If no row/column parameters are provided (ie. "\x1b[H), the cursor will move
// to the home position, at the upper left of the screen.
#define CURSOR_HOME "\x1b[\x48"
#define CURSOR_SET "\x1b[%d;%d\x48"
// Moves the cursor up by COUNT rows; the default count is 1.
#define CURSOR_UP "\x1b[%dA"
// Moves the cursor down by COUNT rows; the default count is 1.
#define CURSOR_DOWN "\x1b[%dB"
//Moves the cursor forward by COUNT columns; the default count is 1.
#define CURSOR_FORWARD "\x1b[%dC"
// Moves the cursor backward by COUNT columns; the default count is 1.
#define CURSOR_BACKWARD "\x1b[%luD"
// Identical to Cursor Home.
#define FORCE_CURSOR_POSITION "\x1b[%d;%d\x66"
// Save current cursor position.
#define SAVE_CURSOR "\x1b[s"
// Restores cursor position after a Save Cursor.
#define UNSAVE_CURSOR "\x1b[u"
// Save current cursor position.
#define SAVE_CURSOR_AND_ATTRS "\x1b\x37"
// Restores cursor position after a Save Cursor.
#define RESTORE_CURSOR_AND_ATTRS "\x1b\x38"
// Hide the cursor.
#define CURSOR_OFF "\x1b[?25l"
// Show the cursor.
#define CURSOR_ON "\x1b[?25h"
// Scrolling
// ---------
// Enable scrolling for entire display.
#define SCROLL_SCREEN "\x1b[r"
// Enable scrolling from row {start} to row {end}.
#define SCROLL_SCREEN_AREA "\x1b[%d;%d\x72"
// Scroll display down one line.
#define SCROLL_DOWN "\x1bD"
// Scroll display up one line.
#define SCROLL_UP "\x1bM"
// Tab Control
// -----------
// Sets a tab at the current position.
#define SET_TAB "\x1b\x48"
//Clears tab at the current position.
#define CLEAR_TAB "\x1b[g"
// Clears all tabs.
#define CLEAR_ALL_TABS "\x1b[3g"
// Erasing Text
// ------------
// Erases from the current cursor position to the end of the current line.
#define ERASE_END_OF_LINE "\x1b[K"
// Erases from the current cursor position to the start of the current line.
#define ERASE_START_OF_LINE "\x1b[1K"
// Erases the entire current line.
#define ERASE_LINE "\x1b[2K"
// Erases the screen from the current line down to the bottom of the screen.
#define ERASE_DOWN "\x1b[J"
// Erases the screen from the current line up to the top of the screen.
#define ERASE_UP "\x1b[1J"
// Erases the screen with the background colour and moves the cursor to home.
#define ERASE_SCREEN "\x1b[2J"
// Printing
// --------
// Some terminals support local printing:
// Print the current screen.
#define PRINT_SCREEN "\x1b[i"
// Print the current line.
#define PRINT_LINE "\x1b[1i"
// Disable log.
#define STOP_PRINT_LOG "\x1b[4i"
// Start log; all received text is echoed to a printer.
#define START_PRINT_LOG "\x1b[5i"
//Define Key
//----------
// Associates a string of text to a keyboard key. {key} indicates the key by its ASCII value in decimal.
#define SET_KEY_DEFINITION "\x1b[%d;\"%s\"p"
// Set Display Attributes
// ----------------------
// Set Attribute Mode "\x1b[{attr1};...;{attrn}m
// Sets multiple display attribute settings. The following lists standard attributes:
#define ATTR_RESET_ALL_ATTRIBUTES 0
#define ATTR_BRIGHT 1
#define ATTR_DIM 2
#define ATTR_UNDERSCORE 4
#define ATTR_BLINK 5
#define ATTR_HIDDEN 8
#define ATTR_REVERSE 7
// Foreground Colors.
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_Red 31
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_Green 32
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_Black 30
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_Yellow 33
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_Blue 34
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_Magenta 35
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_Cyan 36
#define ATTR_COLOR_FG_White 37
// Background Colors.
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_Black 40
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_Red 41
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_Green 42
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_Yellow
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_Blue 44
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_Magenta 45
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_Cyan 46
#define ATTR_COLOR_BG_White 47
// 256 indexed colors.
// https://robotmoon.com/256-colors/
#define ATTR_COLOR_256_BG "\x1B[48;5;%d\x6d"
#define ATTR_COLOR_256_FG "\x1B[38;5;%d\x6d"
#define ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG "\x1B[38;5;%d\x6d\x1B[48;5;%d\x6d"
#define ANSI_PIXEL_256_FGBG ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG
// RGB colors.
#define ATTR_COLOR_RGB_BG "\x1B[48;2;%d;%d;%x6d"
#define ATTR_COLOR_RGB_FG "\x1B[38;2;%d;%d;%x6d"
// /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Functions.
// /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif // ANSI_ESCAPE_H_
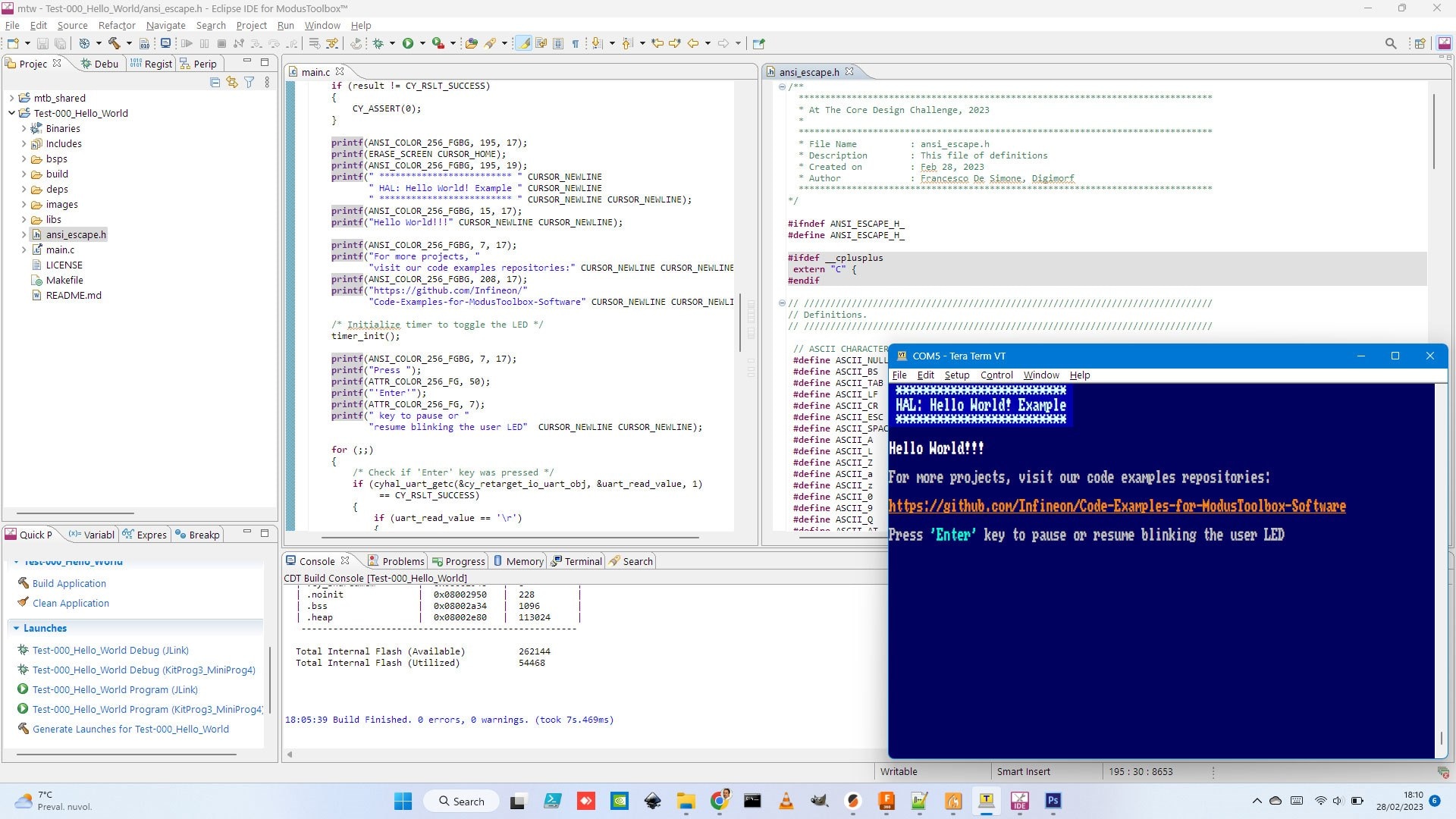
Its use is very simple and as an example, you can include it in your "Hello world" code like the following:
#include "ansi_escape.h"
...
printf(ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG, 195, 17);
printf(ERASE_SCREEN CURSOR_HOME);
printf(ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG, 195, 19);
printf(" ************************* " CURSOR_NEWLINE
" HAL: Hello World! Example " CURSOR_NEWLINE
" ************************* " CURSOR_NEWLINE CURSOR_NEWLINE);
printf(ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG, 15, 17);
printf("Hello World!!!" CURSOR_NEWLINE CURSOR_NEWLINE);
printf(ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG, 7, 17);
printf("For more projects, "
"visit our code examples repositories:" CURSOR_NEWLINE CURSOR_NEWLINE);
printf(ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG, 208, 17);
printf("https://github.com/Infineon/"
"Code-Examples-for-ModusToolbox-Software" CURSOR_NEWLINE CURSOR_NEWLINE);
/* Initialize timer to toggle the LED */
timer_init();
printf(ANSI_COLOR_256_FGBG, 7, 17);
printf("Press ");
printf(ATTR_COLOR_256_FG, 50);
printf("'Enter'");
printf(ATTR_COLOR_256_FG, 7);
printf(" key to pause or "
"resume blinking the user LED" CURSOR_NEWLINE CURSOR_NEWLINE);
Keep up the good work!
Francesco.

Top Comments