In the Second Blog, I mentioned how to create a minimalistic hardware design based on Vivado. As mentioned in the First Blog, This blog post will be focussed on Petalinux. I will use the .xsa file from the minimalistic hardware design generated in the previous blog post to configure and build a Petalinux system. I will be configuring the rootfs to my requirements to include python, examining the build outputs to validate our modifications. Let's get started.
Petalinux Introduction:
Petalinux is an embedded Linux development environment specifically designed for AMD Zynq and MicroBlaze-based FPGA systems. It is a toolset provided by AMD that facilitates the creation, customization, and deployment of Linux-based systems on AMD SoC (System-on-Chip) and MPSoC (MultiProcessor SoC) devices. Petalinux streamlines the process of building and configuring the Linux kernel, root filesystem, and associated components, making it easier for developers to integrate their custom hardware designs with Linux software.
Overview of various Petalinux commands:
petalinux-create: This command is used to create a new petalinux project. It initializes the directory structure and sets up the project environment.
petalinux-config: After creating a project, this command allows you to configure various aspects of the Linux system, including the kernel, device tree, and user-space packages. It opens a menu-driven interface to customize the project settings.
| petalinux-config example |
|---|
|
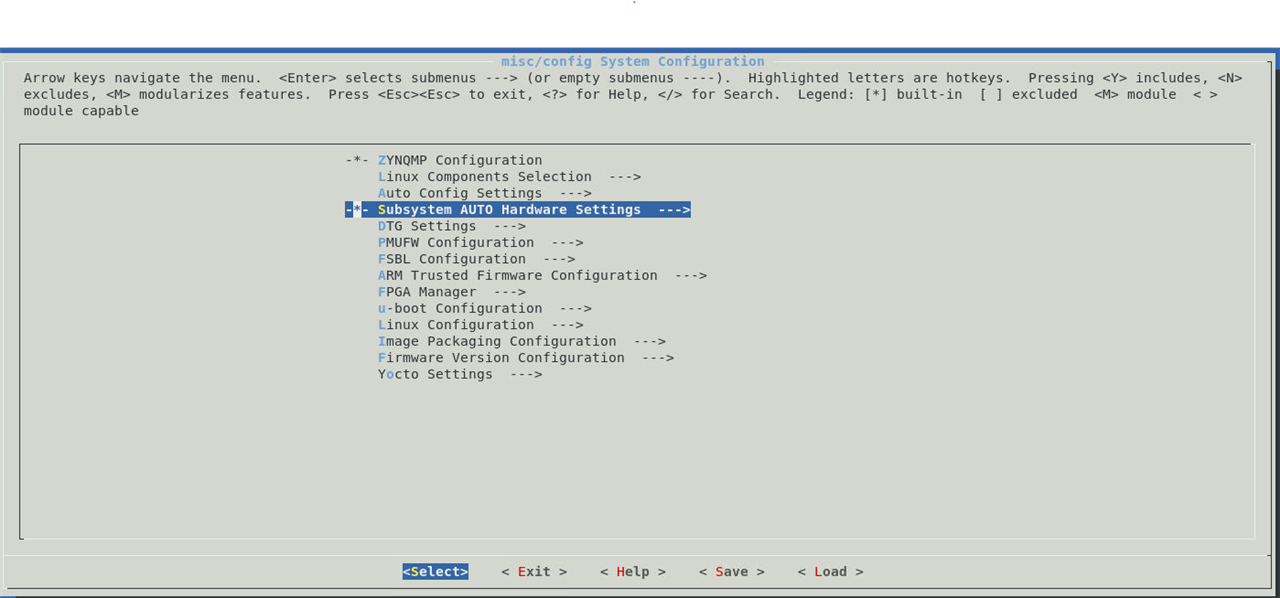
Configuraiton of hardware settings |
|
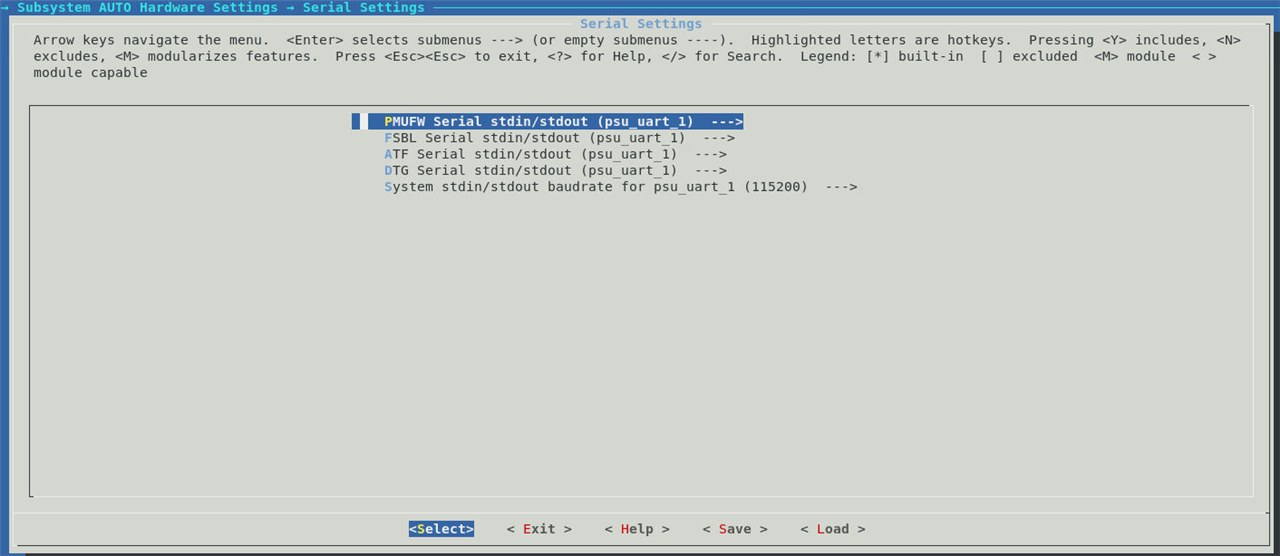
With in the hardware setting, we can modify memory, serial port, flash (if available), SD card settings. |
|
In our case the UART1 is selected by default as that is the only UART available in the design. |
In petalinux, the petalinux-config command is used to configure various aspects of the Linux system, including the root filesystem, U-Boot bootloader, and the kernel. It opens a menu-driven interface where you can customize the settings based on your specific requirements. Here's a brief explanation of each configuration:
petalinux-config for Root Filesystem:
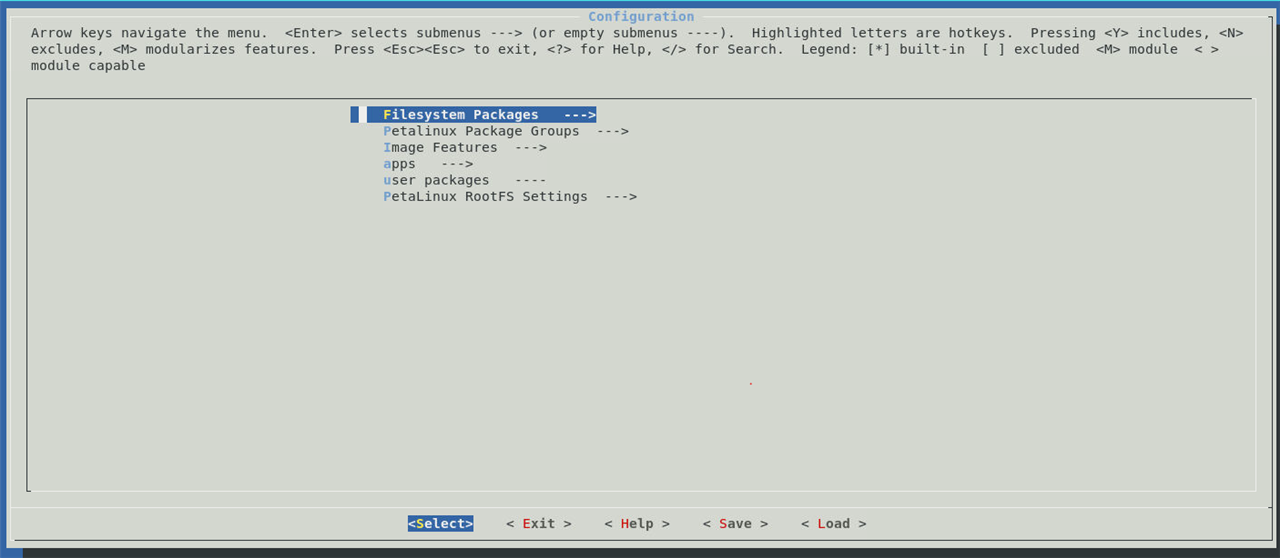
When you run petalinux-config -c rootfs, it opens the menu configuration interface specifically for the root filesystem. Here, you can add or remove user-space packages, libraries, and applications that will be included in the final Linux image. You can also set up system initialization scripts, configure network settings, enable/disable services, and more.
Example:
petalinux-config -c rootfs
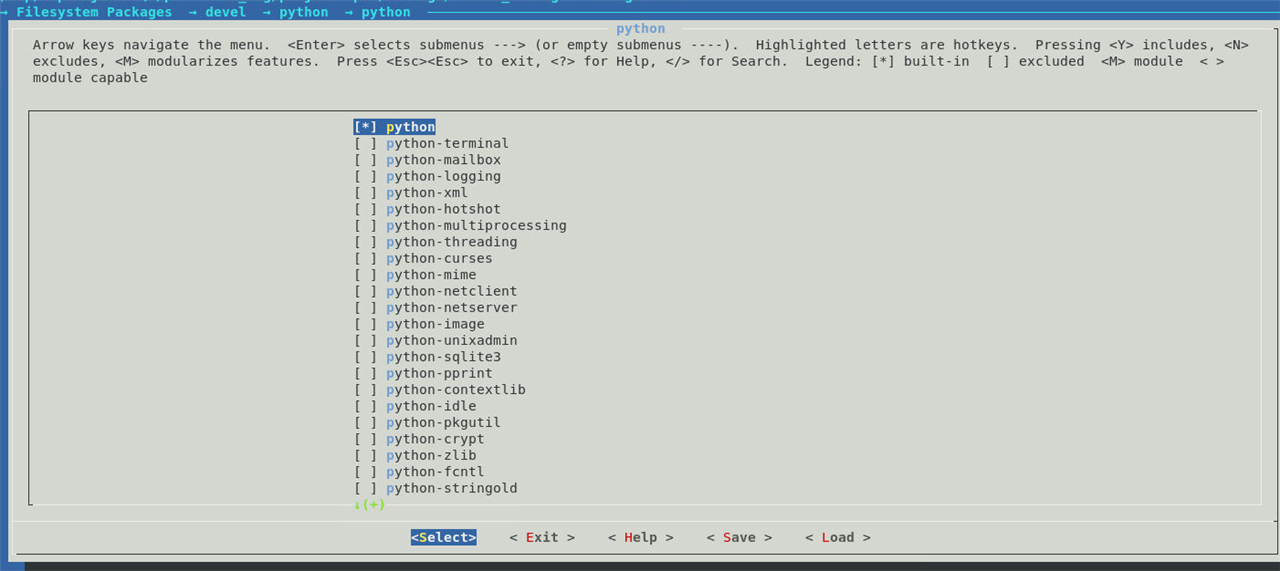
In the menu interface, navigate to "Filesystem Packages" -> "misc" and select "nano" to include it in the root filesystem.
| rootfs configuration (adding python) example |
|---|
|
On the menu config, we have to select the Filesystem packages which includes various libraries and useful packages |
|
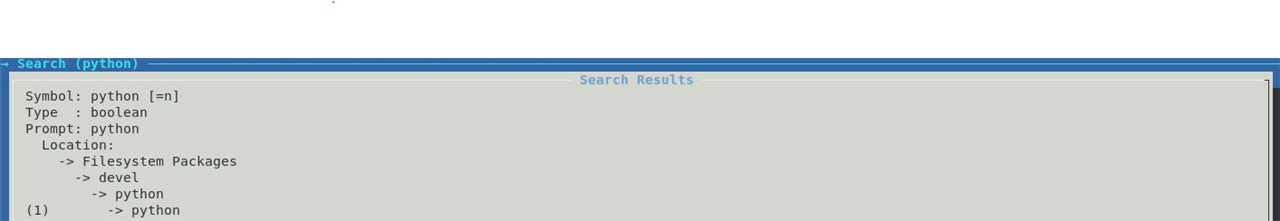
We are specifically interested in python package, so we can search for it using "/" command in the menuconfig and typing python |
|
This shows the list of matching packages and their location. |
|
We can then trace the location and enable the package by pressing the "space button in keyboard", which result in "*" selection |
|
You can save the settings and then start a petalinux-build to get an image with your required modifications |
petalinux-config for U-Boot:
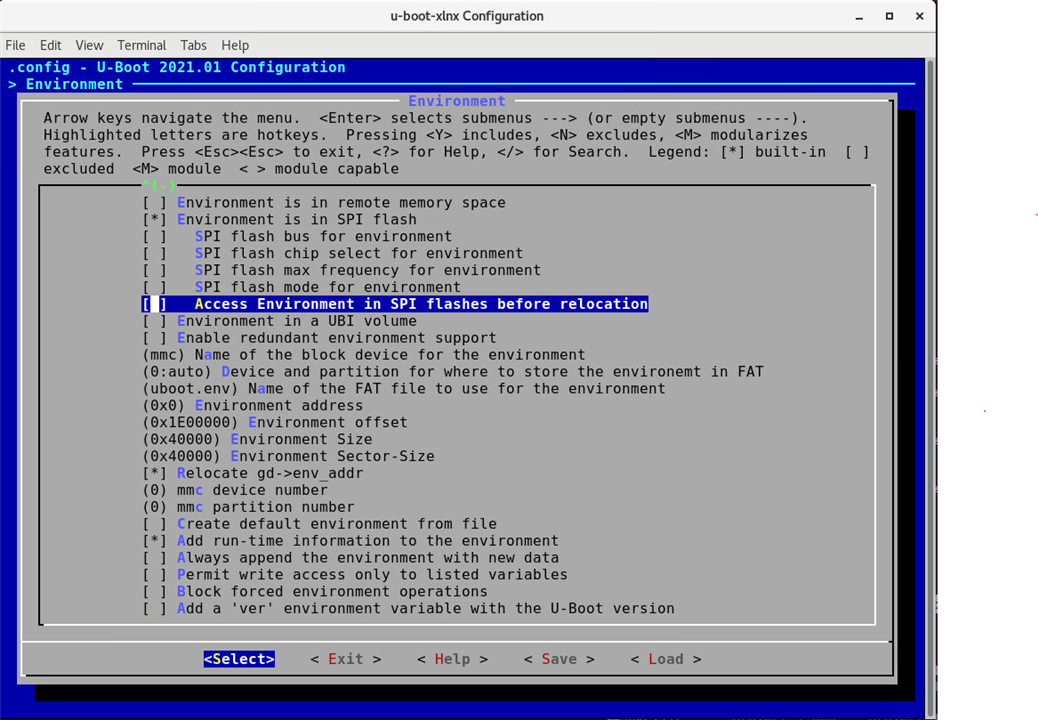
For U-Boot configuration, you can use petalinux-config -c u-boot. This allows you to customize the U-Boot bootloader settings, such as boot arguments, boot order, environment variables, and other board-specific configurations.
Example:
To modify the U-Boot environment to set the bootargs:
petalinux-config -c u-boot
It takes a bit of time before the menu interface appears.
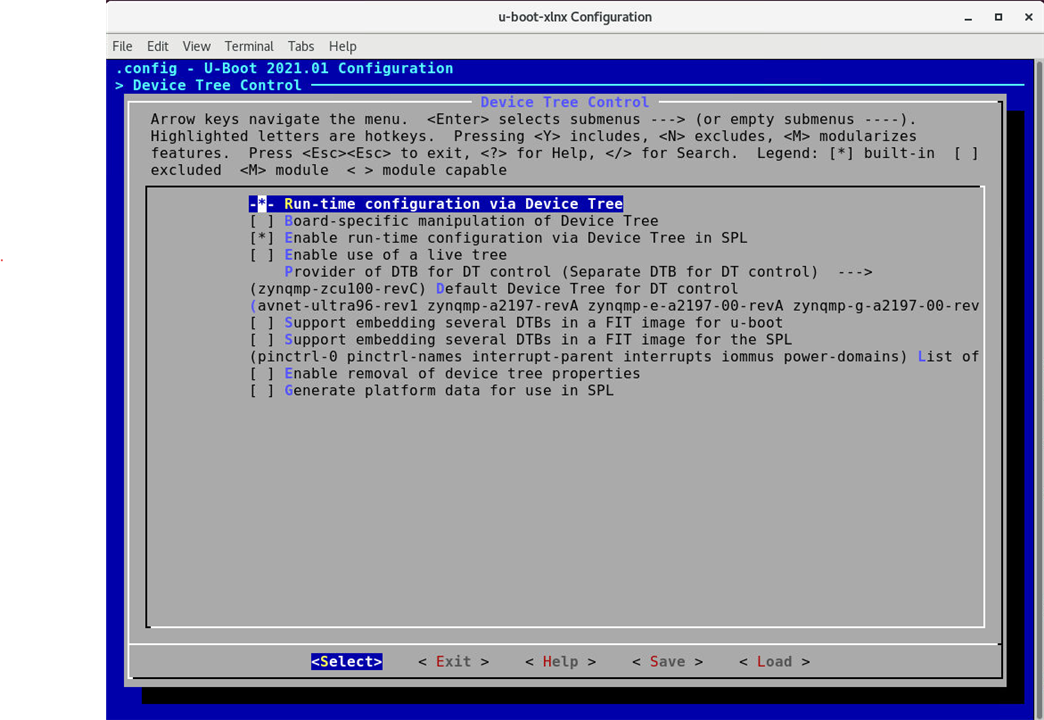
In the menu interface, navigate to "U-Boot Configuration" -> "Environment variables" and set the desired bootargs.
| u-boot configuration example |
|---|
|
Shows the u-boot menu config and the plethora of options available to customize |
|
I have just shown the example for modifying the run time device tree configuration. |
|
You also have the options for changing the u-boot environment by changing its size, offset etc. |
petalinux-config for Kernel:
For kernel configuration, the command is petalinux-config -c kernel. This opens the Linux kernel configuration menu, where you can enable or disable kernel features, drivers, and other options relevant to your hardware and application requirements.
Example:
To enable support for a specific hardware driver, e.g., I2C driver:
petalinux-config -c kernel
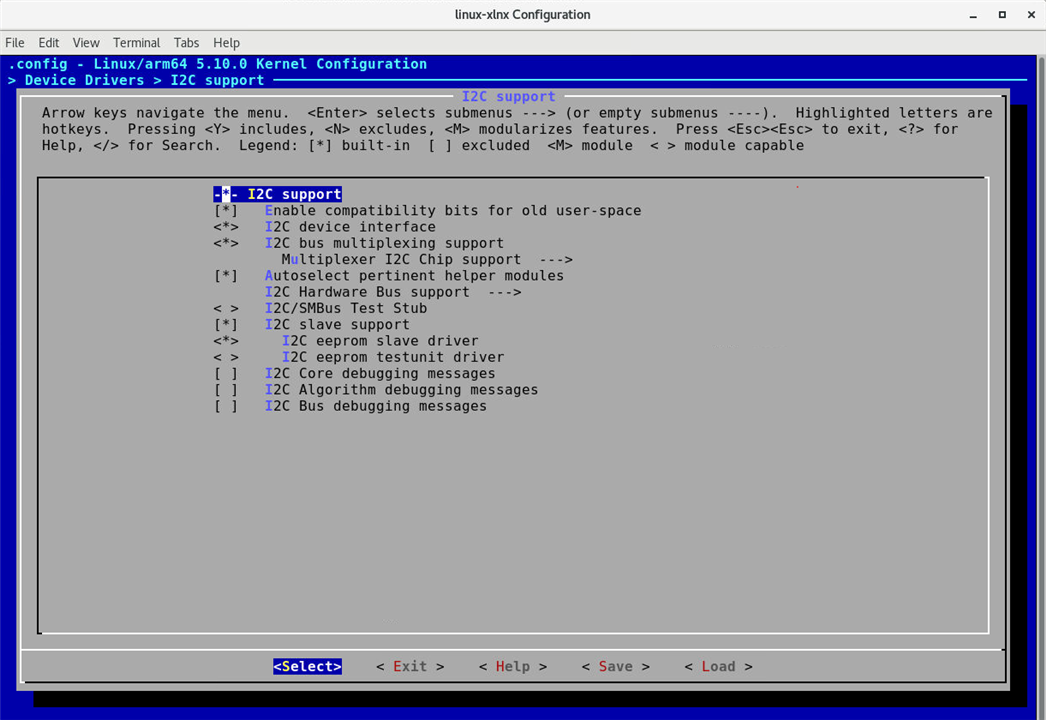
In the menu interface, navigate to "Device Drivers" -> "I2C support" and select the appropriate options.
| config kernel options |
|---|
|
Similar to u-boot, kernel also has a lot of features that you can enable (showing a sample menuconfig). |
|
A simple example is to enable the i2c support, so that it enables drivers that allows you to talk with i2c compatible device |
|
Another useful kernel config is to enable device drivers for specific networking device. In this case some wireless and bluetooth drivers are enabled by default. |
Once you make the necessary configurations using the petalinux-config command, you can save the changes and exit the interface. After that, you typically run petalinux-build to build the project with the updated settings. Keep in mind that the specific options and menu structure may vary depending on your petalinux version and project configuration. Always refer to the official documentation for the version you are using for the most accurate instructions.
petalinux-build: This command is used to build the petalinux project. It compiles the Linux kernel, builds the root filesystem, and generates bootable images.
petalinux-package: Once the build is complete, this command helps package the project into various formats suitable for booting the system, like BOOT.BIN, image.ub, etc.
petalinux-boot: Used to boot the petalinux image on the target hardware. It is typically done through a boot medium like SD card or TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server.
petalinux-config --get: This command retrieves the current configuration settings of the petalinux project, which can be helpful for scripting or reference purposes.
petalinux-package --boot: Helps to package the files needed for the boot process, such as the bootloader, device tree, and kernel image.
petalinux-package --image: Used to package the root filesystem and other components into an image that can be flashed to storage media.
The above commands are some of the fundamental commands used in petalinux. As the toolset evolves new commands gets introduced in newer versions of petalinux. Always refer to the official Petalinux documentation (Overview • PetaLinux Tools Documentation: Reference Guide (UG1144) • Reader • AMD Adaptive Computing Documentation Portal (xilinx.com)) for the most up-to-date information.
Petalinux usage in custom project:
The following section provides details on how petalinux was used for this project to customise the rootfs to include python. The below sequence of commands outlines the process of creating a petalinux project, configuring it with the hardware description, building the project, and packaging it into a bootable binary format.
petalinux-create --type project --template zynqMP --name petalinux_img
cp /path_to_your_xsa_file/*.xsa .
petalinux-config -p petalinux_img --silentconfig --get-hw-description=.
# This is the point we can configure the u-boot, rootfs (to include python), kernel etc.
petalinux-build -p petalinux_img
cp /path_to_your_bif_file/boot.bif .
petalinux-package --boot --format BIN --bif boot.bif --force
Let's break down each command step by step:
1. `petalinux-create --type project --template zynqMP --name petalinux_img`:
This command creates a new petalinux project named "petalinux_img" using the ZynqMP template. It sets up the directory structure and initializes the project environment.
2. `cp /path_to_your_xsa_file/*.xsa .`:
This command copies the hardware description file (XSA file) from the specified path to the current working directory. The XSA file contains information about the hardware platform, including the FPGA fabric and the processing system.
3. `petalinux-config -p petalinux_img --silentconfig --get-hw-description=.`:
This command runs the petalinux configuration for the "petalinux_img" project in silent mode. It automatically detects and configures the project based on the hardware description (XSA file) present in the current directory (denoted by "."). This step is crucial as it ensures that the Linux kernel and root filesystem are set up to match the hardware platform.
4. Before building the project, we can customize the various components (in our case rootfs to include python, or modify u-boot to change certain parameters, modify kernel to include certain device drivers or certain kernel features). The options are very vast and is beyond the scope of this blog. This is itself is an entire domain to explore.
5. `petalinux-build -p petalinux_img`:
This command initiates the build process for the "petalinux_img" project. It compiles the Linux kernel, builds the root filesystem, and generates the necessary components to create a bootable image.
5. `cp /path_to_your_bif_file/boot.bif .`:
Here, the command copies the Boot Image Format (BIF) file from the specified path to the current working directory. The BIF file is a configuration file that specifies how different components are combined to create the bootable image.
6. `petalinux-package --boot --format BIN --bif boot.bif --force`:
Finally, this command packages the built files into a bootable binary format. The `--boot` option indicates that it is creating a boot image. The `--format BIN` specifies the format of the boot image as a binary file. The `--bif boot.bif` option tells petalinux to use the provided BIF file for packaging, and `--force` ensures that the process proceeds without manual confirmation.
After completing these steps, you should have a bootable binary image that can be used to program the target hardware and boot your petalinux-based system. Please note that the actual paths for XSA file and BIF file should be provided in the respective commands, and the exact commands and options might vary based on the petalinux version used. Always consult the official petalinux documentation for the version you are working with to ensure accuracy and compatibility.
Demo:

Below is a UART port result of the minimal hardware design based petalinux boot image that has a customized rootfs to include python. We write a simple program to print "Hello Ultra96v2 from python !!!"
▒Xilinx Zynq MP First Stage Boot Loader
Release 2021.2 Oct 13 2021 - 07:15:53
NOTICE: BL31: v2.4(release):xlnx_rebase_v2.4_2021.1_update1-23-g9188496b9
NOTICE: BL31: Built : 07:41:24, Oct 13 2021
U-Boot 2021.01 (Oct 12 2021 - 09:28:42 +0000)
CPU: ZynqMP
Silicon: v3
Board: Xilinx ZynqMP
DRAM: 2 GiB
PMUFW: v1.1
EL Level: EL2
Chip ID: zu3eg
NAND: 0 MiB
MMC: mmc@ff160000: 0
Loading Environment from FAT... *** Warning - bad CRC, using default environment
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Bootmode: SD_MODE
Reset reason: EXTERNAL
Net: No ethernet found.
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
switch to partitions #0, OK
mmc0 is current device
Scanning mmc 0:1...
Found U-Boot script /boot.scr
2710 bytes read in 21 ms (126 KiB/s)
## Executing script at 20000000
Trying to load boot images from mmc0
31847380 bytes read in 2293 ms (13.2 MiB/s)
## Loading kernel from FIT Image at 10000000 ...
Using 'conf-system-top.dtb' configuration
Trying 'kernel-1' kernel subimage
Description: Linux kernel
Created: 2021-10-12 9:30:57 UTC
Type: Kernel Image
Compression: gzip compressed
Data Start: 0x100000f8
Data Size: 9386420 Bytes = 9 MiB
Architecture: AArch64
OS: Linux
Load Address: 0x00200000
Entry Point: 0x00200000
Hash algo: sha256
Hash value: 9ab12d25a498da274e0d325e9f90e49e862d85cef5f67ed3077fcd47de6679bd
Verifying Hash Integrity ... sha256+ OK
## Loading ramdisk from FIT Image at 10000000 ...
Using 'conf-system-top.dtb' configuration
Trying 'ramdisk-1' ramdisk subimage
Description: petalinux-image-minimal
Created: 2021-10-12 9:30:57 UTC
Type: RAMDisk Image
Compression: uncompressed
Data Start: 0x108fca1c
Data Size: 22422589 Bytes = 21.4 MiB
Architecture: AArch64
OS: Linux
Load Address: unavailable
Entry Point: unavailable
Hash algo: sha256
Hash value: 300b2bcf65e0586a736b86ca88512100e270e85caf31504d6bb5ab03189e93cb
Verifying Hash Integrity ... sha256+ OK
## Loading fdt from FIT Image at 10000000 ...
Using 'conf-system-top.dtb' configuration
Trying 'fdt-system-top.dtb' fdt subimage
Description: Flattened Device Tree blob
Created: 2021-10-12 9:30:57 UTC
Type: Flat Device Tree
Compression: uncompressed
Data Start: 0x108f3bbc
Data Size: 36238 Bytes = 35.4 KiB
Architecture: AArch64
Hash algo: sha256
Hash value: 76bcbf9c35c0a52e3dd7538e02df2462e7ca197580750f92333d0b8c44458175
Verifying Hash Integrity ... sha256+ OK
Booting using the fdt blob at 0x108f3bbc
Uncompressing Kernel Image
Loading Ramdisk to 7c7b0000, end 7dd1243d ... OK
Loading Device Tree to 000000007c7a4000, end 000000007c7afd8d ... OK
Starting kernel ...
[ 0.000000] Booting Linux on physical CPU 0x0000000000 [0x410fd034]
[ 0.000000] Linux version 5.10.0-xilinx-v2021.2 (oe-user@oe-host) (aarch64-xilinx-linux-gcc (GCC) 10.2.0, GNU ld (GNU Binutils) 2.35.1) #1 SMP Tue Oct 12 09:30:57 UTC 2021
[ 0.000000] Machine model: xlnx,zynqmp
[ 0.000000] earlycon: cdns0 at MMIO 0x00000000ff010000 (options '115200n8')
[ 0.000000] printk: bootconsole [cdns0] enabled
[ 0.000000] efi: UEFI not found.
[ 0.000000] cma: Reserved 256 MiB at 0x000000006c400000
[ 0.000000] Zone ranges:
[ 0.000000] DMA32 [mem 0x0000000000000000-0x000000007fefffff]
[ 0.000000] Normal empty
[ 0.000000] Movable zone start for each node
[ 0.000000] Early memory node ranges
[ 0.000000] node 0: [mem 0x0000000000000000-0x000000007fefffff]
[ 0.000000] Zeroed struct page in unavailable ranges: 256 pages
[ 0.000000] Initmem setup node 0 [mem 0x0000000000000000-0x000000007fefffff]
[ 0.000000] psci: probing for conduit method from DT.
[ 0.000000] psci: PSCIv1.1 detected in firmware.
[ 0.000000] psci: Using standard PSCI v0.2 function IDs
[ 0.000000] psci: MIGRATE_INFO_TYPE not supported.
[ 0.000000] psci: SMC Calling Convention v1.2
[ 0.000000] percpu: Embedded 22 pages/cpu s50968 r8192 d30952 u90112
[ 0.000000] Detected VIPT I-cache on CPU0
[ 0.000000] CPU features: detected: ARM erratum 845719
[ 0.000000] Built 1 zonelists, mobility grouping on. Total pages: 515844
[ 0.000000] Kernel command line: earlycon console=ttyPS0,115200 clk_ignore_unused root=/dev/ram0 rw
[ 0.000000] Dentry cache hash table entries: 262144 (order: 9, 2097152 bytes, linear)
[ 0.000000] Inode-cache hash table entries: 131072 (order: 8, 1048576 bytes, linear)
[ 0.000000] mem auto-init: stack:off, heap alloc:off, heap free:off
[ 0.000000] Memory: 1749904K/2096128K available (13952K kernel code, 982K rwdata, 3928K rodata, 2112K init, 586K bss, 84080K reserved, 262144K cma-reserved)
[ 0.000000] rcu: Hierarchical RCU implementation.
[ 0.000000] rcu: RCU event tracing is enabled.
[ 0.000000] rcu: RCU calculated value of scheduler-enlistment delay is 25 jiffies.
[ 0.000000] NR_IRQS: 64, nr_irqs: 64, preallocated irqs: 0
[ 0.000000] GIC: Adjusting CPU interface base to 0x00000000f902f000
[ 0.000000] GIC: Using split EOI/Deactivate mode
[ 0.000000] random: get_random_bytes called from start_kernel+0x31c/0x524 with crng_init=0
[ 0.000000] arch_timer: cp15 timer(s) running at 33.33MHz (phys).
[ 0.000000] clocksource: arch_sys_counter: mask: 0xffffffffffffff max_cycles: 0x7b0074340, max_idle_ns: 440795202884 ns
[ 0.000004] sched_clock: 56 bits at 33MHz, resolution 30ns, wraps every 2199023255543ns
[ 0.008319] Console: colour dummy device 80x25
[ 0.012403] Calibrating delay loop (skipped), value calculated using timer frequency.. 66.66 BogoMIPS (lpj=133332)
[ 0.022668] pid_max: default: 32768 minimum: 301
[ 0.027418] Mount-cache hash table entries: 4096 (order: 3, 32768 bytes, linear)
[ 0.034616] Mountpoint-cache hash table entries: 4096 (order: 3, 32768 bytes, linear)
[ 0.043834] rcu: Hierarchical SRCU implementation.
[ 0.047412] EFI services will not be available.
[ 0.051825] smp: Bringing up secondary CPUs ...
[ 0.228272] Detected VIPT I-cache on CPU1
[ 0.228332] CPU1: Booted secondary processor 0x0000000001 [0x410fd034]
[ 0.595597] Detected VIPT I-cache on CPU2
[ 0.595622] CPU2: Booted secondary processor 0x0000000002 [0x410fd034]
[ 0.956914] Detected VIPT I-cache on CPU3
[ 0.956938] CPU3: Booted secondary processor 0x0000000003 [0x410fd034]
[ 0.956990] smp: Brought up 1 node, 4 CPUs
[ 0.986847] SMP: Total of 4 processors activated.
[ 0.991520] CPU features: detected: 32-bit EL0 Support
[ 0.996624] CPU features: detected: CRC32 instructions
[ 1.001779] CPU: All CPU(s) started at EL2
[ 1.005806] alternatives: patching kernel code
[ 1.011664] devtmpfs: initialized
[ 1.018077] clocksource: jiffies: mask: 0xffffffff max_cycles: 0xffffffff, max_idle_ns: 7645041785100000 ns
[ 1.023193] futex hash table entries: 1024 (order: 4, 65536 bytes, linear)
[ 1.037813] pinctrl core: initialized pinctrl subsystem
[ 1.038608] DMI not present or invalid.
[ 1.041431] NET: Registered protocol family 16
[ 1.047383] DMA: preallocated 256 KiB GFP_KERNEL pool for atomic allocations
[ 1.052747] DMA: preallocated 256 KiB GFP_KERNEL|GFP_DMA32 pool for atomic allocations
[ 1.060566] audit: initializing netlink subsys (disabled)
[ 1.065977] audit: type=2000 audit(1.008:1): state=initialized audit_enabled=0 res=1
[ 1.073597] cpuidle: using governor menu
[ 1.077548] hw-breakpoint: found 6 breakpoint and 4 watchpoint registers.
[ 1.084278] ASID allocator initialised with 65536 entries
[ 1.089698] Serial: AMBA PL011 UART driver
[ 1.111621] HugeTLB registered 1.00 GiB page size, pre-allocated 0 pages
[ 1.112677] HugeTLB registered 32.0 MiB page size, pre-allocated 0 pages
[ 1.119351] HugeTLB registered 2.00 MiB page size, pre-allocated 0 pages
[ 1.126015] HugeTLB registered 64.0 KiB page size, pre-allocated 0 pages
[ 2.177890] cryptd: max_cpu_qlen set to 1000
[ 2.205068] DRBG: Continuing without Jitter RNG
[ 2.285472] raid6: neonx8 gen() 2137 MB/s
[ 2.353525] raid6: neonx8 xor() 1596 MB/s
[ 2.421587] raid6: neonx4 gen() 2186 MB/s
[ 2.489650] raid6: neonx4 xor() 1561 MB/s
[ 2.557718] raid6: neonx2 gen() 2076 MB/s
[ 2.625775] raid6: neonx2 xor() 1435 MB/s
[ 2.693843] raid6: neonx1 gen() 1774 MB/s
[ 2.761903] raid6: neonx1 xor() 1219 MB/s
[ 2.829961] raid6: int64x8 gen() 1437 MB/s
[ 2.898026] raid6: int64x8 xor() 771 MB/s
[ 2.966089] raid6: int64x4 gen() 1601 MB/s
[ 3.034159] raid6: int64x4 xor() 815 MB/s
[ 3.102237] raid6: int64x2 gen() 1398 MB/s
[ 3.170284] raid6: int64x2 xor() 750 MB/s
[ 3.238374] raid6: int64x1 gen() 1031 MB/s
[ 3.306433] raid6: int64x1 xor() 517 MB/s
[ 3.306475] raid6: using algorithm neonx4 gen() 2186 MB/s
[ 3.310424] raid6: .... xor() 1561 MB/s, rmw enabled
[ 3.315356] raid6: using neon recovery algorithm
[ 3.320497] iommu: Default domain type: Translated
[ 3.325082] SCSI subsystem initialized
[ 3.328685] usbcore: registered new interface driver usbfs
[ 3.333991] usbcore: registered new interface driver hub
[ 3.339262] usbcore: registered new device driver usb
[ 3.344310] mc: Linux media interface: v0.10
[ 3.348505] videodev: Linux video capture interface: v2.00
[ 3.353982] EDAC MC: Ver: 3.0.0
[ 3.357527] zynqmp-ipi-mbox mailbox@ff990400: Registered ZynqMP IPI mbox with TX/RX channels.
[ 3.365750] FPGA manager framework
[ 3.369032] Advanced Linux Sound Architecture Driver Initialized.
[ 3.375342] Bluetooth: Core ver 2.22
[ 3.378517] NET: Registered protocol family 31
[ 3.382914] Bluetooth: HCI device and connection manager initialized
[ 3.389232] Bluetooth: HCI socket layer initialized
[ 3.394073] Bluetooth: L2CAP socket layer initialized
[ 3.399098] Bluetooth: SCO socket layer initialized
[ 3.404253] clocksource: Switched to clocksource arch_sys_counter
[ 3.410167] VFS: Disk quotas dquot_6.6.0
[ 3.413933] VFS: Dquot-cache hash table entries: 512 (order 0, 4096 bytes)
[ 3.425602] NET: Registered protocol family 2
[ 3.426085] tcp_listen_portaddr_hash hash table entries: 1024 (order: 2, 16384 bytes, linear)
[ 3.433545] TCP established hash table entries: 16384 (order: 5, 131072 bytes, linear)
[ 3.441498] TCP bind hash table entries: 16384 (order: 6, 262144 bytes, linear)
[ 3.448991] TCP: Hash tables configured (established 16384 bind 16384)
[ 3.455258] UDP hash table entries: 1024 (order: 3, 32768 bytes, linear)
[ 3.461843] UDP-Lite hash table entries: 1024 (order: 3, 32768 bytes, linear)
[ 3.469040] NET: Registered protocol family 1
[ 3.473596] RPC: Registered named UNIX socket transport module.
[ 3.479110] RPC: Registered udp transport module.
[ 3.483775] RPC: Registered tcp transport module.
[ 3.488450] RPC: Registered tcp NFSv4.1 backchannel transport module.
[ 3.495484] PCI: CLS 0 bytes, default 64
[ 3.498874] Trying to unpack rootfs image as initramfs...
[ 4.539871] Freeing initrd memory: 21896K
[ 4.618790] Initialise system trusted keyrings
[ 4.618964] workingset: timestamp_bits=46 max_order=19 bucket_order=0
[ 4.624899] NFS: Registering the id_resolver key type
[ 4.629056] Key type id_resolver registered
[ 4.633178] Key type id_legacy registered
[ 4.637181] nfs4filelayout_init: NFSv4 File Layout Driver Registering...
[ 4.643837] jffs2: version 2.2. (NAND) (SUMMARY) © 2001-2006 Red Hat, Inc.
[ 4.686865] NET: Registered protocol family 38
[ 4.686917] xor: measuring software checksum speed
[ 4.694601] 8regs : 2363 MB/sec
[ 4.698262] 32regs : 2799 MB/sec
[ 4.703206] arm64_neon : 2380 MB/sec
[ 4.703395] xor: using function: 32regs (2799 MB/sec)
[ 4.708420] Key type asymmetric registered
[ 4.712483] Asymmetric key parser 'x509' registered
[ 4.717356] Block layer SCSI generic (bsg) driver version 0.4 loaded (major 247)
[ 4.724683] io scheduler mq-deadline registered
[ 4.729177] io scheduler kyber registered
[ 4.735093] ps_pcie_dma init()
[ 4.764761] Serial: 8250/16550 driver, 4 ports, IRQ sharing disabled
[ 4.766726] Serial: AMBA driver
[ 4.770365] cacheinfo: Unable to detect cache hierarchy for CPU 0
[ 4.780115] brd: module loaded
[ 4.785837] loop: module loaded
[ 4.786632] mtdoops: mtd device (mtddev=name/number) must be supplied
[ 4.791299] libphy: Fixed MDIO Bus: probed
[ 4.795226] tun: Universal TUN/TAP device driver, 1.6
[ 4.798946] CAN device driver interface
[ 4.803187] usbcore: registered new interface driver asix
[ 4.808066] usbcore: registered new interface driver ax88179_178a
[ 4.814084] usbcore: registered new interface driver cdc_ether
[ 4.819876] usbcore: registered new interface driver net1080
[ 4.825505] usbcore: registered new interface driver cdc_subset
[ 4.831383] usbcore: registered new interface driver zaurus
[ 4.836935] usbcore: registered new interface driver cdc_ncm
[ 4.843443] usbcore: registered new interface driver uas
[ 4.847840] usbcore: registered new interface driver usb-storage
[ 4.854508] rtc_zynqmp ffa60000.rtc: registered as rtc0
[ 4.858981] rtc_zynqmp ffa60000.rtc: setting system clock to 1970-01-01T00:00:07 UTC (7)
[ 4.867041] i2c /dev entries driver
[ 4.871791] usbcore: registered new interface driver uvcvideo
[ 4.876171] USB Video Class driver (1.1.1)
[ 4.880581] Bluetooth: HCI UART driver ver 2.3
[ 4.884651] Bluetooth: HCI UART protocol H4 registered
[ 4.889752] Bluetooth: HCI UART protocol BCSP registered
[ 4.895046] Bluetooth: HCI UART protocol LL registered
[ 4.900130] Bluetooth: HCI UART protocol ATH3K registered
[ 4.905506] Bluetooth: HCI UART protocol Three-wire (H5) registered
[ 4.911752] Bluetooth: HCI UART protocol Intel registered
[ 4.917098] Bluetooth: HCI UART protocol QCA registered
[ 4.922302] usbcore: registered new interface driver bcm203x
[ 4.927926] usbcore: registered new interface driver bpa10x
[ 4.933459] usbcore: registered new interface driver bfusb
[ 4.938909] usbcore: registered new interface driver btusb
[ 4.944383] usbcore: registered new interface driver ath3k
[ 4.949871] EDAC MC: ECC not enabled
[ 4.953505] EDAC DEVICE0: Giving out device to module zynqmp-ocm-edac controller zynqmp_ocm: DEV ff960000.memory-controller (INTERRUPT)
[ 4.965821] sdhci: Secure Digital Host Controller Interface driver
[ 4.971585] sdhci: Copyright(c) Pierre Ossman
[ 4.975906] sdhci-pltfm: SDHCI platform and OF driver helper
[ 4.981816] ledtrig-cpu: registered to indicate activity on CPUs
[ 4.987513] SMCCC: SOC_ID: ARCH_SOC_ID not implemented, skipping ....
[ 4.993949] zynqmp_firmware_probe Platform Management API v1.1
[ 4.999696] zynqmp_firmware_probe Trustzone version v1.0
[ 5.048313] securefw securefw: securefw probed
[ 5.048699] alg: No test for xilinx-zynqmp-aes (zynqmp-aes)
[ 5.052780] zynqmp_aes firmware:zynqmp-firmware:zynqmp-aes: AES Successfully Registered
[ 5.060900] alg: No test for xilinx-keccak-384 (zynqmp-keccak-384)
[ 5.067046] alg: No test for xilinx-zynqmp-rsa (zynqmp-rsa)
[ 5.072598] usbcore: registered new interface driver usbhid
[ 5.077926] usbhid: USB HID core driver
[ 5.084650] ARM CCI_400_r1 PMU driver probed
[ 5.085136] fpga_manager fpga0: Xilinx ZynqMP FPGA Manager registered
[ 5.092817] usbcore: registered new interface driver snd-usb-audio
[ 5.099314] pktgen: Packet Generator for packet performance testing. Version: 2.75
[ 5.106852] Initializing XFRM netlink socket
[ 5.110366] NET: Registered protocol family 10
[ 5.115234] Segment Routing with IPv6
[ 5.118525] sit: IPv6, IPv4 and MPLS over IPv4 tunneling driver
[ 5.124639] NET: Registered protocol family 17
[ 5.128628] NET: Registered protocol family 15
[ 5.133042] can: controller area network core
[ 5.137389] NET: Registered protocol family 29
[ 5.141765] can: raw protocol
[ 5.144703] can: broadcast manager protocol
[ 5.148860] can: netlink gateway - max_hops=1
[ 5.153287] Bluetooth: RFCOMM TTY layer initialized
[ 5.158036] Bluetooth: RFCOMM socket layer initialized
[ 5.163147] Bluetooth: RFCOMM ver 1.11
[ 5.166854] Bluetooth: BNEP (Ethernet Emulation) ver 1.3
[ 5.172121] Bluetooth: BNEP filters: protocol multicast
[ 5.177319] Bluetooth: BNEP socket layer initialized
[ 5.182245] Bluetooth: HIDP (Human Interface Emulation) ver 1.2
[ 5.188127] Bluetooth: HIDP socket layer initialized
[ 5.193205] 9pnet: Installing 9P2000 support
[ 5.197327] Key type dns_resolver registered
[ 5.201792] registered taskstats version 1
[ 5.205605] Loading compiled-in X.509 certificates
[ 5.211720] Btrfs loaded, crc32c=crc32c-generic
[ 5.225900] ff010000.serial: ttyPS0 at MMIO 0xff010000 (irq = 45, base_baud = 6249999) is a xuartps
[ 5.234934] printk: console [ttyPS0] enabled
[ 5.234934] printk: console [ttyPS0] enabled
[ 5.239238] printk: bootconsole [cdns0] disabled
[ 5.239238] printk: bootconsole [cdns0] disabled
[ 5.248718] of-fpga-region fpga-full: FPGA Region probed
[ 5.258951] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd500000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.266178] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd510000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.273376] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd520000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.280573] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd530000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.287780] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd540000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.294973] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd550000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.302169] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd560000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.309364] xilinx-zynqmp-dma fd570000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.316635] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffa80000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.323838] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffa90000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.331036] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffaa0000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.338229] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffab0000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.345420] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffac0000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.352611] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffad0000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.359802] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffae0000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.366994] xilinx-zynqmp-dma ffaf0000.dma: ZynqMP DMA driver Probe success
[ 5.374527] xilinx-axipmon ffa00000.perf-monitor: Probed Xilinx APM
[ 5.381139] xilinx-axipmon fd0b0000.perf-monitor: Probed Xilinx APM
[ 5.387679] xilinx-axipmon fd490000.perf-monitor: Probed Xilinx APM
[ 5.394232] xilinx-axipmon ffa10000.perf-monitor: Probed Xilinx APM
[ 5.401010] cdns-i2c ff030000.i2c: 400 kHz mmio ff030000 irq 38
[ 5.412571] of_cfs_init
[ 5.415071] of_cfs_init: OK
[ 5.418008] cfg80211: Loading compiled-in X.509 certificates for regulatory database
[ 5.432355] zynqmp_pll_disable() clock disable failed for dpll_int, ret = -13
[ 5.447768] mmc0: SDHCI controller on ff160000.mmc [ff160000.mmc] using ADMA 64-bit
[ 5.535295] mmc0: error -110 whilst initialising SD card
[ 5.559566] cfg80211: Loaded X.509 cert 'sforshee: 00b28ddf47aef9cea7'
[ 5.566101] clk: Not disabling unused clocks
[ 5.570547] ALSA device list:
[ 5.573506] No soundcards found.
[ 5.577371] platform regulatory.0: Direct firmware load for regulatory.db failed with error -2
[ 5.585988] cfg80211: failed to load regulatory.db
[ 5.592056] Freeing unused kernel memory: 2112K
[ 5.608311] Run /init as init process
INIT: version 2.97 booting
Starting udev
[ 5.731683] udevd[248]: starting version 3.2.9
[ 5.736591] random: udevd: uninitialized urandom read (16 bytes read)
[ 5.743111] random: udevd: uninitialized urandom read (16 bytes read)
[ 5.749571] random: udevd: uninitialized urandom read (16 bytes read)
[ 5.761097] udevd[249]: starting eudev-3.2.9
bootlogd: /dev/ttyPS0Fri Mar 9 12:34:56 UTC 2018
Configuring packages on first boot....
(This may take several minutes. Please do not power off the machine.)
Running postinst /etc/rpm-postinsts/100-sysvinit-inittab...
update-rc.d: /etc/init.d/run-postinsts exists during rc.d purge (continuing)
Removing any system startup links for run-postinsts ...
INIT: Entering runlevel: 5
Configuring network interfaces... ip: SIOCGIFFLAGS: No such device
Starting haveged: haveged: command socket is listening at fd 3
haveged: haveged starting up
Starting Dropbear SSH server: Waiting for kernel randomness to be initialised...
haveged: haveged: ver: 1.9.13; arch: generic; vend: ; build: (gcc 10.2.0 CTV); collect: 128K
haveged: haveged: cpu: (VC); data: 16K (D); inst: 16K (D); idx: 11/40; sz: 15456/64452
haveged: haveged: tot tests(BA8): A:1/1 B:1/1 continuous tests(B): last entropy estimate 8.00043
haveged: haveged: fills: 0, generated: 0
[ 7.305880] random: crng init done
Generating 2048 bit rsa key, this may take a while...
[ 7.309313] random: 5 urandom warning(s) missed due to ratelimiting
Public key portion is:
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDK9E3I71UoeNyJZ2RjViCrE27f3qc/wzfTNK6QmAII61TZkldYT6tViC6twp5EuovfxWn5gXLW5OLJBxBnBjW3XopPaBBp9ex/EAgidC/GzglKwwc7dGRABOd9i9+HEsZkROxA8Cy9J0gNlb3xXGwmoATLPk8FyUCIkywV4I9M52FAd2+U8ZDLgcdwcUU8eiJ99GHvjgO3LkIdBZ8lC1GS69jBl/CTcQBjia2ybMg1ga86RvCjsCjTm7LkcQLDY9wI/rHdoVeQ+8WIDMQEIamB5W9d6w91iOJk5yq+samokCBOVedA4AxGomhewhgxWN3Jj6S+/v6s61fOXUhoIxOb root@petalinux_img
Fingerprint: sha1!! b4:6b:63:1a:59:59:eb:09:66:91:ef:d8:80:1a:67:f8:c2:7f:43:0f
dropbear.
Starting internet superserver: inetd.
Starting syslogd/klogd: done
Starting tcf-agent: OK
root@petalinux_img:~# py
pydoc python python-config python2 python2-config python2.7 python2.7-config
root@petalinux_img:~# python -v
# installing zipimport hook
import zipimport # builtin
# installed zipimport hook
# /usr/lib/python2.7/site.pyc has bad mtime
import site # from /usr/lib/python2.7/site.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/site.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/os.pyc has bad mtime
import os # from /usr/lib/python2.7/os.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/os.pyc
import errno # builtin
import posix # builtin
# /usr/lib/python2.7/posixpath.pyc has bad mtime
import posixpath # from /usr/lib/python2.7/posixpath.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/posixpath.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/stat.pyc has bad mtime
import stat # from /usr/lib/python2.7/stat.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/stat.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/genericpath.pyc has bad mtime
import genericpath # from /usr/lib/python2.7/genericpath.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/genericpath.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/warnings.pyc has bad mtime
import warnings # from /usr/lib/python2.7/warnings.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/warnings.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/linecache.pyc has bad mtime
import linecache # from /usr/lib/python2.7/linecache.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/linecache.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/types.pyc has bad mtime
import types # from /usr/lib/python2.7/types.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/types.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/UserDict.pyc has bad mtime
import UserDict # from /usr/lib/python2.7/UserDict.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/UserDict.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/_abcoll.pyc has bad mtime
import _abcoll # from /usr/lib/python2.7/_abcoll.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/_abcoll.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/abc.pyc has bad mtime
import abc # from /usr/lib/python2.7/abc.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/abc.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/_weakrefset.pyc has bad mtime
import _weakrefset # from /usr/lib/python2.7/_weakrefset.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/_weakrefset.pyc
import _weakref # builtin
# /usr/lib/python2.7/copy_reg.pyc has bad mtime
import copy_reg # from /usr/lib/python2.7/copy_reg.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/copy_reg.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/traceback.pyc has bad mtime
import traceback # from /usr/lib/python2.7/traceback.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/traceback.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/sysconfig.pyc has bad mtime
import sysconfig # from /usr/lib/python2.7/sysconfig.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/sysconfig.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/re.pyc has bad mtime
import re # from /usr/lib/python2.7/re.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/re.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_compile.pyc has bad mtime
import sre_compile # from /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_compile.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_compile.pyc
import _sre # builtin
# /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_parse.pyc has bad mtime
import sre_parse # from /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_parse.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_parse.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_constants.pyc has bad mtime
import sre_constants # from /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_constants.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/sre_constants.pyc
dlopen("/usr/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload/_locale.so", 2);
import _locale # dynamically loaded from /usr/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload/_locale.so
# /usr/lib/python2.7/_sysconfigdata.pyc has bad mtime
import _sysconfigdata # from /usr/lib/python2.7/_sysconfigdata.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/_sysconfigdata.pyc
import sitecustomize # from /usr/lib/python2.7/sitecustomize.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/sitecustomize.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/rlcompleter.pyc has bad mtime
import rlcompleter # from /usr/lib/python2.7/rlcompleter.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/rlcompleter.pyc
dlopen("/usr/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload/readline.so", 2);
import readline # dynamically loaded from /usr/lib/python2.7/lib-dynload/readline.so
# /usr/lib/python2.7/atexit.pyc has bad mtime
import atexit # from /usr/lib/python2.7/atexit.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/atexit.pyc
import encodings # directory /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings
# /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/__init__.pyc has bad mtime
import encodings # from /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/__init__.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/__init__.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/codecs.pyc has bad mtime
import codecs # from /usr/lib/python2.7/codecs.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/codecs.pyc
import _codecs # builtin
# /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/aliases.pyc has bad mtime
import encodings.aliases # from /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/aliases.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/aliases.pyc
# /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/ascii.pyc has bad mtime
import encodings.ascii # from /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/ascii.py
# wrote /usr/lib/python2.7/encodings/ascii.pyc
Python 2.7.18 (default, Apr 19 2020, 21:45:35)
[GCC 10.2.0] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> print("Hello Ultra96v2 from python !!!")
Hello Ultra96v2 from python !!!
>>>
Thanks for reading.