In a connected world with smart products, many devices communicate with each other through communication protocols on wired or wireless networks. Z-Wave is one of them. It enables smart home products such as locks, light bulbs, alarms, and thermostats to communicate with one another to create the backbone of your smart home. Z-Wave is a low-power wireless technology protocol, developed by Sigma Designs, specifically for the Internet of Things and smart home applications.
It is an open source, mesh network protocol similar to Zigbee, but with lower speed and lower power consumption. Due to the mesh network topology, all the devices on the network function as signal repeaters. Z-Wave signals can travel through most obstacles in the home (e.g., walls, floors and ceilings). Z-wave devices can also route signals around obstacles to ensure coverage in the entire home.
Z- Wave Network
Z-wave has a three-layer network structure:
- Radio layer: describes how the signal is exchanged between the transmitter and receiver
- Network layer: takes care of network organization addressing and routing. Moreover, the network layer is subdivided into three more layers (See below for details)
- Application layer: defines which messages need to be exchanged to specific applications
Z-Wave Radio Layer
Z-wave devices operate in the low bandwidth ISM band since home automation systems do not require large bandwidth data. It uses 868.42 MHz in Europe and 908.42 MHz in the USA. These bands are free without the need of certifications and permits, but have limited transmitting power and range. The latest version provides an optional radio of 2.4 GHz. They have a peak transmission power of 10 mW. Since the peak power is only required in short bursts, the average power will be in the range of 1 mW. It uses a Gaussian Frequency Shift Key modulation with the ability to achieve speeds of 40 kbps. The maximum line of sight distance is about 200 meters, but is limited to less than 30 meters for a typical indoor home environment, since the obstacles of the indoor home attenuates the RF signal being transmitted.
Z- Wave Network Layer
The network layer takes care of network organization, addressing, and routing. Moreover, the network layer is subdivided into three more layers:
- Media Access Layer: controls the usage of wireless hardware
- Transport Layer: assures that exchange of messages between the two wireless nodes is free of any error
- Routing Layer: ensures that a message is passed between the original sender and the desired receiver
Z-wave networks consist of a minimum of two nodes. Every node in a network must have unique identification to distinguish it from other nodes within the network. The Z-wave protocol uses two identification methods for the organization of the network:
- HOME ID: Home ID will be pre-programmed in all the controller devices and is needed by all slave nodes in the network. It identifies all nodes belonging to one Z-wave network. It has a length of 32-bits.
- NODE ID: Node ID is used to address individual nodes in a Z-wave network. It is an 8-bit value and is assigned by the controller.
Within one network there is only one HOME ID, and it is not possible to have the same NODE ID for two different nodes.The controller that establishes the network and transfers its HOME ID to other devices is referred as the primary controller. In a larger network, there may be many controllers, but the primary controller alone has the privilege to include other controllers.
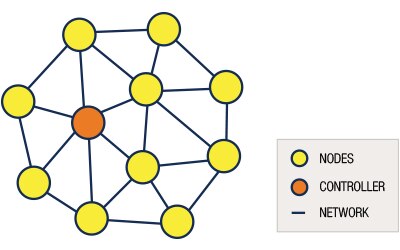
Normally, a wireless network has a central controller that requires a direct radio link from the devices or nodes. When any disturbance occurs in the nodes, the controller does not have any backup route to reach the nodes. In a Z-wave system, this limitation has been overcome. An individual node can work as a repeater. If any node is not in the direct line of sight of the controller, this repeater node can interact with the other nodes and the controller can continue to communicate with the node which is not in the direct radio link.
A controller can communicate with every device in the network (See figure on left). It has access to the complete routing table. Slave nodes can only reply to the node from which the message has been sent and it has no information about the routing table. When the node works as a routing slave, it has partial knowledge about the routing table and can reply to the node from which the message has been sent and can send a message to a number of predefined nodes it has a route to.
Establishing the Network
When a device is added to the network, the controller requests the list of all nodes from the neighboring nodes, and updates the routing table.
If a second controller is included in the network, the primary controller hands over the routing table to the secondary controller and both the controllers have the same routing table. If at a later time more nodes are included, the primary controller updates the routing table but the secondary controller shows the old routing table.
If the nodes are removed from the network, the entries in the routing table are deleted. When the secondary controller is removed, it will delete both its assigned HOME ID and the routing table, which is now not relevant to the secondary controller.
If a slave is moved to a location where it is not in a direct wireless link, the controller will not able to find this node and moves it to the failed node list. To find a moved node, the controller scans the network and asks every node. If the moved node is in the range of any other node, the controller updates the routing table and removes it from the failed node list.
The controller may be static or portable. A static controller should not be moved while the portable controller is battery-powered and supposed to be moved around, since with battery power, the portable controller sleeps most of the time and will not able to route a message from other nodes.
If the static controller is moved, a network scan, as well as reorganization is required.
Z-wave Products
There are many Z-wave products already available in the marketplace. Few examples are:
GoControl Z-Wave Dimmable LED Light Bulb
Aeotec Z-Wave Plus Siren
FAKRO Centre Pivot Windows Z-WAVE controlled





Top Comments
-

mcb1
-
Cancel
-
Vote Up
+1
Vote Down
-
-
Sign in to reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Comment-

mcb1
-
Cancel
-
Vote Up
+1
Vote Down
-
-
Sign in to reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Children