RoadTest: Review the Nordic Wi-Fi Locationing Solution with nRF7002-EK and nRF9160-DK
Author: dimiterk
Creation date:
Evaluation Type: Evaluation Boards
Did you receive all parts the manufacturer stated would be included in the package?: True
What other parts do you consider comparable to this product?: ESP32 board
What were the biggest problems encountered?: VScode examples can be more thorough
Detailed Review:
Introduction
This road-test will review the nRF7002-EK WIFI-6 chipset and the nRF9160- Development Kit together with Nordic Cloud using a Basis SIM card. The kit I received contained the NRF9160, the nRF7002 and a Basis IOT enabled SIM card with 10Mb of prepaid data. The nRF9160 DK comes with a pre-certified single-board development kit for evaluation and development on the nRF9160 SiP for LTE-M, NB-IoT and GNSS. The board also includes an nRF52840 board controller that for example can be used to build a Bluetooth Low Energy gateway. In Canada, the nRF9160 DK can be connected to either LTE-M or NB-IoT networks if equipped with an IoT enabled SIM card.

The SD card on the backside is not populated. The board makes use of a microSIM socket.

Hardware setup
Setting up the hardware is a breeze as all one has to do for the hardware assembly simply involves pairing the nRF7002 with the nRF9160-DK board and switching the slider switch on. Once powered on the nRF9160-DK LEDs will blink.
The kit is Arduino Uno Rev3 compatible, and the nRF7002-EK follows the Arduino shield form factor. Programming and debugging is enabled through the on-board Segger J-Link OB, which also supports external targets.
Software Setup
Testing of the kit was done on a Ubuntu 22.04 machine. First I downloaded and installed https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-tools/nRF-Command-Line-Tools/Download
After installing the command line tools.
sudo dpkg -i --force-overwrite nrf-command-line-tools_10.24.2_amd64.deb
sudo apt install /opt/nrf-command-line-tools/share/JLink_Linux_V794e_x86_64.deb --fix-broken
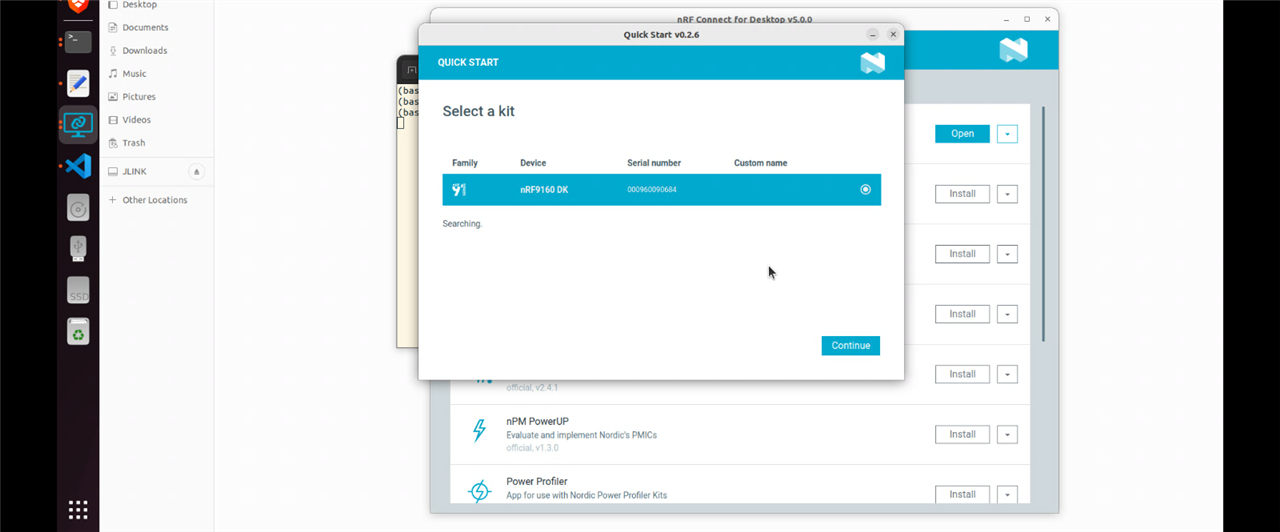
Next I installed nRF Connect for Desktop. This application allows to test the Nordic cloud using a GPS asset tracer application.
The pre-compiled package located at https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-hardware/nRF9160-DK/Download#infotabs
contains all the following applications
Testing Nordic cloud solution
nRF Cloud offers a suite of services that allows provisioning of IOT filed devices as well as implementation of multiple communication protocols such as MQTT, COAP and alos REST APIs.
To test the Nordic dashboard that allows provisioning of the nRF9160-DK the most accessible method is to use the nRF Connect for Desktop.
I tested the GNSS tracking application using A-GNSS. From Nordic Wiki A-GNSS provides real-time tracking.
"A-GNSS provides the latest current (not predicted) satellite positioning data to devices to help them find a satellite more quickly. This data is for all satellites, regardless of the device’s position, and is typically reliable for four hours. A-GNSS also includes an SCELL request as part of its operations. This SCELL request results in an additional data point in the location history."
One thing to keep in mind is that using A-GNSS requires frequent use of an LTE connection to update assistance information (typically every 2 hours) , hence it will make more requests to the cloud.
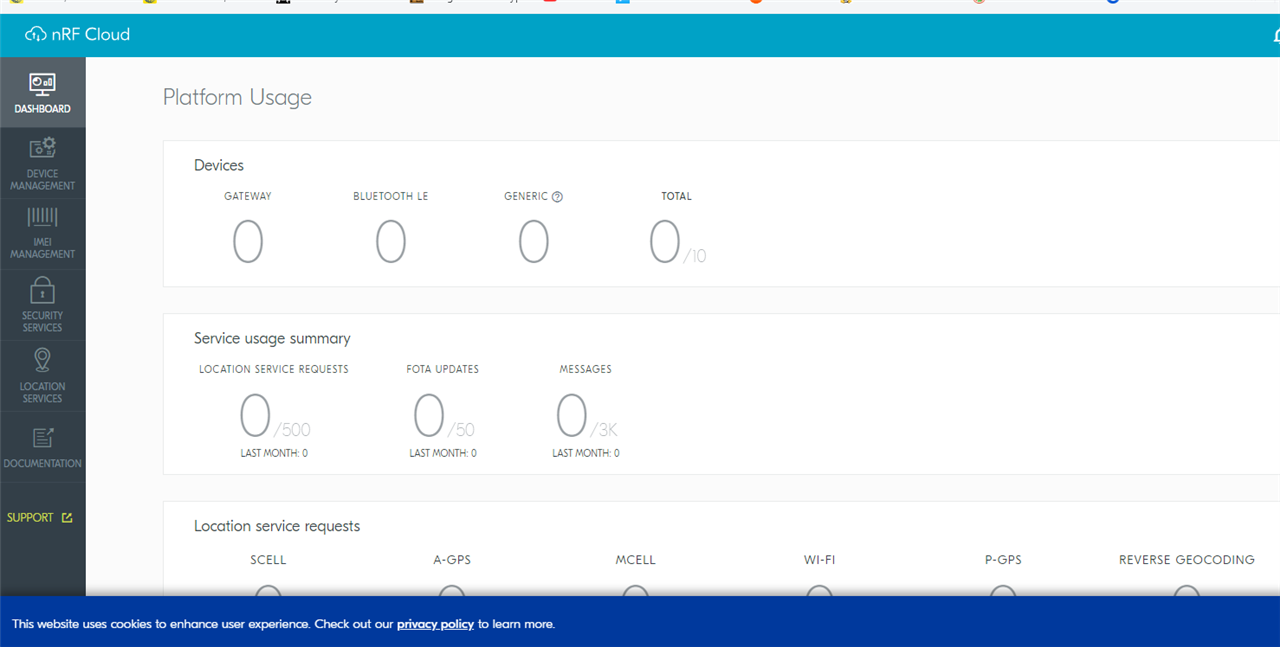
1. First register for the cloud access. Once registration is done you will have access to the dashboard below.
a) Go to nRF Cloud at https://nrfcloud.com/
b) Click Register
c) Next create an account by entering your address.
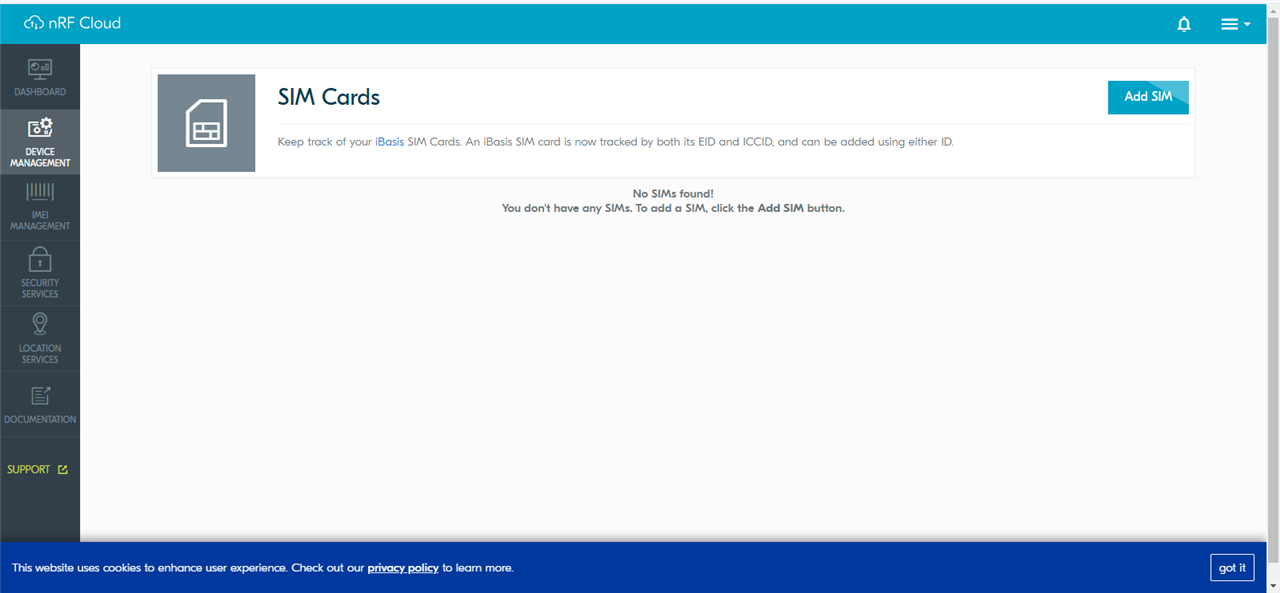
Next Add a SIM card. Record the SIM card data and enter the micro SIM on the NRF9160 -DK.

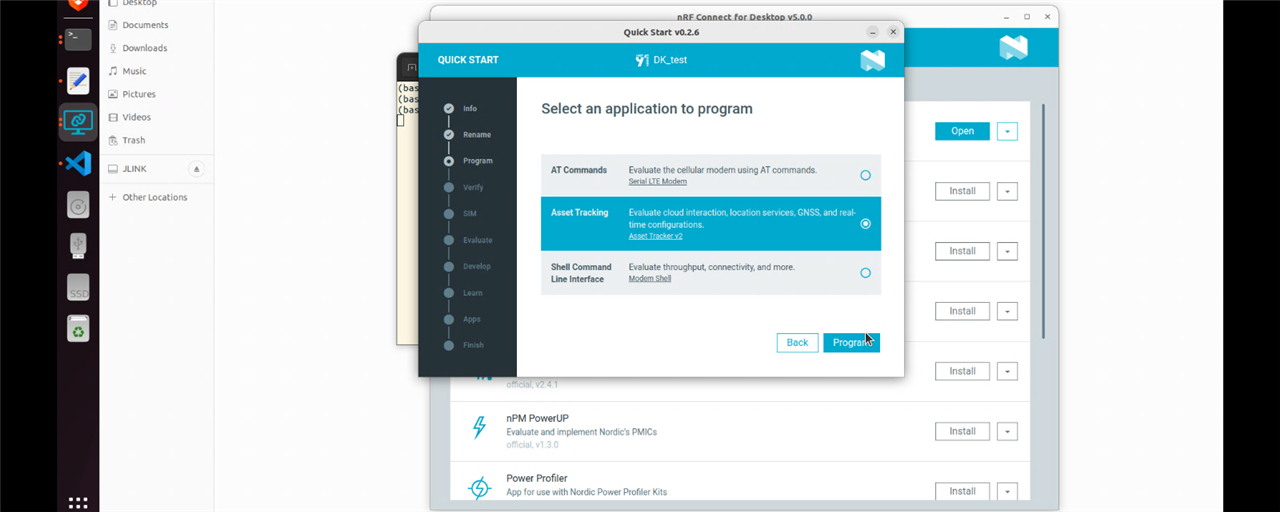
At this point you will be asked for the IMEI and PIN. These are located on the underside of the board of the nRF9160DK.
Same for the MAC of the nRF7002. It's located on the bottom side of the shield.
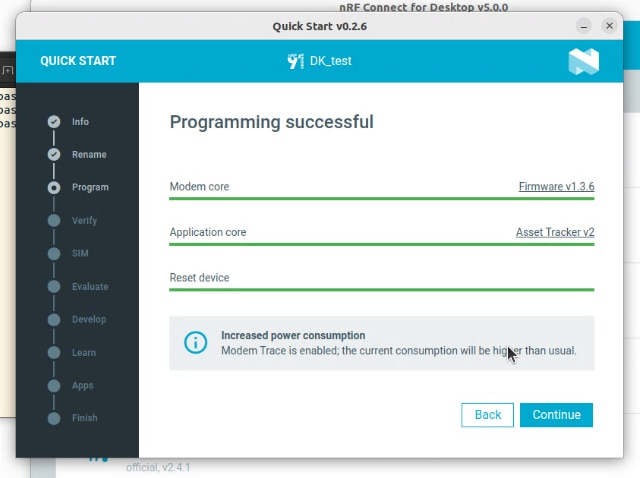
You'll notice that LED 3 starts blinking as soon as the LTE link is established.

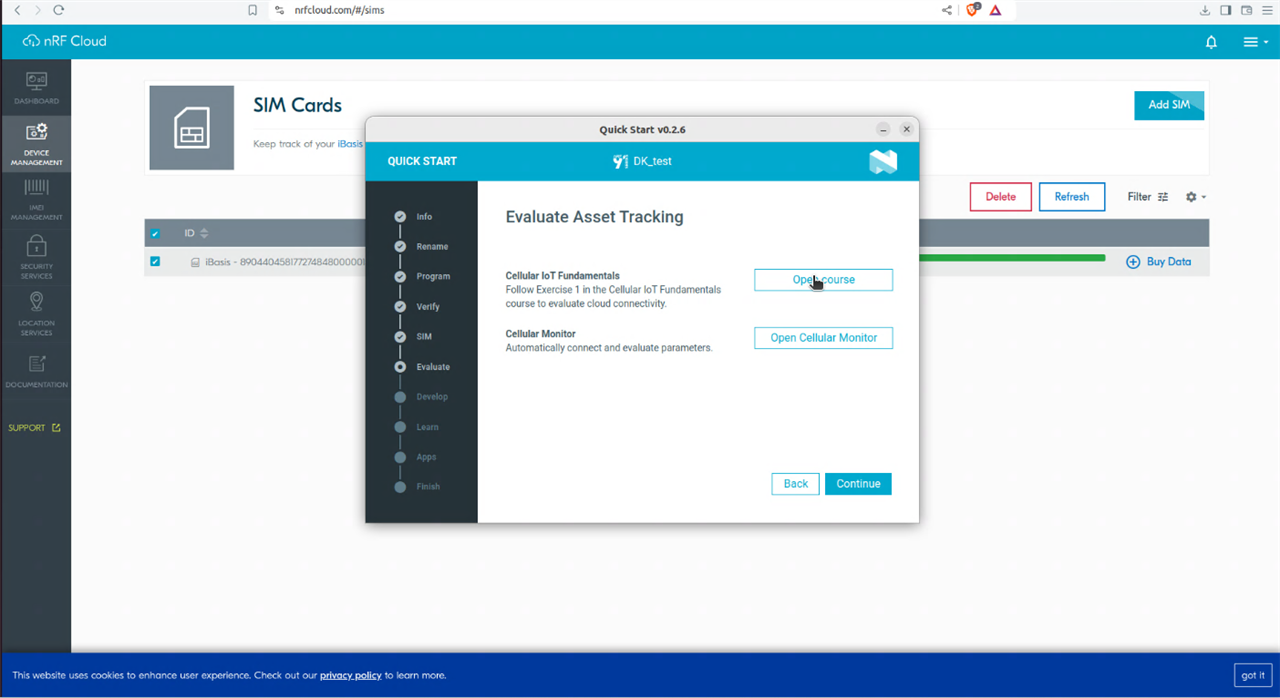
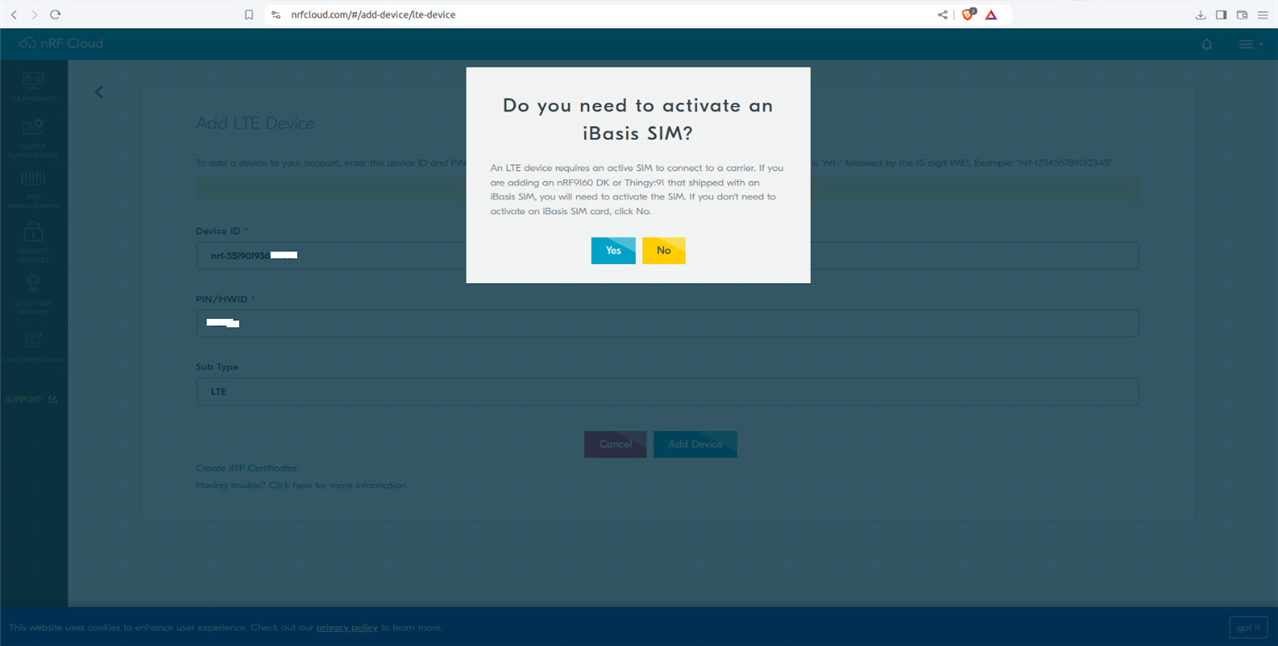
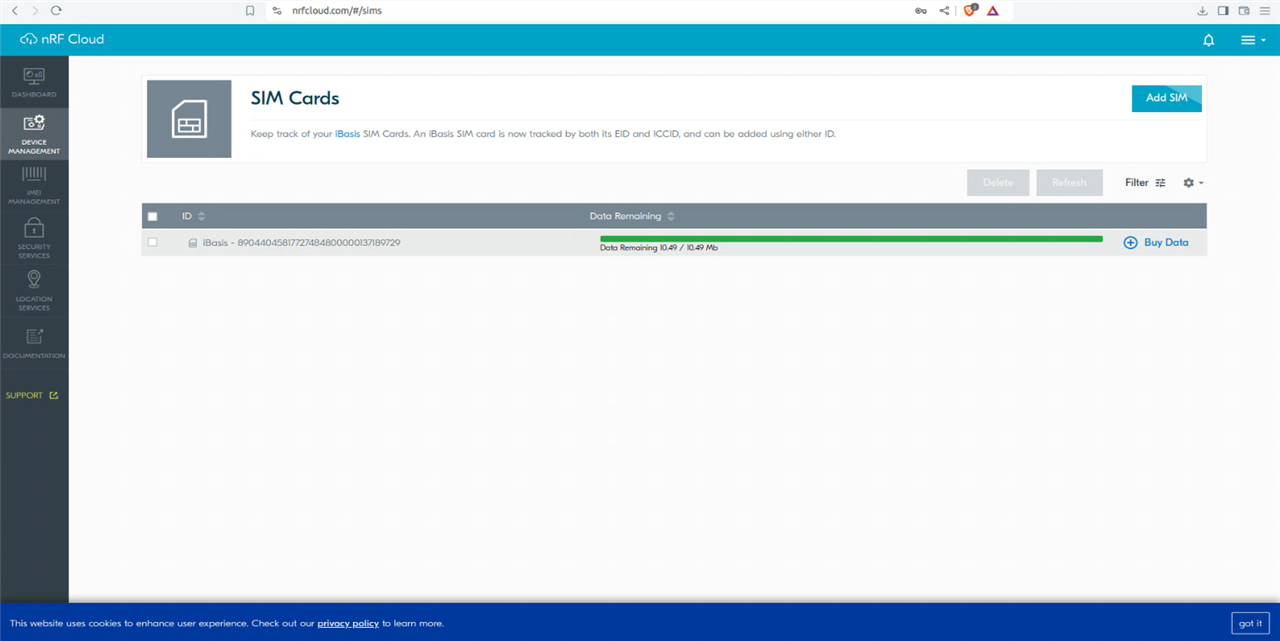
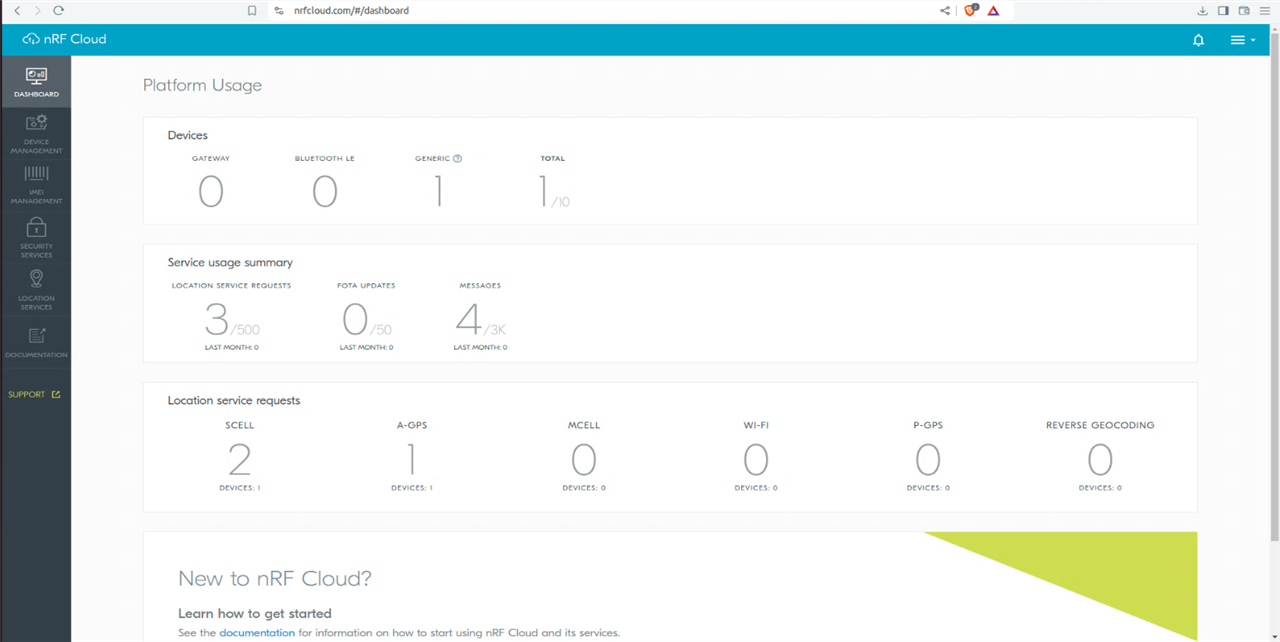
The example can also infer Location based on Wi-Fi networks. Specifically it uses Wi-Fi location assistance, where a device can query nRF Cloud for its location using the MAC addresses of Wi-Fi networks in its area. The device performs an SSID scan of Wi-Fi access points in its surrounding area and sends this data to nRF Cloud. nRF Cloud calculates the location based on the data according to a third-party database, and responds with latitude, longitude and uncertainty.
This example also uses a cellular connection for data transfer and connectivity to nRF Cloud, so a valid SIM is also needed.
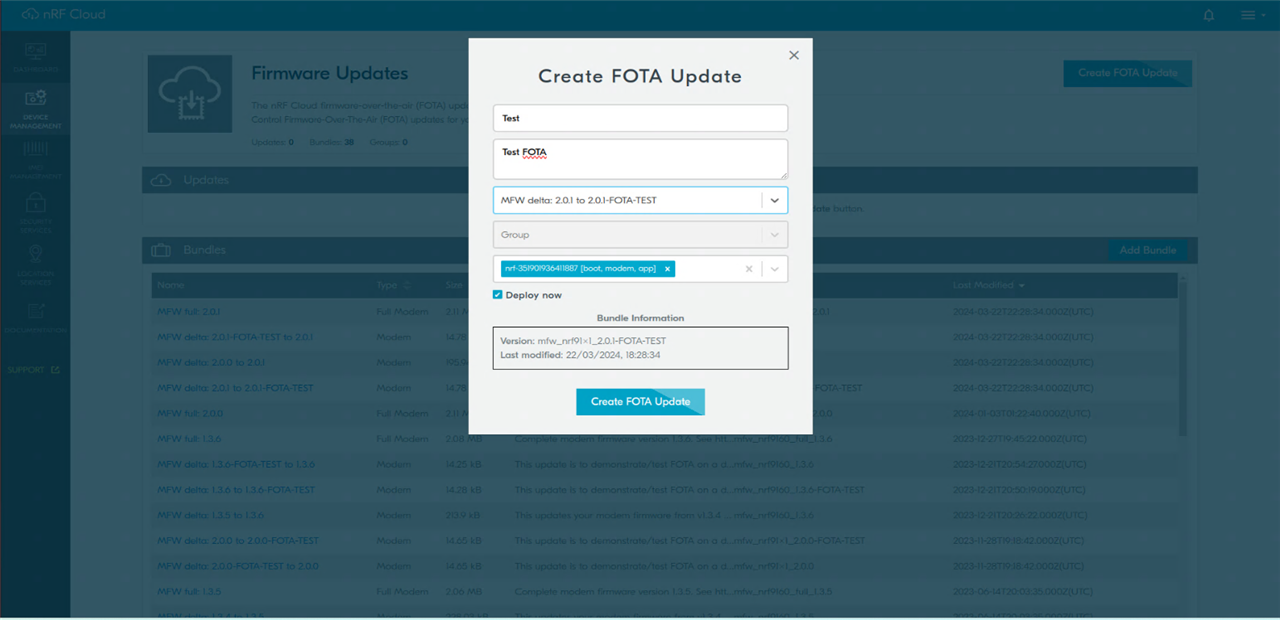
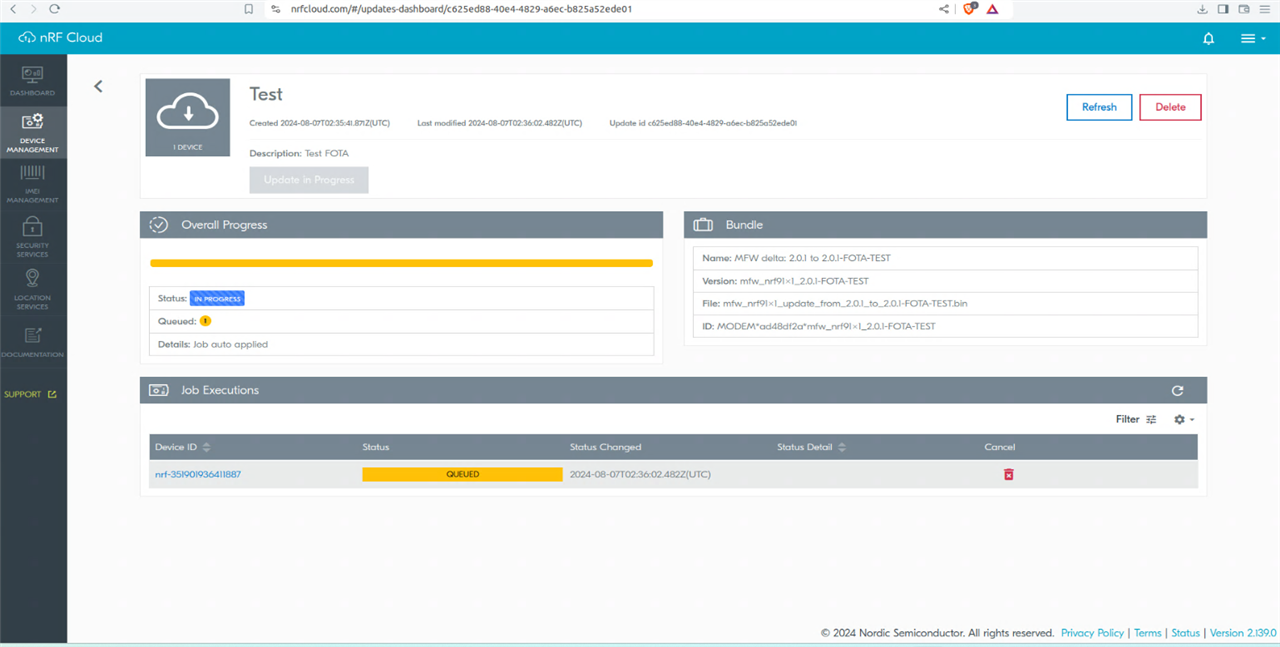
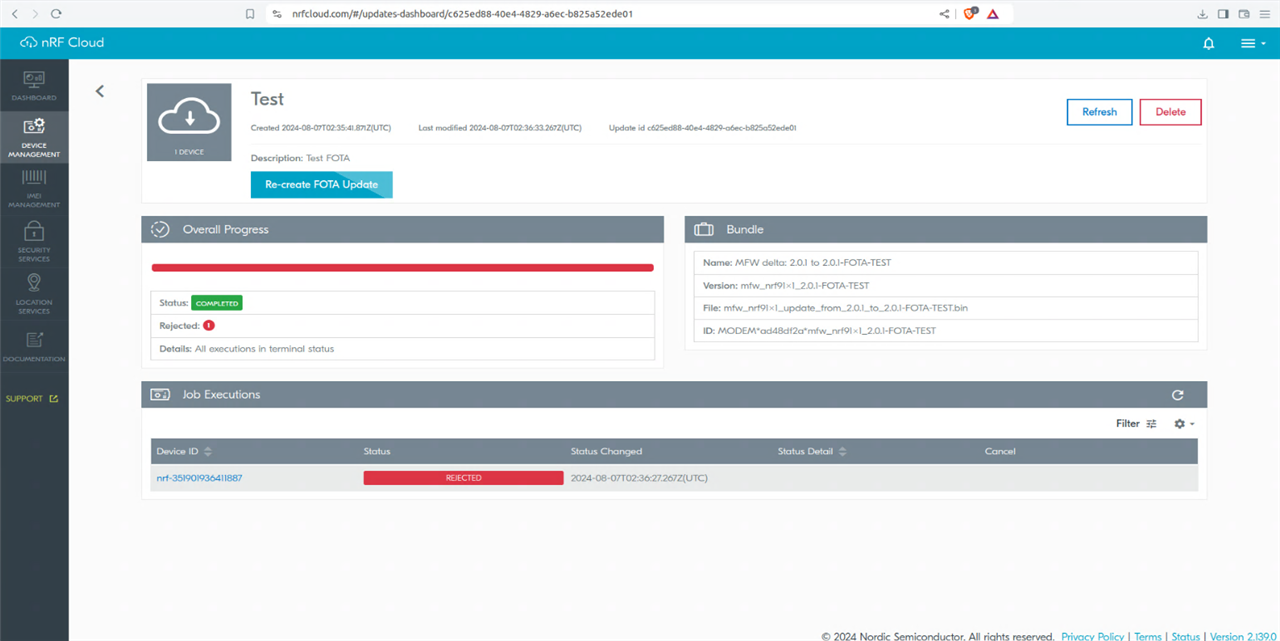
Firmware Over the Air Update (FOTA)
The Nordic cloud application supports updating the firmware of the nRF9160 DK board remotely via cellular radio. (LTE-M or nb-IOT).For this roadtest, a simple FOTA upgrade was tested.
The kit comes pre-loaded with the latest FW update so when downgrading it will not accept the downgrade binary.

Custom app development
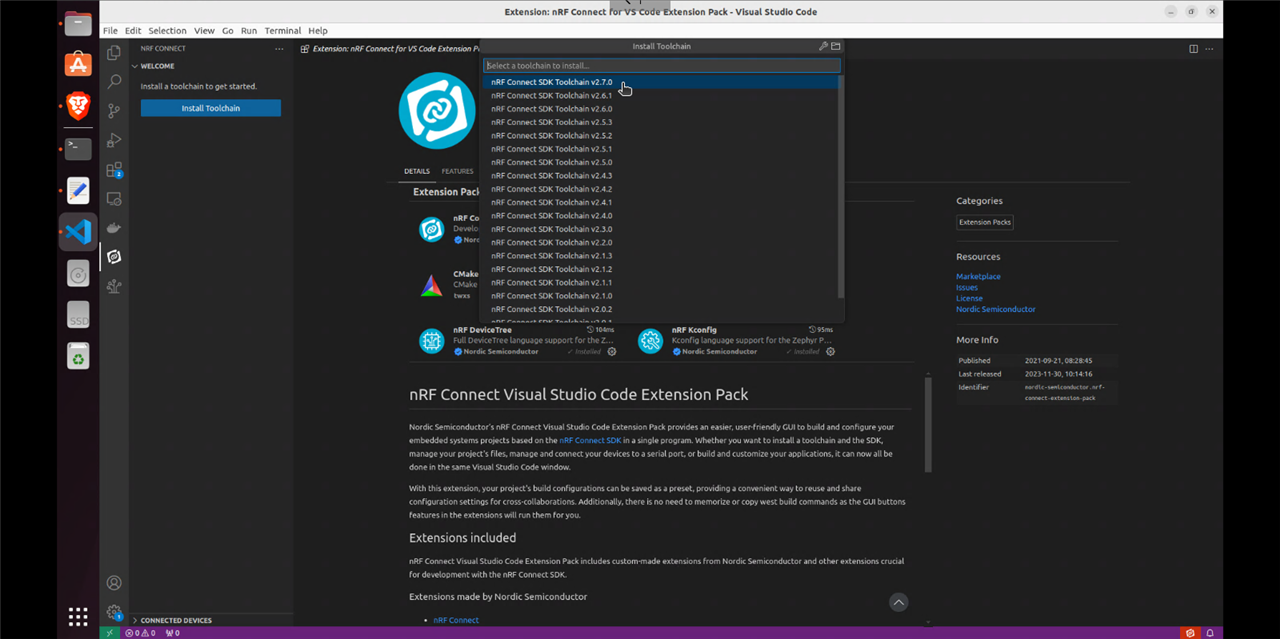
To build custom applications on this board one can use a number of IDEs with VScode or SNES being the most well-known.
For this application I tested one of the VScode example after installing the nRF extensions.

References
[1] https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-hardware/nRF9160-DK/GetStarted
[2] https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-tools/nRF-Connect-for-Desktop
[3] https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Cloud-services
[4] https://docs.nordicsemi.com/bundle/nrf-cloud/page/LocationServices/Features.html?h=#wi-fi-anchors
[5] https://www.nordicsemi.com/Products/Development-hardware/nRF9160-DK/Download#infotabs
-

dougw
-
Cancel
-
Up
0
Down
-
-
Reply
-
More
-
Cancel
-

dimiterk
in reply to dougw
-
Cancel
-
Up
0
Down
-
-
Reply
-
More
-
Cancel
-

kmikemoo
in reply to dimiterk
-
Cancel
-
Up
0
Down
-
-
Reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Comment-

kmikemoo
in reply to dimiterk
-
Cancel
-
Up
0
Down
-
-
Reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Children