
(Image credit: CES)
CES 2026 in Las Vegas made one thing clear: embedded hardware and on-device intelligence are no longer interesting curiosities; they’re core technologies shaping robotics, industrial automation, AI at the edge, and even playful interactive platforms. From high-performance AI compute modules and vision systems to real-time software stacks and wireless-enabled sensors, this roundup spotlights the embedded products and technologies unveiled at this year’s show that engineers, makers, and system designers should know about.
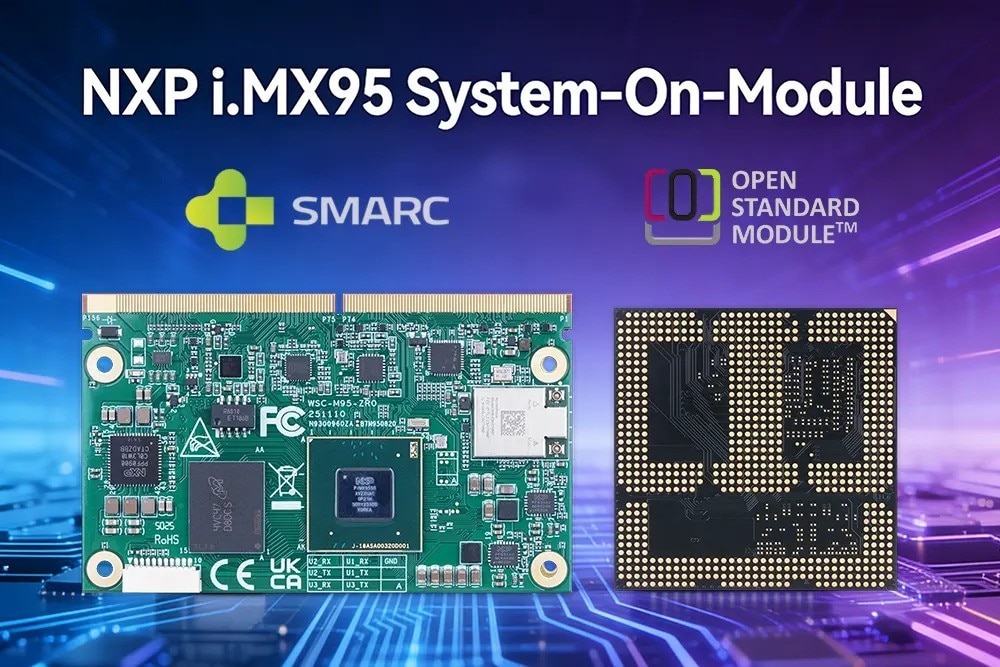
Geniatech’s i.MX95 SOM Series
(Image credit: Geniatech)
Geniatech’s new i.MX95 System-on-Modules bring NXP’s i.MX95 application processor for compact embedded compute hardware applications in both OSM 1.1 and SMARC 2.1 form factors. The new modules are designed around a multi-core Arm Cortex-A55 SoC with dual real-time cores (Cortex-M7/M33), integrated Mali-G310 graphics, eIQ Neutron neural processing (for up to 2 TOPS of edge AI), and up to 16 GB LPDDR5 and 128 GB eMMC. These modules are ideal for industrial automation, intelligent transportation, and smart retail and medical gateways with robust industrial-grade support and long-term supply commitments.
Leopard Imaging’s Dragonfly Series Imaging Sensors

(Image credit: Leopard Imaging)
Leopard Imaging’s new Dragonfly USB 3.0 YUV series was also highlighted at this year’s CES, and offers compact, embedded-friendly machine vision cameras with onboard Image Signal Processing (ISP) and USB 3.0 interfaces for plug-and-play deployment across multiple platforms (Windows, Linux, and arm-based systems like NVIDIA Jetson). The imaging sensors feature an integrated Image Signal Processor (ISP) to provide optimized image quality, real-time performance, and direct YUV data output, eliminating the need for external image processing.
The built-in ISP enables consistent image tuning, including auto-exposure, white balance, and color correction, making Dragonfly cameras ideal for rapid prototyping, machine vision, robotics, smart factories, AI-enabled systems, and more.
Ambarella CV7 Edge AI Vision SoC
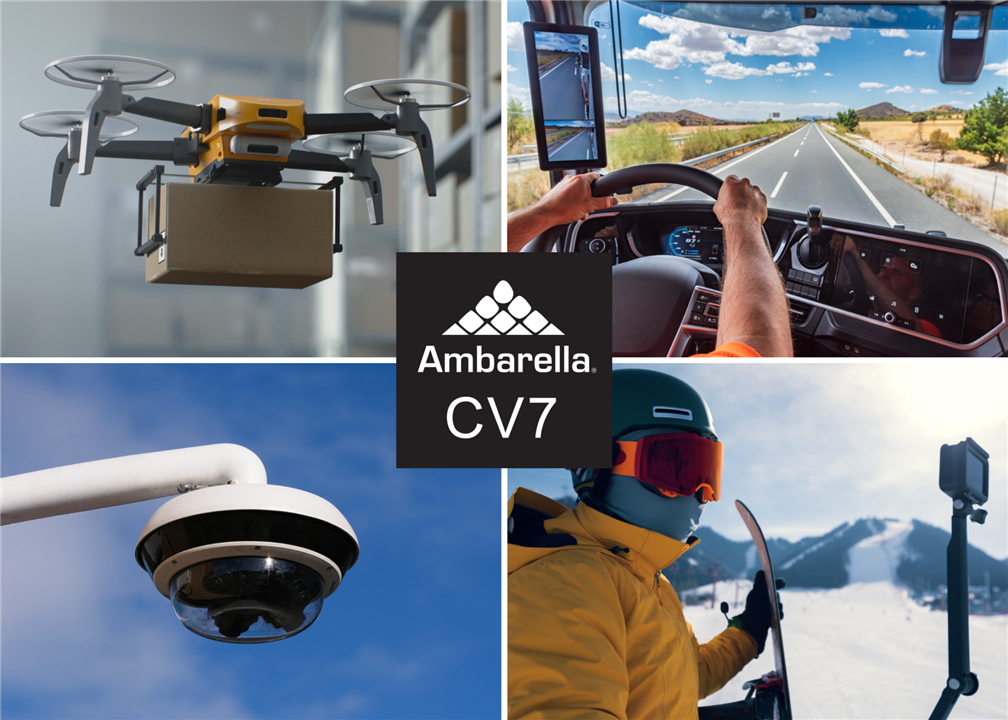

(Image credit: Ambarella)
Ambarella’s CV7 is a powerful 4 nm AI vision SoC that merges a quad-core Arm Cortex-A73 CPU cluster with Ambarella’s third-gen CVflow AI engine, hardware vision ISPs, and multi-stream video processing up to 8Kp60. The CV7 offers advanced HDR imaging pipelines and on-chip neural inference, providing high-performance imaging + AI for edge devices including drones, robots, industrial gateways, and smart cameras.
According to Ambarella, the CV7 comes equipped with the company’s proprietary AI accelerator, image signal processor (ISP), and video encoding to deliver 2.5x the AI performance of the previous-generation CV5 SoC. This allows the CV7 to support a combination of CNNs and transformer networks running simultaneously.
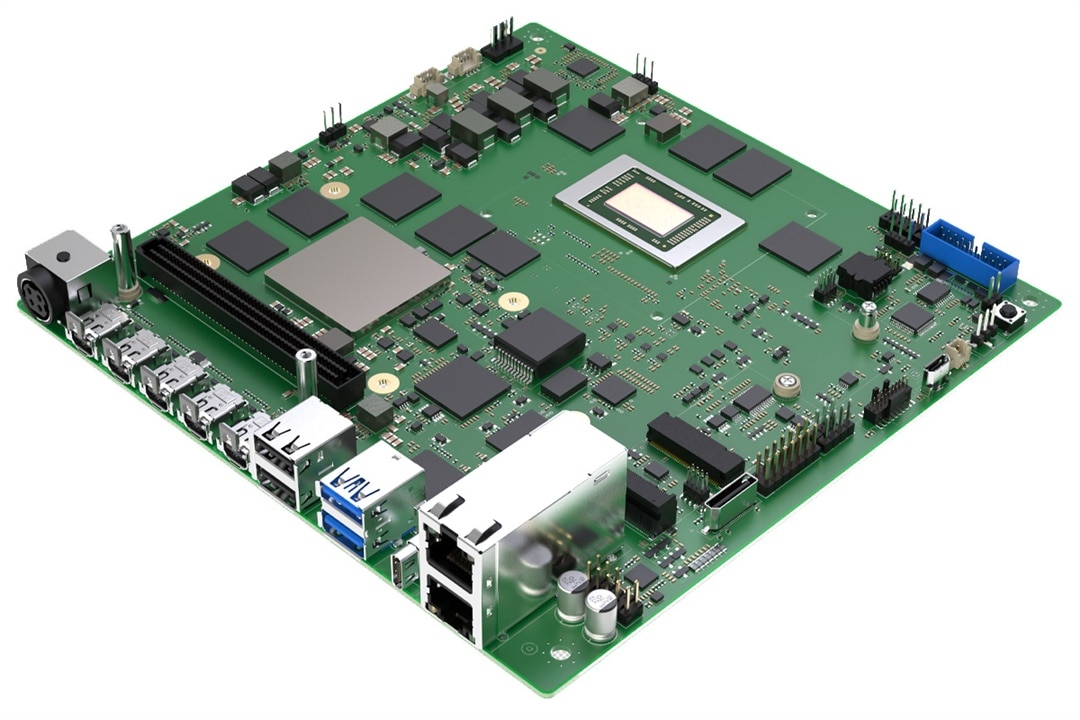
Sapphire EDGE+ VPR-7P132 Mini-ITX AI Edge Motherboard
(Image Credit: Sapphire)
Known for its gaming video cards, Sapphire unveiled its EDGE+ VPR-7P132 Mini-ITX Motherboard, which combines AMD’s Ryzen AI Embedded P132 APU with an AMD Versal AI Edge Gen 2 VE3558 SoC FPGA. The hardware splits workloads between a high-performance Zen 5-based CPU (handling OS/networking/visualization), an XDNA 2 NPU for up to 50 TOPS, and programmable logic for real-time sensor and inference applications. Outfitted with LPDDR5, UFS storage, 10 GbE networking, USB-4 and USB-3, and compatibility with Yocto Linux, Ubuntu, QNX, and VxWorks, it’s an ideal board for real-time embedded AI, robotics, and industrial automation projects.
Synaptics Astra and Veros Edge AI Platforms

(Image credit: Synaptics)
Synaptics used CES 2026 to highlight its Astra AI-native SoC family and Veros wireless edge systems, designed to embed low-latency voice, gesture, and motion sensing directly on devices without requiring the cloud. The Astra line is based on a scalable family of AI SoCs designed around Arm-based CPUs, integrated neural processing units (NPUs), DSPs, and GPUs. The SL2610 line is capable of multi-modal AI workloads, including audio, vision, voice, and sensor fusion, and offers performance scaling up to 8 TOPS of inferencing power in certain SL-Series devices.
Synaptics also unveiled its Veros wireless portfolio of high-performance connectivity SoCs that integrate tri-combo radio stacks and are designed for embedded IoT and edge devices. The Veros SYN438x and SYN461x families offer multi-band 2x2 Wi-Fi (2.4/5/6 GHz), Bluetooth 5.x with LE Audio and advanced coexistence, and low-latency, low-power wireless modes, all in a compact, power-optimized package. Veros chips also support secure boot and integration with Astra compute platforms, making them ideal for smart home, industrial automation, robotics, wearables, and other embedded Edge systems.
Qualcomm Snapdragon X2 Plus

(Image credit: Qualcomm)
Qualcomm’s CES 2026 announcements included expansions to its Snapdragon X2 Plus platform and to its high-performance SoC family, with Oryon CPUs that can deliver up to 80 TOPS of NPU performance. The Snapdragon X2 Plus targets embedded PCs, agentic AI, and on-device AI workflows, with high compute and up to 128 GB of unified memory. Designed around Qualcomm’s third-generation Oryon CPUs, the X2 Plus comes in two main SKUs (a 10-core X2P-64-100 and a 6-core X2P-42-100) with clocks up to 4.0 GHz, up to 34 MB of combined cache, and an Adreno X2-45 GPU. Qualcomm pairs this with a Hexagon NPU rated at 80 TOPS of AI throughput, and up to 128 GB of LPDDR5X RAM. According to Qualcomm, devices using the X2 Plus are expected in thin-and-light laptops and other devices beginning in the first half of 2026.
LEGO SMART Play System
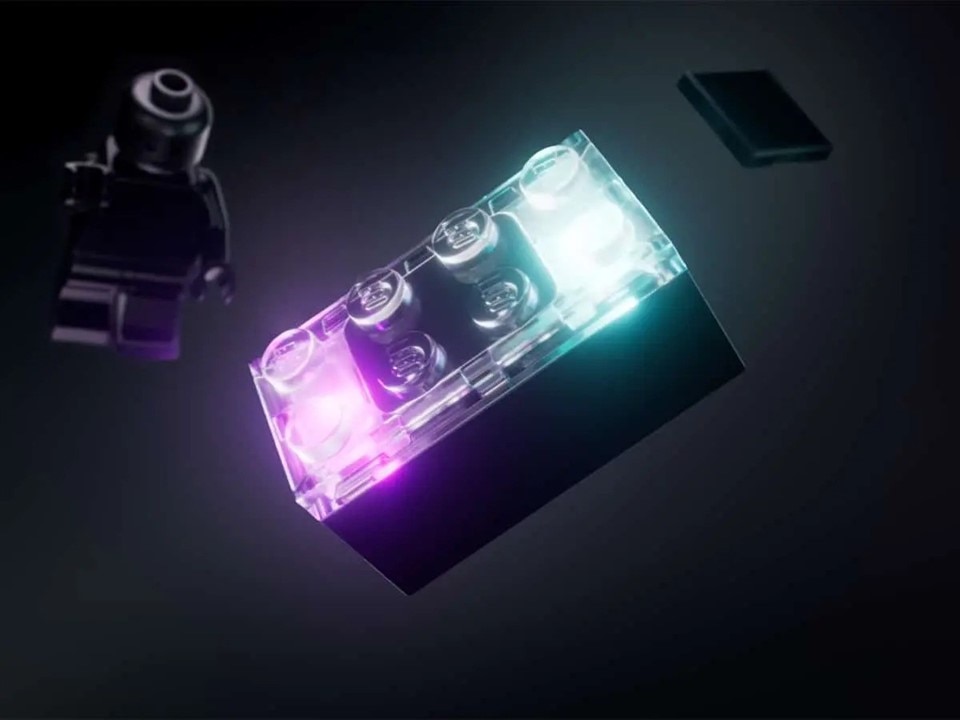

(Image credit: LEGO)
LEGO was on hand to showcase its new SMART Play System, which transforms a standard 2x4 brick into an embedded interactive device with a custom 4.1 mm ASIC chip that packs motion sensors, an accelerometer, RGB LEDs, a speaker, wireless mesh (BrickNet), and near-field magnetic sensing. The tiny embedded controller reads Smart Tags and Smart Minifigures to trigger context-aware sound and lighting effects, all without the need for screens. The SMART PLAY System uses a trio of technologies to bring builds to life, including the Smart Brick, LEGO Smart Tags, and Minifigures that respond to external actions during play.
e-con Systems DARSI Pro AI Compute Box
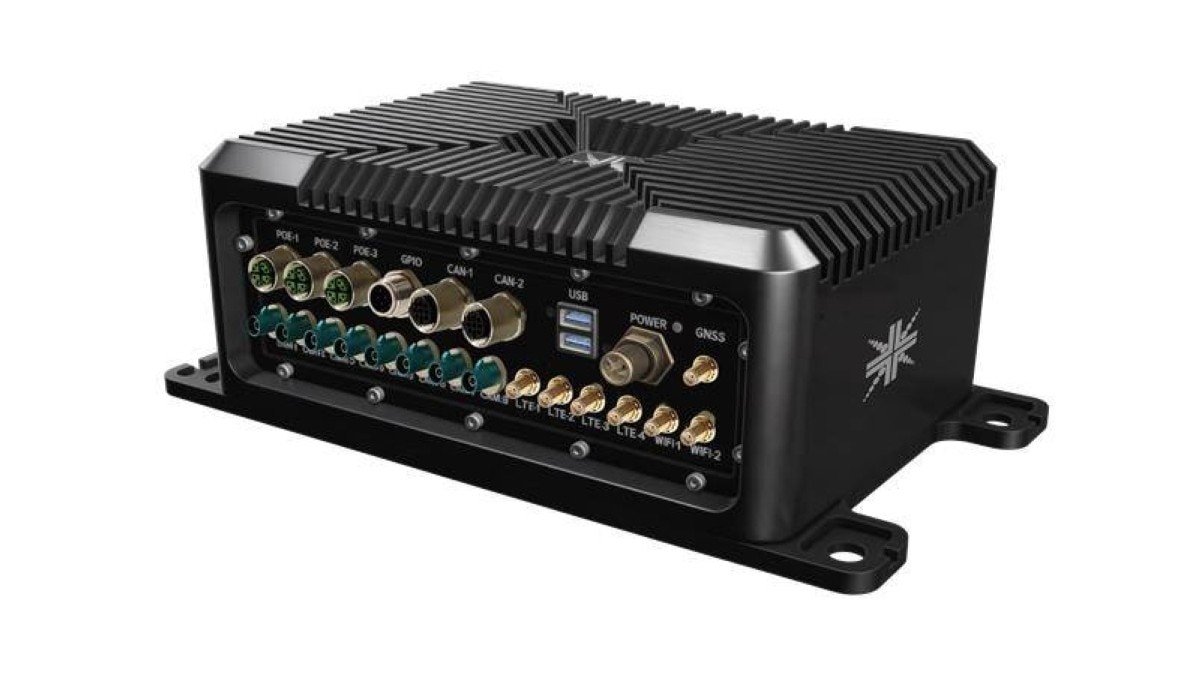

(Image credit: e-con Systems)
e-con Systems unveiled its DARSI Pro, a ruggedized AI compute box powered by NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX, and capable of delivering up to 100 TOPS of AI performance with multi-sensor fusion, synchronized GMSL camera support (up to 8), and NVIDIA JetPack compatibility. Designed for autonomy, robotics, intelligent transport, and perception-heavy use cases, the DARSI Pro integrates high-speed GbE, USB, GPIO, CAN, wireless modules, and cloud-based device management for remote OTA updates and fleet monitoring.
QNX Embedded Platforms
(Image credit: QNX)
QNX demonstrated how its real-time embedded software frameworks, including QNX Cabin (cloud-first digital cockpit development) and QNX Sound (software-defined audio/compute for vehicles), drive mission-critical systems for automotive and other industries. The QNX Cabin digital cockpit platform garners mission-critical functions (instrument clusters, audio, sensor fusion) from less critical features (Android Automotive or Linux infotainment) via virtualization on supported embedded SoCs from Qualcomm, MediaTek, and AMD. This allows developers to run safety-certified QNX components side-by-side with user environments without degrading real-time performance.
The company’s QNX Sound provides a software-defined audio stack that’s designed to replace legacy DSP hardware with a centralized, embedded audio processing solution that runs on the same SoC as other vehicle controllers.
SECO Pi Vision 10.1 CM5
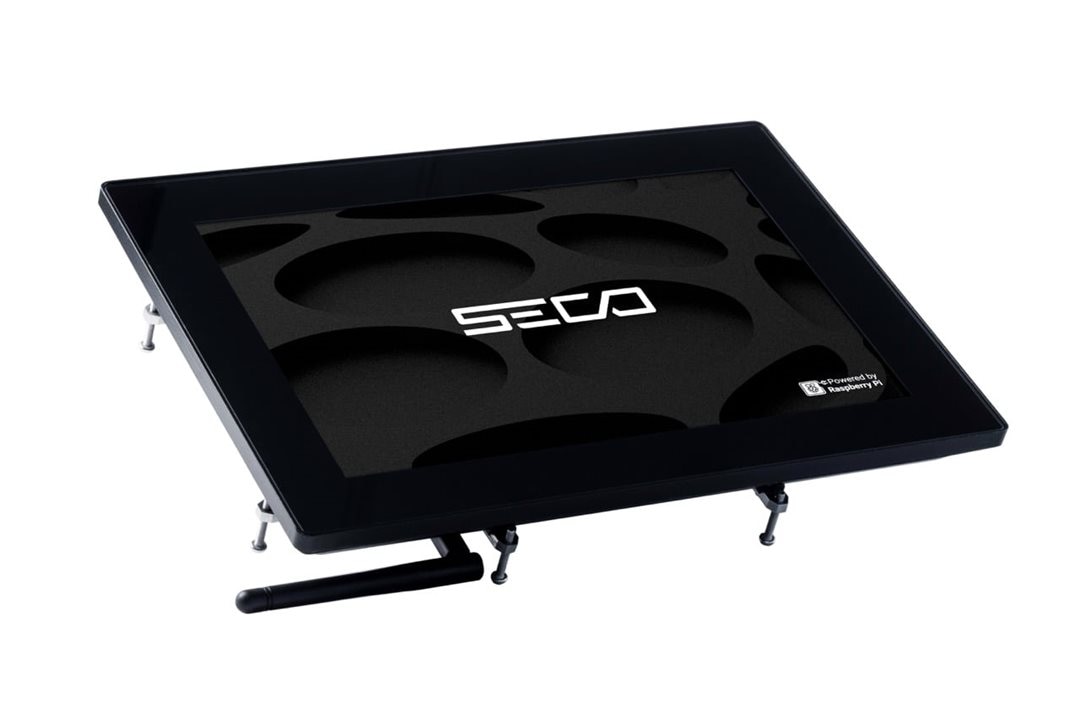

(Image credit: SECO)
SECO showcased its Pi Vision 10.1 CM5, an industrial-grade human-machine interface (HMI) designed around the Raspberry Pi Compute Module 5 (CM5), transforming it into an embedded compute platform for industrial IoT, smart buildings, vending, retail kiosks, and factory interfaces. The Pi Vision 10.1 CM5 integrates a 10.1-inch capacitive multi-touch display (1280x800) with a rugged IP66-rated front panel and fanless, panel-mount aluminium enclosure. The CM5 module is equipped with a Broadcom BCM2712 quad-core Arm Cortex-A76 + A53 SoC, up to 8 GB LPDDR4-4267 RAM with ECC, and up to 64 GB of eMMC flash storage.
The Pi Vision 10.1 CM5 also packs Gigabit Ethernet with IEEE 1588 support, Wi-Fi 5 and Bluetooth 5.0, USB 3.0, PCIe M.2 expansion, HDMI outputs, and a 40-pin GPIO for additional expansion via add-on boards and modules. The platform ships with both Raspberry Pi OS for rapid prototyping and Yocto-based Clea OS for secure edge deployment, OTA updates, and remote fleet management.
CES 2026 clearly reminds us that the edge isn’t just a niche development; it’s the foundation of embedded computing, AI, and real-world autonomous systems. From high-performance AI compute platforms like DARSI Pro and Snapdragon X2 Plus to innovative embedded input devices like the LEGO SMART Play brick, this lineup spans vision systems, neural accelerators, rugged embedded compute, and next-gen SoCs that are already driving how developers build the future.
