sponsored by

Most modern devices are capable of transmitting and receiving data through one or more input/output (I/O) ports. Such ports are vulnerable to anomalies, such as lightning and induced power surges, electrostatic discharge (ESD), electrical fast transient (EFT), and power cross. I/O ports are also susceptible to short circuits caused by faulty installation and aging wires. Damaged I/O ports can lead to equipment failure. A design engineer must incorporate I/O port protection that conforms to increasing immunity standards. This blog presents the five essential points regarding I/O port protection.
1. Protection against short circuits
Short circuits increase the potential for arcs, shock, fire hazards, and integrated circuit (IC) failure. To prevent short circuits, fuses can be integrated into the I/O port. A fuse is current-sensitive and its internal fuse wire melts when subject to overload conditions, breaking the circuit. Figure 1 shows an example of a Power over Ethernet (PoE) design with recommended protection components. A fuse protects the entire data line from a short circuit. A slow blow fuse prevents nuisance shutdowns due to current surges caused by the powering of a switching power supply.

Figure 1: Protection Circuit for Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Source: Littelfuse
2. Protection against overload
Overloads occur when excess current flows through a circuit that carries lower operating loads. The extra current generates and accumulates heat, which can result in circuit destruction and possibly fire, electrocution, or explosion. Figure 2 shows a USB 3.0 multi-port hub configuration where a PPTC (Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient) thermistor is installed on Vbus to limit current during a short circuit. A PPTC device has ultra-low internal resistance and offers a fast response to over-current events. They feature high current holding in a small form factor and are suitable for compact portable devices.

Figure 2: Overcurrent Protection for USB 3.0
3. Protection from ESD
ESD is a sudden transfer of static electrical charge when two objects come into contact; often from a body to an electronic circuit. ESD may result in faulty circuit operation, latent defects, and even catastrophic failure of sensitive components. An Ultra-Low Capacitance TVS diode array can protect HDMI, Display, and eSATA ports from damaging transients. A TVS diode array offers air and contact ESD protection (IEC 61000-4-2) of 20 kV while maintaining an extremely low leakage current of 25nA and low dynamic resistance. The TVS diode array is compatible with high-speed interfaces due to its low off-state capacitance and is capable of maintaining high bandwidth signal integrity. The SOD 883 and the standard 2.4 mm x 1.0 mm packaging options reduce trace layout complexity and provide significant PCB layout space savings.

Figure 3: Protection solution for HDMI port, DisplayPort, and eSATA port
4. Protection from surge
A surge is a momentary large current and voltage spike. Surges are transient events that occur when a large energy source connects to an electrical system. IEC61000-4-5 defines this event as a short circuit current pulse with an 8 µs rise time and 20 µs time to half. Figure 4 depicts the circuit diagram for an audio port protection system that utilizes a metal oxide varistor (MOV). A MOV has a tiny form factor and is well-suited for surge protection in compact handheld products. It has low capacitance of 33pF allowing it to support high data rates. MOVs provide stable performance over a wide operating and storage temperature range (-40°C to +85°C).
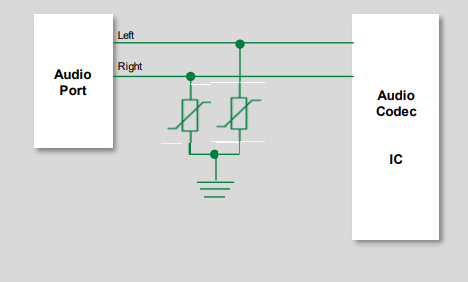
Figure 4: Protection solution for audio port
5. Ground fault protection
A ground fault occurs when an energized conductor accidentally comes into contact with a ground or equipment frame. Ground faults can be prevented by using a varistor, TVS diode or Gas Discharge Tubes (GDT). Figure 5 depicts a 48V DC power supply, with a varistor strapped across the input and a GDT on the ground line. The GDT is capable of withstanding current surges of up to 20 kA and protecting the circuit from floating to a dangerous level above ground when a surge occurs. A GDT draws less than 10 nA during regular operation and have an insulation resistance of 10 GΩ.
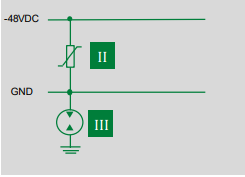
Figure 5: Protection solution for 48V DC power supply
Click here for a list of I/O protection devices from Littelfuse.
