NXP’s i.MX 8M Plus applications processor enables machine learning and intelligent vision for consumer applications and the industrial edge. Learn about the features of this processor and how it can be used in embedded vision systems.
The increase in automation of manufacturing and industrial processes creates more demand for intelligent vision-based systems. These systems capture visual input and then use a variety of processing techniques to make decisions based on that input. These vision systems are often integrated in larger control systems and so they must be capable of real-time communication with other devices.
NXP’s i.MX 8M Plus applications processor enables machine learning and intelligent vision for the industrial edge and a wide range of other applications. Let’s walk through how it can be used in embedded vision systems.
The Benefits of Edge Computing
When utilizing cloud computing, the user relies on computational resources outside the bounds of their local network. With edge computing, much of the processing is brought back within the local network’s bounds, and as a result, sensitive data can also be kept within the local network.
Edge devices can perform a wide variety of tasks. In the cloud computing paradigm, they were often utilized for filtering, pre-processing and storing or buffering the data. New advancements, such as integrated neural processing units (NPUs), open possibilities of what can be accomplished in edge devices. Edge devices can make decisions based on a variety of data sources, such as camera input and enable users to keep essential data within the local network. This reduces the amount of data that must be uploaded to the cloud and increases the system’s overall reliability and security. It can also enable faster real-time decision making, as transmitting data to the cloud and waiting for control responses adds latency, preventing a cloud computing architecture from being able to address some applications.
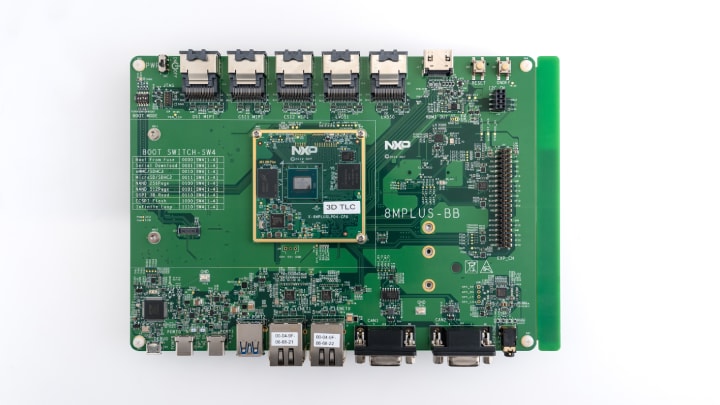
Figure 1. NXP’s i.MX 8M Plus Applications Processor Evaluation Kit
With an embedded NPU, an edge processing system can discard unwanted or noisy results from an input device, such as a camera, and only upload relevant data sets to the cloud. This saves bandwidth from the local site and reduces the amount of storage and processing required in the cloud, which, in turn, reduces the long-term operating cost.
The i.MX 8M Plus Applications Processor
NXP helps to enable vision-based applications at the edge with the new i.MX 8M plus applications processor by integrating two MIPI CSI camera interfaces and dual camera image signal processors (ISPs) with a supported resolution of up to 12 megapixels, along with a 2.3 TOPS neural processing unit (NPU) to accelerate machine learning.
The integrated ISPs reduce the system’s overall complexity, cost and power requirements while offering an optimal imaging solution, particularly at two megapixels and higher resolutions. The multimedia capabilities of the i.MX 8M Plus SoC also includes video encode and decode, 2D and 3D graphic acceleration and audio and voice functionalities.
The i.MX 8M Plus processor brings in communication interfaces such as two gigabit Ethernet controllers. One of them is time-sensitive networking (TSN) capable, while the second supports audio-video bridging (AVB). The device also includes dual CAN-FD interfaces, two USB 3.0/2.0 ports, one PCIe gen 3.0 interface and three SDIO 3.0 controllers.
The i.MX 8M Plus SoC makes use of heterogeneous computing, by providing developers with several different programmable processing cores. The Arm Cortex
-A53 cores are enabled with Yocto Linux
, providing enablement for application developers. The integrated M7 core provides real-time performance or it can be used to enable low power operating modes.
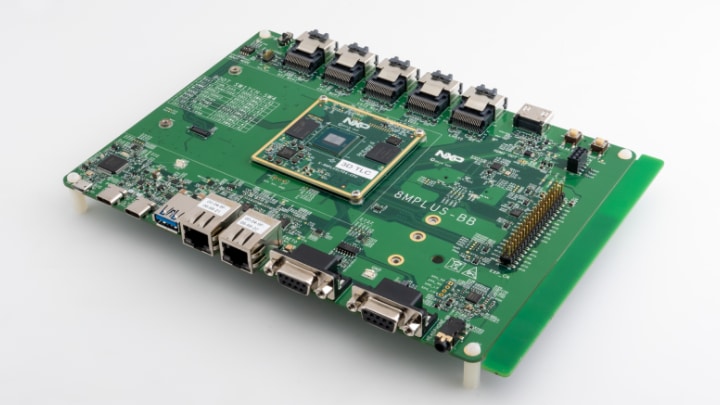

Figure 2. This evaluation board showcases the wide variety of available ports to connect the i.MX 8M Plus SoC to existing equipment.
Many manufacturing and controlling applications require high reliability. To ensure high reliability, NXP included DRAM inline ECC support and ECC on on-chip RAM to detect and correct memory errors.
Putting all of the features mentioned above together, the i.MX 8M Plus applications processor is well suited to enable vision-based embedded system at the edge. These systems can range from quality control mechanisms in a factory that detect faulty items on a production line, to intelligent smart home controllers, for example, an automated climate and security controller.

Figure 3. The i.MX 8M Plus Applications Processor works in multiple applications.
Extreme Operating Conditions, Longevity and Reliability
Many industrial use cases require a processor that can run in the field for extended periods of time. The i.MX 8M Plus applications processor is industrial qualified, capable of running for up to 10 years in an extended temperature range from -40°C up to 105°C.
In addition, the device will be part of the NXP 15-year longevity program, guaranteeing supply for 15 years after product launch. This makes the i.MX 8M Plus processor work for applications that require much longer product life cycles, either due to certification requirements or extended software development timelines.
Comprehensive Ecosystem for ML Development: eIQ
Breakthrough ML applications require a design and development ecosystem that is up to the task.
The 2019 Embedded Markets Study by EE Times indicated that 55% of developers said their current or future work requires machine learning. To cross the chasm and enable machine learning for the majority of developers, machine learning support must become more comprehensive and easier-to-use. More comprehensive support means that NXP must provide an end-to-end workflow, allowing developers to bring in their training data, select the right model for their application, perform model training, optimization and quantization and finally perform on-target profiling and subsequently move to production.
Easier-to-use is a matter of perspective, but for majority adoption this means that NXP must provide a simplified yet optimized user interface. Theoretically, this would enable a machine learning development environment that could essentially hide the details, and with the click of a few options, import the user’s training data and deploy the model on the target device.
Crossing the Chasm with Au-Zone Technologies
To make this a reality and cross that adopter chasm, NXP has made an investment in Canada-based Au-Zone Technologies, establishing an exclusive, strategic partnership to expand the eIQ machine learning software development environment with easy-to-use ML tools and expand its offering of silicon-optimized inference engines for Edge ML. Au-Zone’s DeepView
ML Tool Suite will augment eIQ with an intuitive, graphical user interface (GUI) and workflow, enabling developers of all experience levels (e.g. embedded developer, data scientist, ML expert) to import datasets and/or models, rapidly train and deploy NN models and ML workloads across the NXP Edge processing portfolio (See Figure 4.0).
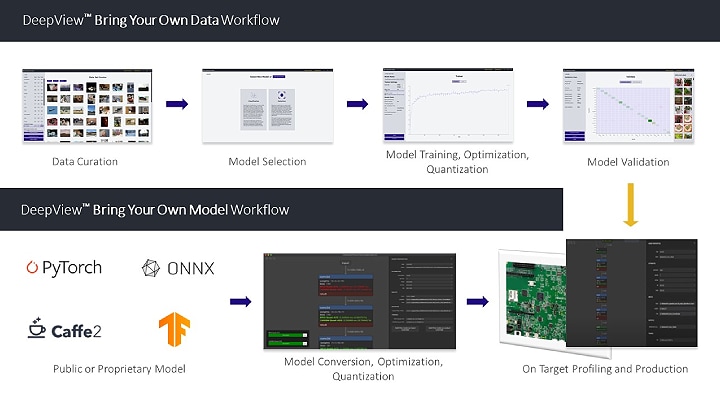
Figure 4. Au-Zone’s DeepView ML Tool Suite.
Use Cases
The i.MX 8M Plus applications processor is well-suited to be utilized in a wide variety of applications, ranging from industrial-grade controllers to energy-efficient consumer devices. Some of the target applications include industrial HMI, automation controllers, machine vision systems, medical equipment, home security and surveillance and fleet management. Find a list of all the target applications of the i.MX 8M Plus on the i.MX 8M Plus processor product page.
The following three application notes highlight a few use cases and studies:
- Using Code-Signing Tool with Hardware Security Module
- Strengthening Public Key Cryptography Using CAAM Secure Key
- i.MX 8M Plus NPU Warmup Time
For more information please visit nxp.com/imx8mplus and nxp.com/industrial

