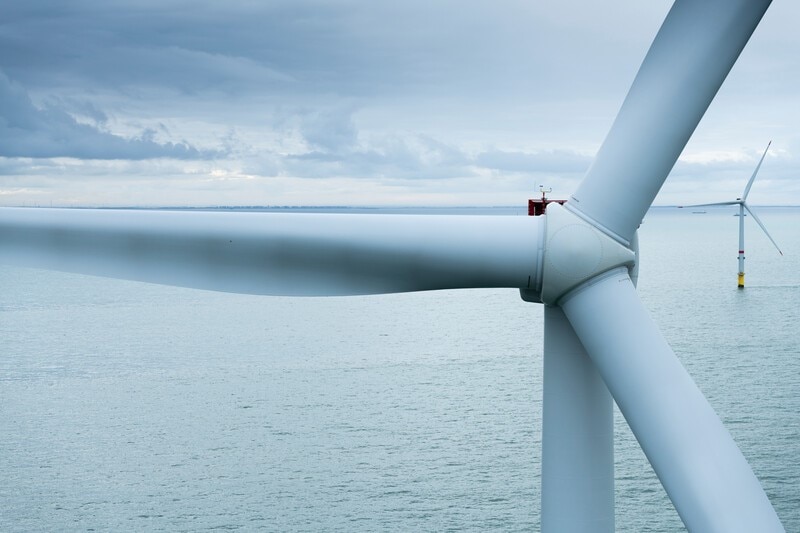

Vestas developed a new solution to recycle wind turbine blades. (Image Credit: Vestas)
Vestas, a Danish wind turbine maker, recently developed a new solution to recycle turbine blades, especially those in landfills. The company’s solution revolves around rendering “epoxy-based turbine blades as circular, without the need for changing the design or composition of blade material.” Vestas partnered with Aarhus University, Danish Technological Institute, and epoxy maker Olin to create the process that essentially breaks down epoxy resin into virgin-grade materials. In May 2021, they founded the CETEC project (Circular Economy for Thermosets Epoxy Composites).
“Until now, the wind industry has believed that turbine blade material calls for a new approach to design and manufacture to be either recyclable or beyond this, circular, at end of life. Going forward, we can now view old epoxy-based blades as a source of raw material,” Vestas vice president and head of sustainability Lisa Ekstraid said. “Once this new technology is implemented at scale, legacy blade material currently sitting in landfill, as well as blade material in active wind farms, can be disassembled and reused. This signals a new era for the wind industry, and accelerates our journey towards achieving circularity.”
The company plans to scale up the chemical breakdown process for commercialization through a new value chain supported by Stena Recycling and Olin, a Nordic recycling firm. Vestas says its solution will start a trend toward a circular economy for current and future epoxy-based resin blades. Recycling turbine blades has always been challenging because of the epoxy resin’s chemical properties.
“In the coming years, thousands of turbines will be decommissioned or repowered, representing a major sustainability challenge but also a valuable source of composite materials. As one of Europe’s leading recycling groups with a wide footprint in Europe, we have a central role in the transition to a circular economy. We see this solution as a huge opportunity to take part in making a sustainable solution even more sustainable and circular and are ready to apply our chemical recycling expertise and knowledge to this process”, says Henrik Grand Petersen, MD Stena Recycling Denmark.
Vestas sees this solution as an opportunity to create new turbine blades from reused blade material. It also believes the solution can lead to making all epoxy-based composite material a source of raw material for a broader circular economy, possibly encompassing industries beyond wind energy.
Have a story tip? Message me at: http://twitter.com/Cabe_Atwell

-
Gough Lui
-
Cancel
-
Vote Up
0
Vote Down
-
-
Sign in to reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Comment-

Gough Lui
-
Cancel
-
Vote Up
0
Vote Down
-
-
Sign in to reply
-
More
-
Cancel
Children