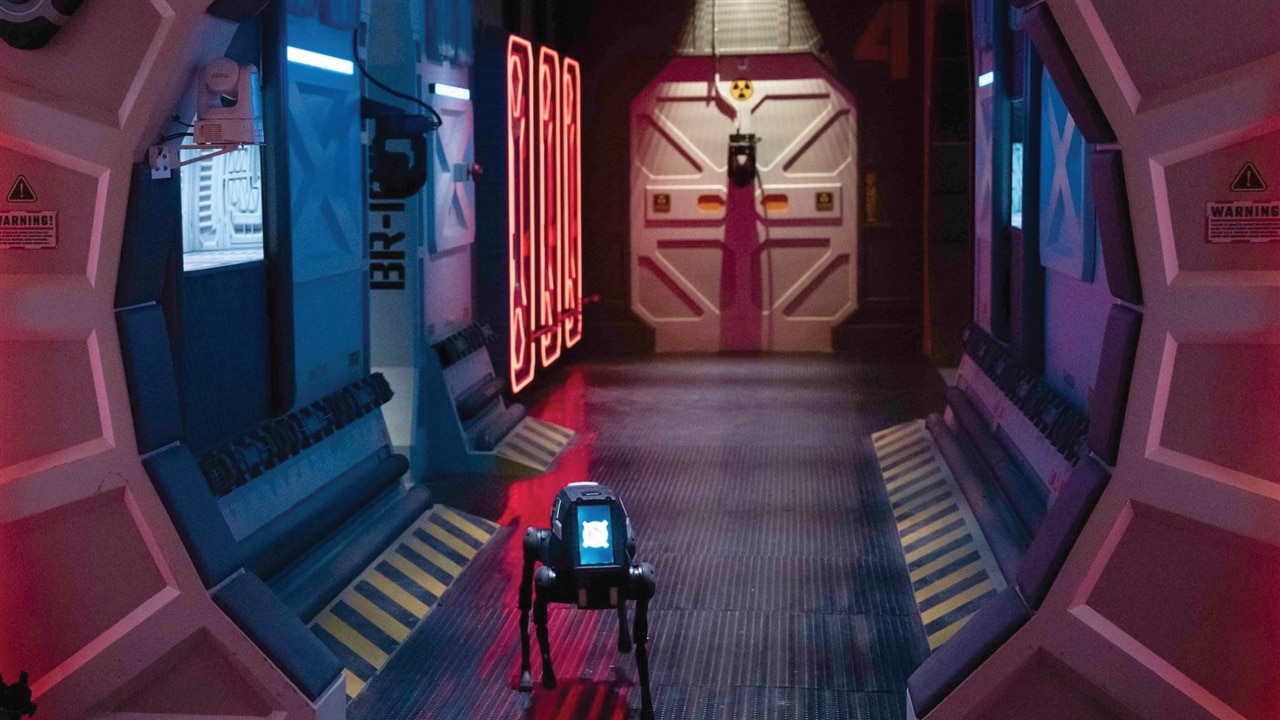
The RADDOG robot accompanies the cast of the Stars on Mars reality TV series. (Image Credit: Twitter/RADDOGAITX)
On June 5th, Fox started airing Stars on Mars, a reality TV series featuring twelve celebrities and former athletes competing in a Mars colony simulation. Some contestants have been eliminated so far, but the RADDOG quadruped robot dogs developed by Robotic Assistance Devices (RAD) stole the show. William Shatner plays the host and captain, assigning interstellar missions to the celebrity cast members from mission control. Richard Sherman, Lance Armstrong, Natasha Leggero, Adam Rippon, Tom Schwartz, Christopher Mintz-Plasse, Tallulah Willis, Ariel Winter, Tinashe, and Prosha Williams participated in the TV show.
RADDOG didn’t show up until episode three, in which the cast took it out for a nice walk. In the next episode, the robot stayed with the crew, racing both the RADDOG bots against each other. In this scenario, a celebrity controlled one bot, while a crew member controlled the other AI-powered one. However, the crew-controlled bot experienced a connectivity issue, causing it to slip and fall, which also meant the celebrity’s bot won the race.
According to AITX, RADDOG serves as a “purpose-built robot dog for law enforcement,” and operators can use it for “missions and operate it remotely to observe perilous scenarios or examine hazardous situations from a distance.”
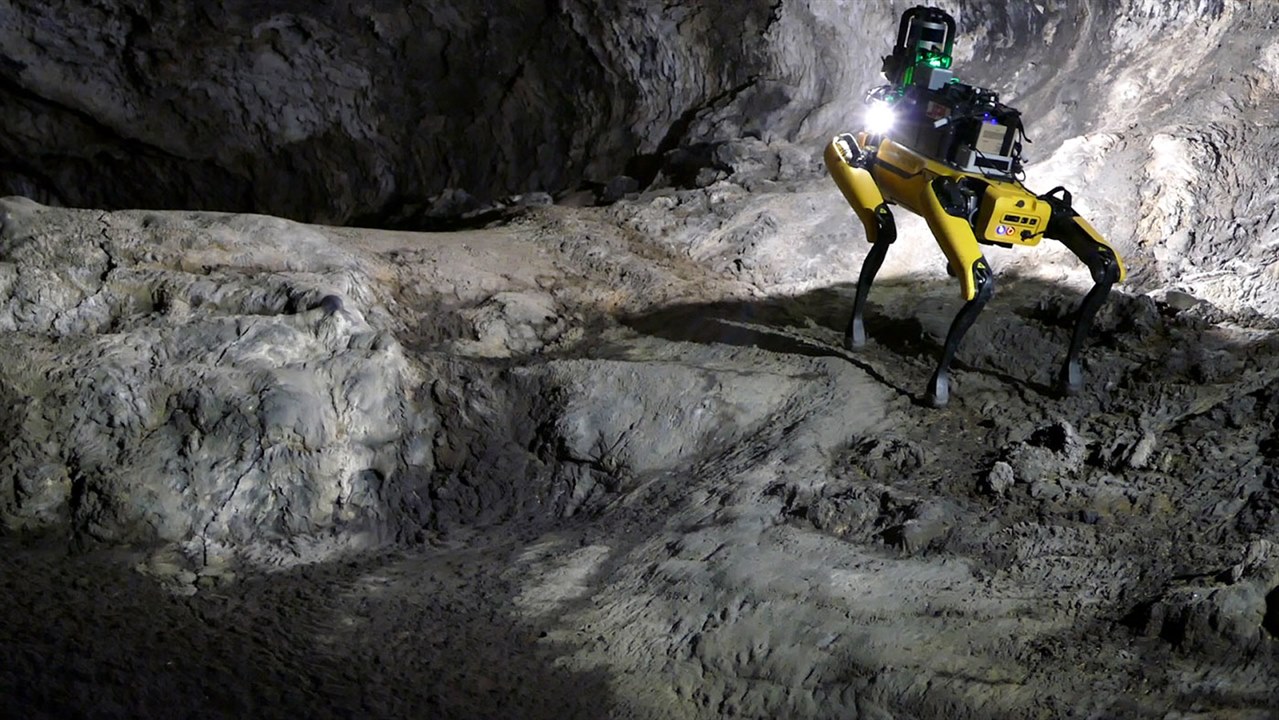

NASA’s Au-Spot could be used for cave exploring on Mars when the agency decides to pursue it. (Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
In 2020, NASA revealed that it’s training Au-Spot, a modified Spot robot dog with AI and various sensing equipment, to explore Mars caves. During the presentation at the American Geophysical Union, NASA revealed that Mars Dogs maneuver in ways the Spirit, Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance couldn’t before. Au-Spot is equipped with network sensors and software so that it can choose from several paths, avoid obstacles, and produce virtual maps of buried caves and tunnels for the home base operators. This robot is also twelve times lighter than today’s rovers and can walk three mph while performing terrestrial tests, faster than today’s rovers. For example, Curiosity reaches speeds of 0.09 mph.
The robot also produces 3D maps via input processing from LIDAR, motion, thermal, and visual sensors. It even has a communication module to send data to the surface as it explores the underground and AI that identifies objects for scientists. It’s gone through tests at obstacle courses with stairs, ramps, tunnels, hallways, and outdoor environments replicating Mars’ landscapes. Doing so helps determine if the robot is ready to navigate caves and generate 3D maps. NASA didn’t reveal plans to send Au-Spot to Mars, but cave exploration is expected to be huge for Mars surveys in the upcoming decade.
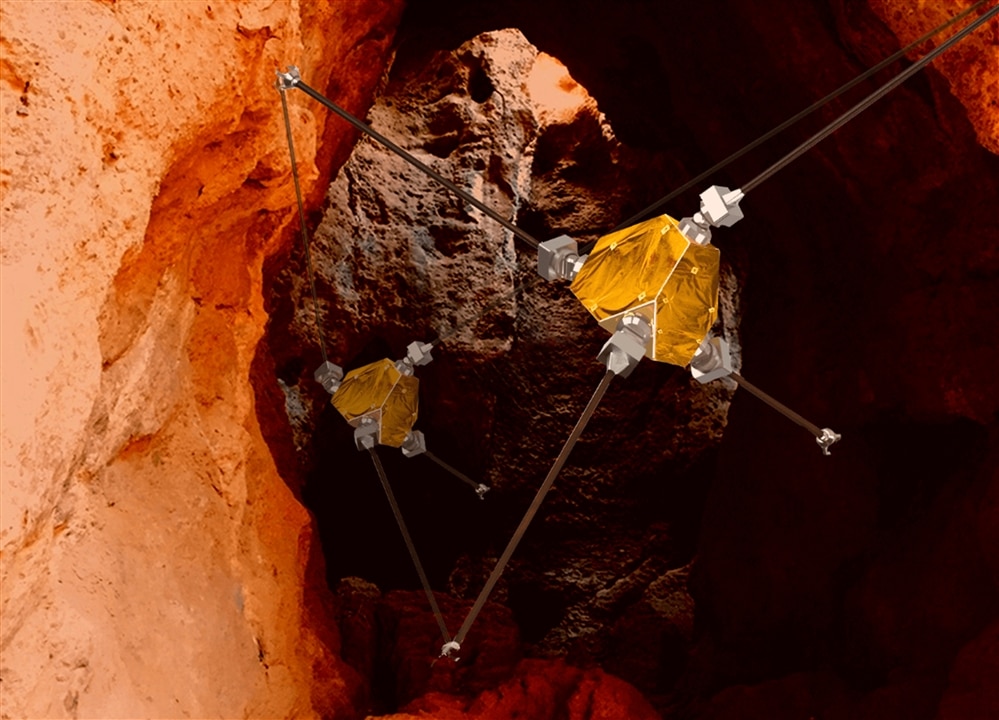

The ReachBot can latch itself onto Mars’ cavern walls. (Image Credit: Marco Pavone/NASA)
NASA teamed up with Stanford University to develop ReachBot, a cave-exploring robot for Mars missions. The bot uses four retractable gripper arms to move around its environment. It even looks fairly similar to a tetrahedron’s tentacles since all the joints are equally spaced out. So far, the retractable arms push outward from their corresponding shoulder joints. ReachBot uses three of its grippers to attach to the cave walls before extending the fourth arm in the direction it wants to move. At the same time, the robot can shorten that arm and extend the others to push itself forward. This method serves as an easy way to peer into Mars’ caves before humans land on the surface. The bot may need to hitch a ride on a rover, dropping it off at the entrance to access Martian caves.
In addition, it could feature cameras, LIDAR, and microscopes in the future. However, these consume power, which it can get by being tethered to the rover that also works like a communication relay. Even then, it may include a conveyer belt system designed to collect samples and send them to the surface. The rover would then carry the required instruments to perform a detailed analysis of each sample.
Have a story tip? Message me at: http://twitter.com/Cabe_Atwell
