IoT connectivity options
The right choice
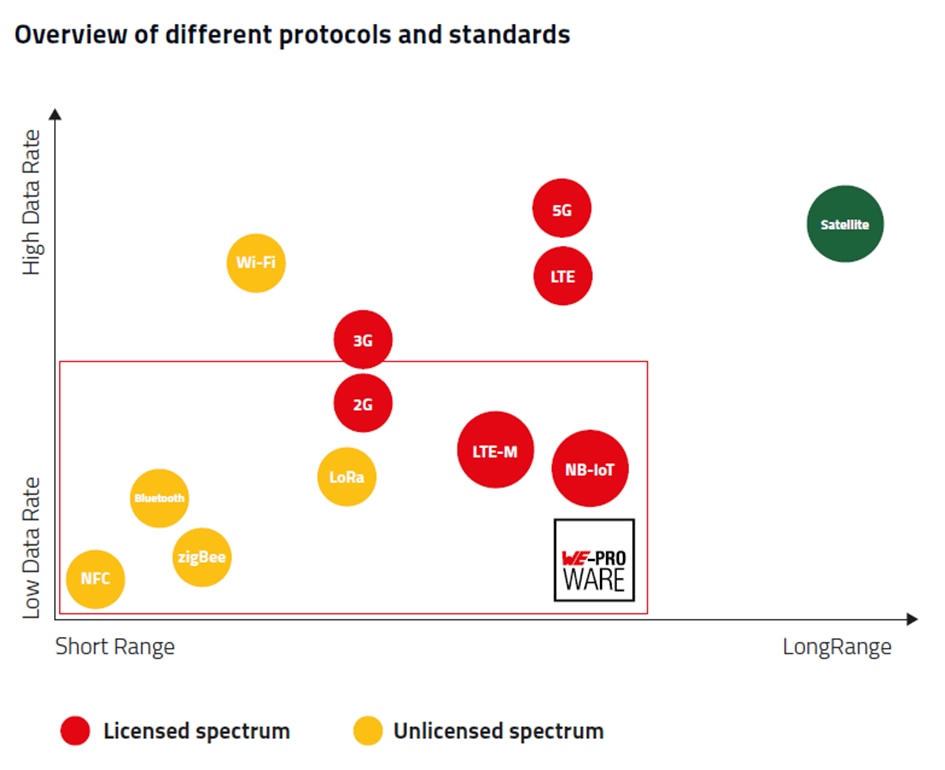
The main purpose of any IoT solution is to get data from the field to the cloud where analysis of the same generates the desired value proposition for the application. With a wide range of IoT connectivity options available, the connectivity decision is increasingly based on the cost, security, coverage, power usage and the potential throughput of the connectivity. Multiple IoT connectivity options are available and at the broader level these solutions can be categorized into two types:
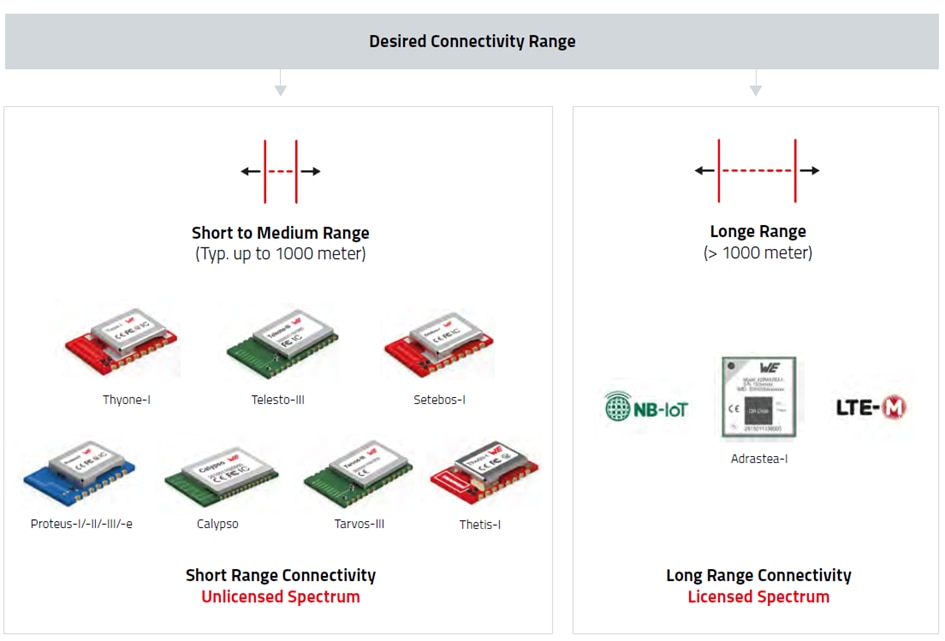
a) Short Range wireless connectivity solutions and
b) Long Range wireless connectivity solutions
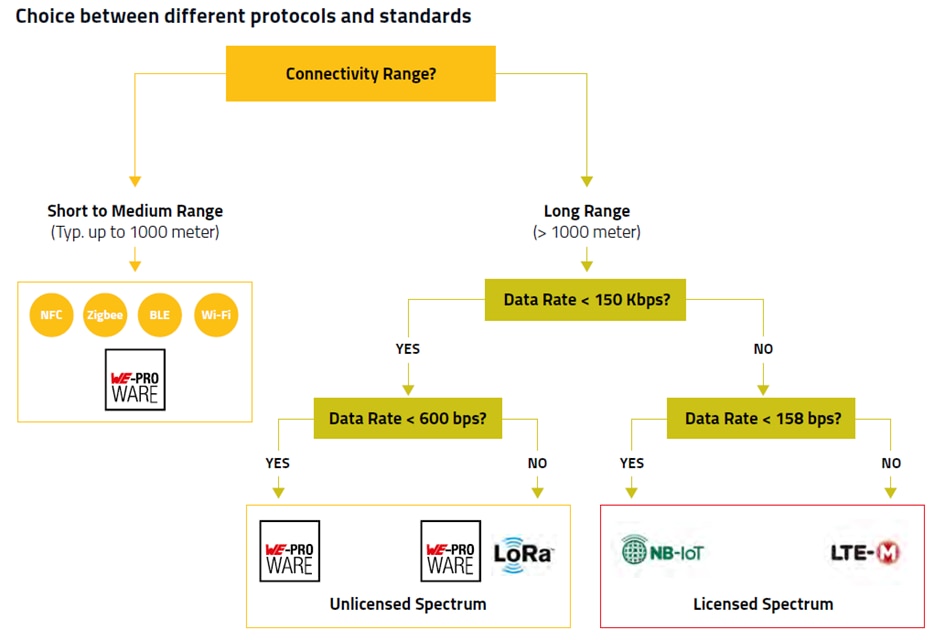
For few applications both short range and long range solutions can fit but application’s requirements and environments determines which connectivity solution shall be used.
GENERAL INFORMATION
LTE – Network Architecture
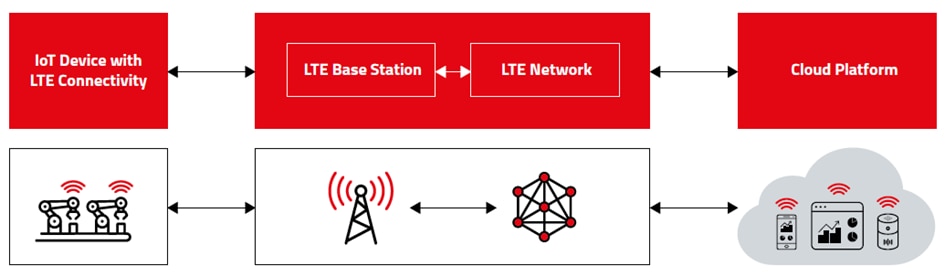
IoT Device transmits generated data directly to LTE base station, which forwards this data to LTE core network. LTE network sends this data to IoT cloud platform.
Example:
An industrial machine equipped with sensors, which collects the data on a wide range of parameters that determines its health and performance, for example, temperature, pressure, vibration frequency. This collected data is transmitted to LTE base station. LTE base station forwards this data to LTE core network. LTE network passes over this data to the cloud platform.
Advantages of Cellular Networks
Global Coverage and Roaming: Cellular networks are available globally, global coverage of cellular technologies makes companies to deploy their IoT devices globally. In-addition global presence of cellular networks enables roaming and mobility.
Secure and Reliable Transmission: Cellular technologies have default security procedures enabled, this procedure make sure only certified, subscribed and authenticated devices can access mobile network for data, SMS and voice services.
Standardized: 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) develops standards for cellular communication. These standards are internationally agreed standards. The device manufactures and network service providers follows cellular communication standards.
Network Quality of Service: Licensed spectrum is assigned exclusively to network service providers for independent usage. In this licensed spectrum service provider deploys his network. IoT devices has to subscribe for data or SMS services to network service provider, they are contractually bound to provide quality of Service for subscribers.
Certified Device Access: Certified devices access the cellular network this enables efficient utilization of licensed spectrum and minimizes the risk. Secured connectivity and strong authentication of IoT devices.
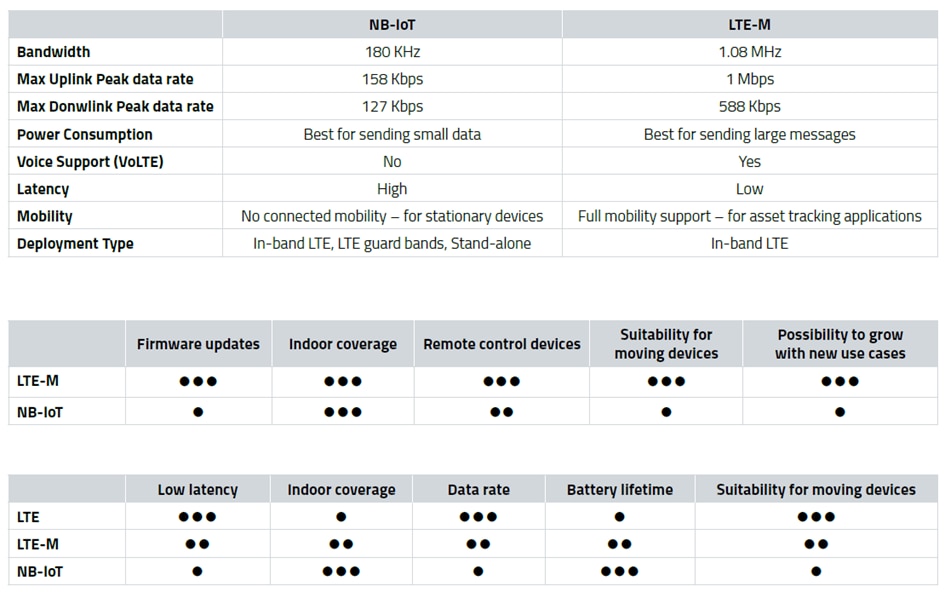
LTE-M and NB-IoT
Both LTE-M and NB-IoT are two new standards of Radio Access Technology designed for Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN), which are very energy-efficient radio transmission technologies. LTE-M and NB-IoT features low power consumption, wide coverage, massive connectivity and lower cost. LTE-M and NB-IoT enable a wide range of IoT applications where low cost, low power consumption and good building penetration are important.
Generally, NB-IoT is suitable for applications that only need to transmit small data volumes. NB-IoT offers maximum uplink data rate 158 Kbps. This data rate is adequate for transmitting the sensor generated data such as Temperature, pressure, filling levels etc.
LTE-M fills the gaps where NB-IoT is no longer sufficient or where NB-IoT is not available. For example, LTE-M has a higher uplink data rate of up to 1 Mbit/s and can thus transmit a large amount of data in less time. LTE-M is suitable for asset tracking type of applications where higher data rate with mobility support is required.
Difference between LTE-M and NB-IoT
If you want to read more find here the whole Product Guide.

