Frequently Asked Questions
Question Overview
- What is sequential voltage tracking?
- What is synchronization?
- What is adjustable soft start?
- What is meant by a fixed soft start?
- What is meant by adjustable frequency?
- What is meant by fixed frequency?
- What is the power good?
- What is the programmable UVLO (under voltage lockout)?
- What is the overcurrent protection (OCP)?
- What is the overtemperature protection (OTP)?
- What is the difference between inrush and start up current?
- Are the power modules UL certified?
- For what do I need the “power boost” feature?
- Which approvals can I get with the VISM SIP?
- When do I need a functional insulated MagI³C Power?
- What is the isolation voltage level of WE isolated power modules?
- Do the isolated modules need external components to function?
- How high can the output voltage of unregulated SIP4 / SIP -7 / FISM SMD-8 modules go?
- How can I solder the FISM SMD - 8 power modules? And how many solder cycles can it withstand?
- Is the EMI emission filter integrated in power module?
- What is meant by MTBF?
Answers
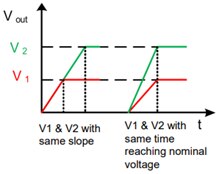
1. What is sequential voltage tracking?
Simultaneous VOUT rise of two power modules during start-up (same slope or same time reaching nominal voltage).
→ e.g. two power supplies in FPGAs with critical VCC rise requirements
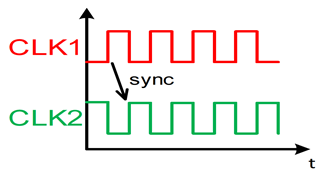
2. What is synchronization?
A power module switching frequency can be synchronized by an external clock.
→ Avoids interference. Reduces input peak currents
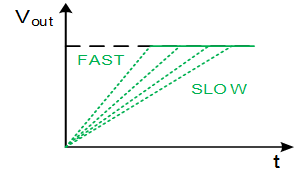
3. What is adjustable soft start?
During start-up the slope of the rise of VOUT can be adjusted.
→ No overshoot at VOUT
→ Smooth start-up current
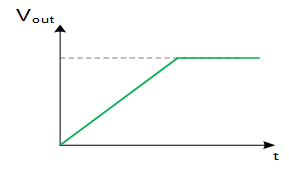
4. What is meant by a fixed soft start?
The slope of the rise of the output voltage during start up is fixed.
→ No overshoot at VOUT
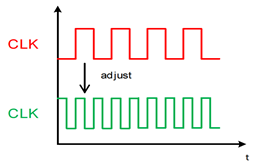
5. What is meant by adjustable frequency?
The switching frequency of the power module can be adjusted.
→ User selectable balance between efficiency and ripple. Avoiding not preferred frequencies
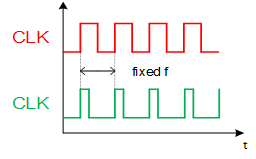
6. What is meant by fixed frequency?
The switching frequency of the power module is fixed.
→ Simple Design
→ Design for optimum balance between speed versus efficiency
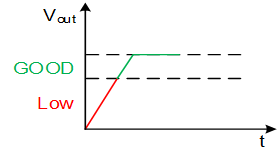
7. What is the power good?
Detects the value of VOUT and indicates if it is within the nominal range.
→ Monitoring for diagnostics/signaling
→ Allows sequencing
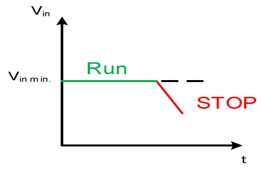
8. What is the programmable UVLO (under voltage lockout)?
Turns off the power module output in the event of a input voltage dropping below a defined limit value.
→ Avoids undefined behavior of the power module during input voltage failures
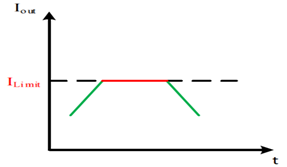
9. What is the overcurrent protection (OCP)?
During an overcurrent condition the output current is limited.
→ Protect overheating of the power module
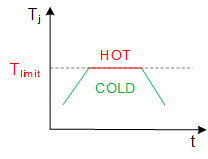
10. What is the overtemperature protection (OTP)?
Turns off the power module when the junction temperature exceeds a dangerous limit.
→ Prevents catastrophic failures during accidental device overheating
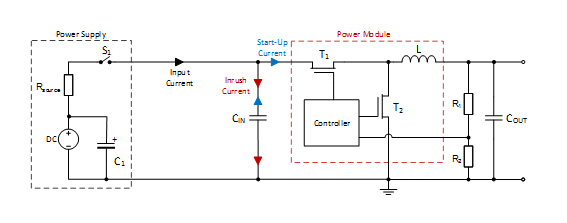
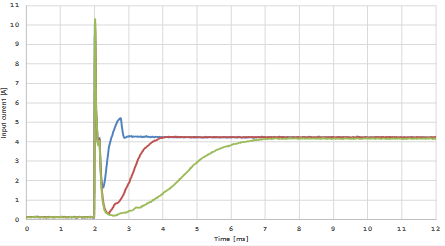
11. What is the difference between inrush and start up current?
- The first input current peak (inrush current) is due to the initial charge of CIN
- The inrush current (red) flows into the uncharged capacitor CIN as the switch S1 is closing
- CIN acts as a virtual short circuit allowing the current to rapidly increase to a high peak and decreases when CIN is fully charged
- This current peak is not affected by the soft-start capacitor
- CIN starts supplying the power module with the start-up current (blue)
- During soft-start the input current smoothly rises
- The different slope of the rising input currents is defined by the different soft-start capacitor values
- At about 7ms the steady state of the input current is reached
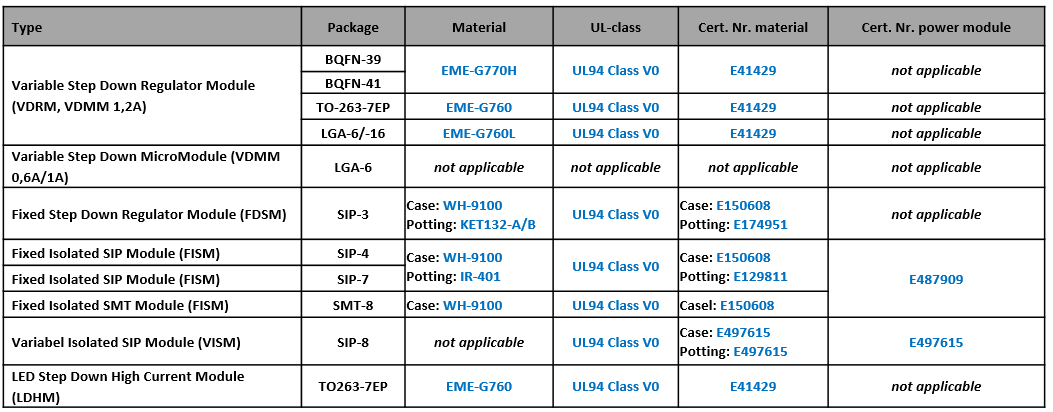
12. Are the power modules UL certified?
Below is a grouped summary of the actual UL certificates of our power modules.
13. For what do I need the “power boost” feature?
The power boost feature provides additional current, allowing the module to fulfill the following demands:
- Unforcasted increases in load demands
- Monotonic charging of capacitive loads – no voltage dips
- Backup power for momentary higher energy demands of the application
- Tripping of input fuses of downstream applications in case of overload (ensures higher current for safe tripping)
All isolated power modules have the power boost feature.
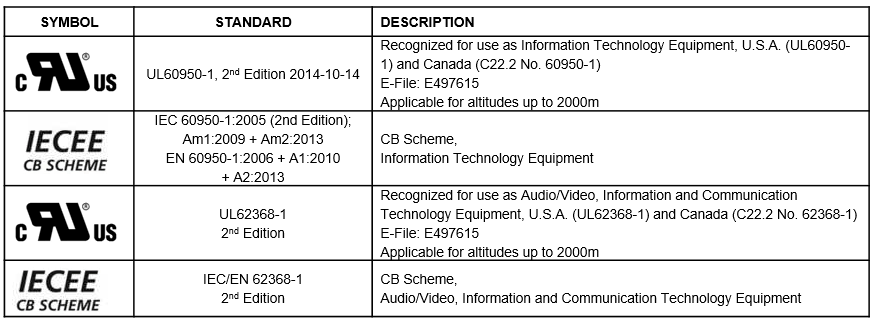
14. Which approvals can I get with the SIP-8?
The SIP-8 has multiple approvals. An overview is listed below:
15. When do I need a functional insulated MagI³C Power?
An insulated, galvanic isolated DC/DC converter avoids:
- Humm loops,
- Overvoltages,
- Excessive EMI
- between signal source and the signal receiver
- generally for avoiding Disturbances / interference due to different ground potentials
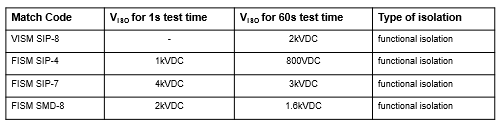
16. What is the isolation voltage level of WE isolated power modules?
17. Do the isolated modules need external components to function?
No these isolated power module families offer all inclusive solution where all the needed components are integrated.
Due to the switching behavior of the power module, however, it is advisable to include an additional input filter in the circuit design.
Würth Elektronik offers an application-specific filter bag for almost every power module.
Application specific emi filter
18. How high can the output voltage of unregulated SIP4 / SIP -7 / FISM SMD-8 modules go?
Since these families are unregulated, under light load conditions <10% of the full load, the voltage can go higher than the specified output voltage value. If that is an issue for the application, it is recommended to use a zener diode or bleeding resistor to avoid that situation
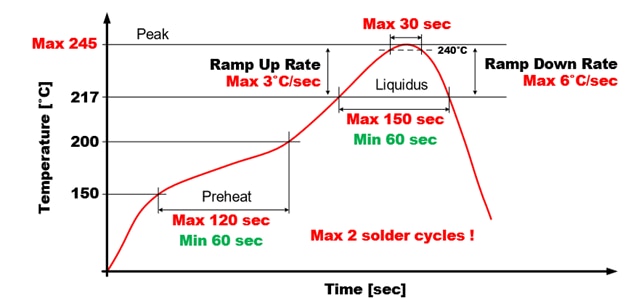
19. How can I solder the FISM SMD - 8 power modules? And how many solder cycles can it withstand?
The recommended soldering profile of SMD-8 module is shown below. The module can withstand two cycles where the 2nd cycle can be a reflow or solder cycle
20. Is the EMI emission filter integrated in power module?
No, because there are many different requirements for each power module.
Würth provides an application specific filter bag for nearly each power module.
Application specific emi filter

21. What is meant by MTBF?
Mean, average operating time between two failures, a specification for the reliability of a component or a component group. Various standards (e.g. MILR-HDBK-217, SN29500 or Telcordia) can be taken for calculation. The basis for calculation is the failure rates of the components taking various specific factors into consideration, such as ambient temperature, voltage, current, power, humidity, shock/vibration, etc.

