Long-range-WAN
General information
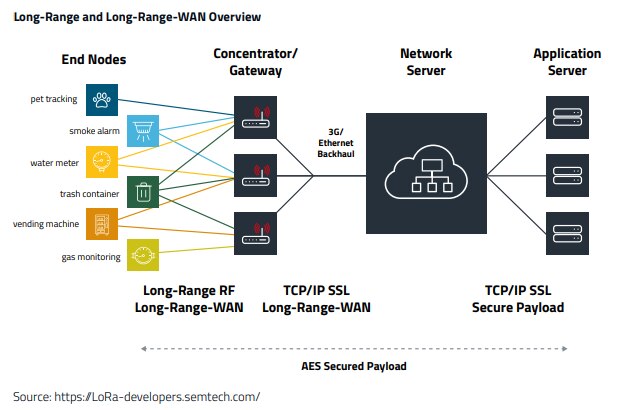
Long-Range-WAN Architecture
A Long-Range-WAN-enabled end device is wirelessly connected to a long-range-WAN through radio gateways.
Uplink Transmission:
A Long-Range-WAN gateway receives messages from any end device and forwards these data messages to the Long-Range-WAN server (LNS). There is no fixed association between an end device and a specific gateway. Instead, multiple gateways can receive the same message from a single end device, the LNS performs data de-duplication and deletes all copies.
Downlink Transmission:
For downlinks communication, the Long-Range-WAN server (LNS) typically selects the gateway that received the message with the best RSSI when transmitting a downlink message. The gateway executes transmission requests coming from the LNS and forwards these data messages to end device.
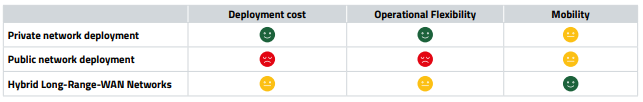
Long-Range-WAN Deployment Options
There are different models for connecting end devices to a Long-Range-WAN network – private network, public network and hybrid network.
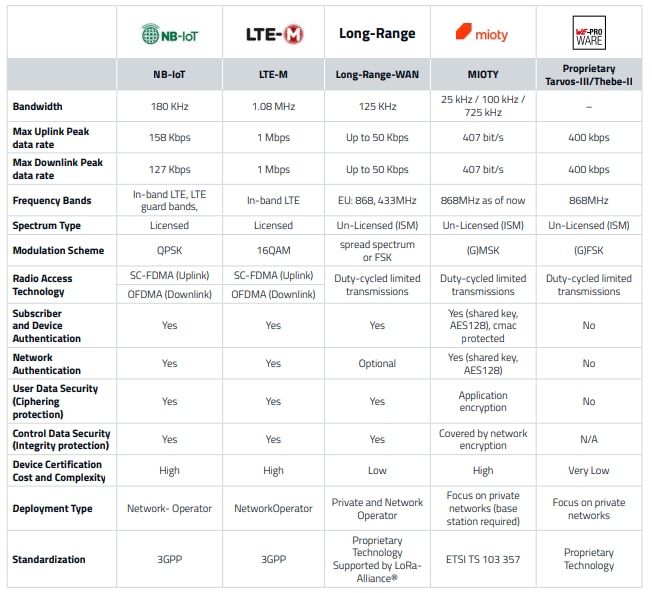
Comparison LowPowerWideAreaNetwork (LPWAN) Systems
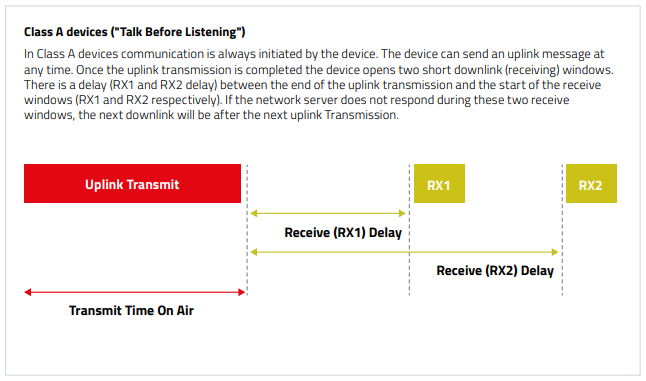
Long-Range-WAN Classes
The Long-Range-WAN specification defines three device types: Class A, Class B, and Class C. In a long-range-WAN network, end devices operate in one of three modes: long-range-WAN Class A, Class B, and Class C.
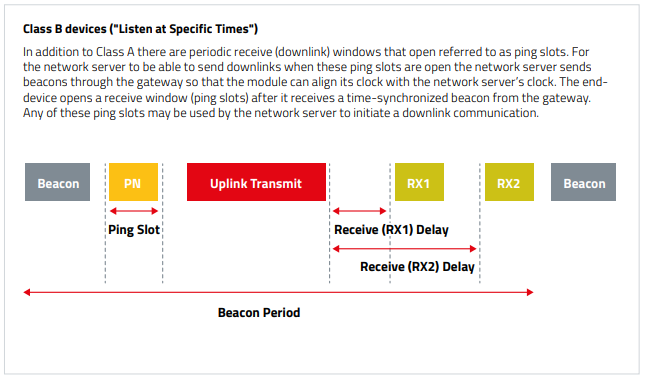
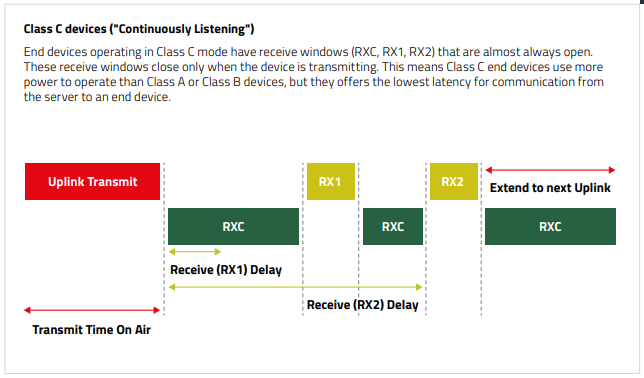
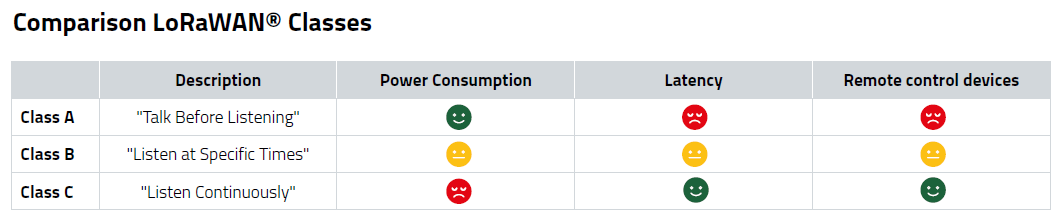
Comparison Long-Range-WAN Classes
If you want to read more find here the whole Product Guide.

