WE-PCM Design Guideline
Phase Changing Material
Thermal Management is the term used to describe the methods used take care of the excess heat that electronic devices and components generate. It is a field of upmost importance in order to guarantee reliability of electronic devices and components as well as to prevent premature failure.
1. What is the WE-PCM used for?
The WE-PCM is designed as an alternative to the use of thermal pastes & greases between high performance components, such as processors or power components, and cooling assemblies. This material changes from solid to liquid at a certain temperature, thus providing a complete wet-out of the interface without any spills or overflow. The thermal interface created is comparable to the one provided by pastes & greases but without the complication implied in the use of the liquids on a production line.
The phase changing material itself is composed by three main components, as shown in Figure 1:
- Release PET film: The WE-PCM is protected by two PET films on top and bottom to protect the material from foreign particles. The PET films must be removed before placing the material.
- Phase changing material: Main component of the product.
- Polyimide film: This component is present in some of the standard parts to provide electrical insulation while maintaining its thermally conductive capabilities
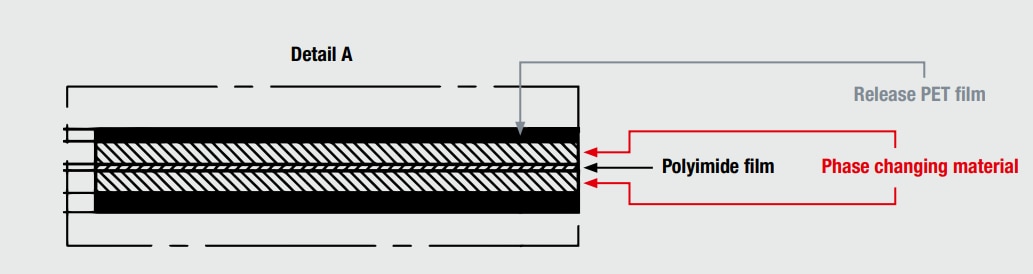
Fig. 1: WE-PCM components
2. Where can the WE-PCM be used?
The WE-PCM is designed to provide a seamless thermal interface between a component and a cooling assembly. A benefit of the complete wet-out of the contact surfaces as well as the thinness is that the thermal resistance provided by the material is very low compared to other interface solutions. Different applications have different requirements. The WE-PCM covers all of them:
- Thermal Conductivity: Wide range from 1.6 up to 5 W/mK.
- Thickness: Standard thickness of 0.2mm when solid at room temperature.
- Electric Insulation: If required there are standard parts with polyamide film with a breakdown voltage of up to 5 kV/mm.
- Phase change temperature: The material is designed to change from solid to liquid between 50 and 60 ºC.
Due to the material’s ability to provide a hassle-free seamless interface it can be used for cooling high-performance ICs such as CPUs or FPGAs (Figure 2).
Another example where a high performance solution is required is power applications, where the WE-PCM can be seen providing the interface transistors (IGBTs, TO packages…) and cooling assemblies, such as shown in figure 3.
Comparing WE-PCM to conventional pastes or greases, the application and use is cleaner and more effective at industrial level.
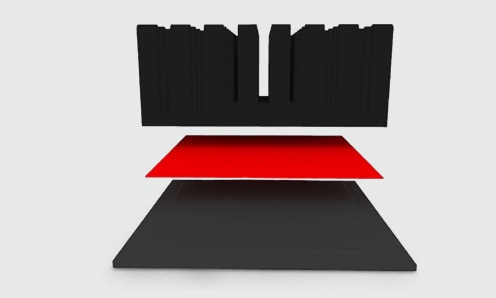
Fig. 2: CPU getting a phase changing material applied
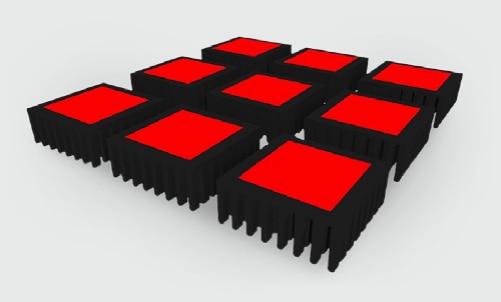
Fig. 3: IGBT with pre-applied WE-PCM
3. Solutions specially tailored for you
Another benefit of the WE-PCM that adds value to its versatility is the ease of shape customization. Würth Elektronik brings this value to you by providing a customization service with no MOQ and no tooling costs.
Reach out to your Würth Elektronik representative with the following information and they will get back to you with a personized quotation:
- Thermal Conductivity needed for the application
- Desired thickness
- Volume or number of parts needed
- Technical drawing of the tailored solution
- Any other requirement you may have
4. General use of the WE-PCM recommendations
- For optimal adhesion properties, the surfaces of the component and the cooling assembly must be clean and dry. It is recommended to use Isopropyl alcohol applied with a lint-free wipe or swab for removing.
- Gaps and/or air bubbles between the gap filler and the contact surfaces must be avoided. Otherwise, the performance of the product may be affected.
- The temperature rise of the component which needs thermal management must be taken into consideration. The operating temperature is comprised of ambient temperature and temperature rise of the component.
- It is recommended to compress the material with equal pressure on the whole surface.
- The material is tacky and self-adhesive, it will stay in place until final compressed assembly.
5. Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I modify standard parts? What if I need aluminium foil embedded in the part?
A: There are many ways of customizing the part to fulfil your requirements :
- Dimensions: Length and width
- Shapes: Breakouts or holes
- Electrical insulation: Polyimide film can be added or removed
Q: What test method has been used for the thermal performance measurements provided by the datasheet?
A: All thermal related measurements have been performed following ASTM D5470.
Q: Is the WE-PCM electrically insulating?
A: Only the standard parts that are reinforced with polyamide film and within the recommended specifications. Keep in mind the WE-PCM is designed as a gap filling solution, not a purely electrically insulating one.
Q: Will the material change its mechanical properties under high temperatures?
A: If the material is used under the parameters specified in the datasheet there will be no significant change in its hardness or any other mechanical property.
Q: Can the WE-PCM be reworked / re-attached?
A: If solid it can be very carefully reworked, but there is a high risk of contaminating the contact surfaces with foreign particles as well as tearing the material. Once the material has changed phase it should not be re-worked.
Q: In which applications should I avoid using phase changers?
A: Avoid using WE-PCM in applications in which the device will not reach phase change temperature. Also avoid applications in which the operating temperature exceeds the maximum recommended operating temperature of the material (130 ºC).
Q: Is it possible to request a WE-PCM with adhesive tape?
A: No, there is no need to use our phase changers with adhesive tape because its tackiness enables easy application.
Q: Will the WE-PCM keep my cooling assembly in position?
A: No, the use of the product still requires a mechanical fixation to keep the cooling assembly on the hot component.
Q: Can I use screws to fix cooling assemblies on my device?
A: You may use screws, but keep in mind that once the phase change temperature is reached, you will need to tighten them a little more. For this reason, the use of clips or a combination of screws, washers and springs is recommended. The continuous force applied by these two suggestions will ensure the performance of the WE-PCM.
6. Thermal Properties & Glossary
Thermal interface materials (TIMs) are materials that are inserted between two surfaces to improve the thermal coupling between them. The usual application is between a heat source and a cooling assembly.
TIMs can be categorized in two main groups:
- Vertical Thermal Interfaces: The commonly used gap filling solution such as silicone elastomers, thermal transfer tapes or greases.
- Heat spreaders: These materials work great at distributing heat from one spot to a large surface.
Besides providing a path for heat energy to flow through, these materials provide a seamless interface between all contact surfaces, conforming to any microscopic irregularities in either the heat source or the cooling assembly. This is an important characteristic, since air is a thermal insulator and it can become a barrier that affects the overall performance of the solution.
As represented in figure 4, we can combine two different TIMs to take advantage of a combination between vertical and horizontal interfaces. In the example TIM 2 could be a WE-TGF silicone gap filler and TIM 1 a WE-TGS graphite heat spreader. This combination would allow the use of a larger heatsink than the footprint of the heat source would allow, thus enhancing the cooling capabilities of the whole assembly.
There are many factors that should be taken into consideration when selecting the optimal Thermal Management Solution of your application. The most common ones are:
- Thermal conductivity: Determines the overall performance of the heat transfer between contact surfaces.
- Thermal resistance: Opposition of the material to transfer heat, the lower the resistance the more efficient the TIM is. This property is the reciprocal of the thermal conductivity.
- Electrical conductivity: Depending on the TIM, electrical insulation can be an intrinsic property of the material. But for those that are not, other layers can be added to the material in order to so insulate it.
- Operating temp range: TIMs work in different temperature ranges so it must be taken into consideration when selecting a solution.
- Thickness/Height: The distance between the mating surfaces is a key factor in order to select a TIM. Depending on the solutions, it must be taken into consideration that the material should be compressed (as recommended in the datasheet) to achieve optimal thermal performance.
- Pressure: Depending on the final application, some materials are designed to withstand higher pressure such as the WE-TINS.
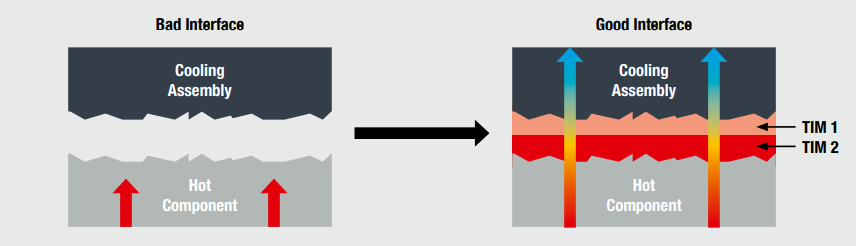
Fig. 4: Detail of contact surfaces
7. Würth Elektronik’s Thermal Management Solutions
Gap filling solutions vary in shape and form, there are different criteria to be considered when looking for a solution: dimensions of the gap that needs filling, evaluation of the heat energy that needs to be managed and if electrical insulation is required between the hot component and the cooling assembly. Würth Elektronik brings to you a broad portfolio with solutions for any gap, interface type and thermal conductivity.

Direct Link: WE-PCM Design Guideline

