1 Arrival of PCBs
With easyEDA, PCB for six PCB for SIX WL-ICLED Integrated Controller LED are designed and just arrived recently as Smart car chamber #3 Comparisons of WL-ICLED Integrated Controllers and schematic designs - element14 Communit

There are various type in desgin and basically fit for different Control Communication Protocols.
2 Analysis of Differences in Control Communication Protocols
The six WL-ICLED integrated controller LEDs (Order Numbers: 1311610030140, 1312020030000, 1312121320437, 1313210530000, 1315050930002, 1315050930246) exhibit core differences in their control communication protocols across four key dimensions: data frame structure, command control capability, synchronization mechanism, and dimming precision.
The specific variations are detailed below:
2.1 Differences in Data Frame Structure: Varied Bit Widths and Content Arrangement
2.2 Differences in Command Control Capability: Varied Functional Complexity
2.3 Differences in Synchronization Mechanism: Varied Reset Pulses and Frame Synchronization Methods
2.4 Differences in Dimming Precision: Varied PWM Bit Widths and Current Control Granularity
| Precision Level | Corresponding Order Number | Dimming Parameter Details | Precision Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Precision | 1312020030000, 1313210530000, 1315050930002 | 1. PWM bit width: 8 bits (256 dimming levels per color) 2. No current gain control; current is fixed by supply voltage and internal circuits | Fewer brightness adjustment levels (256 levels); no current fine-tuning capability; suitable for scenarios with low precision requirements (e.g., ambient lights). |
| Medium Precision | 1311610030140, 1315050930246 | 1. PWM bit width: 8 bits (256 dimming levels per color) 2. Current control: 5-bit global current gain (32 adjustment levels); all colors share the same gain value | 256 brightness levels; supports 32-level global current fine-tuning; suitable for scenarios requiring unified current adjustment (e.g., smart home panels). |
| High Precision | 1312121320437 | 1. PWM bit width: 12 bits (4096 dimming levels per color) 2. Current control: 4-bit independent current gain (16 adjustment levels); red, green, and blue colors are adjusted independently | Extremely high number of brightness adjustment levels (4096 levels); supports independent current fine-tuning for single colors; suitable for professional scenarios (e.g., stage lighting, display devices). |
3 Core differences and data transmission diagram
3.1 Cross-checkTable
3.2 Detail diagram
data transmission diagram 1311610030140
data transmission diagram 1312020030000
data transmission diagram 1312121320437
data transmission diagram 1313210530000
data transmission diagram 1315050930002
data transmission diagram 1315050930246
4 Blink the LED with Arduino FastLED library
The have been example for Arduino FastLED library. The simpliest application is same as that of WS2816
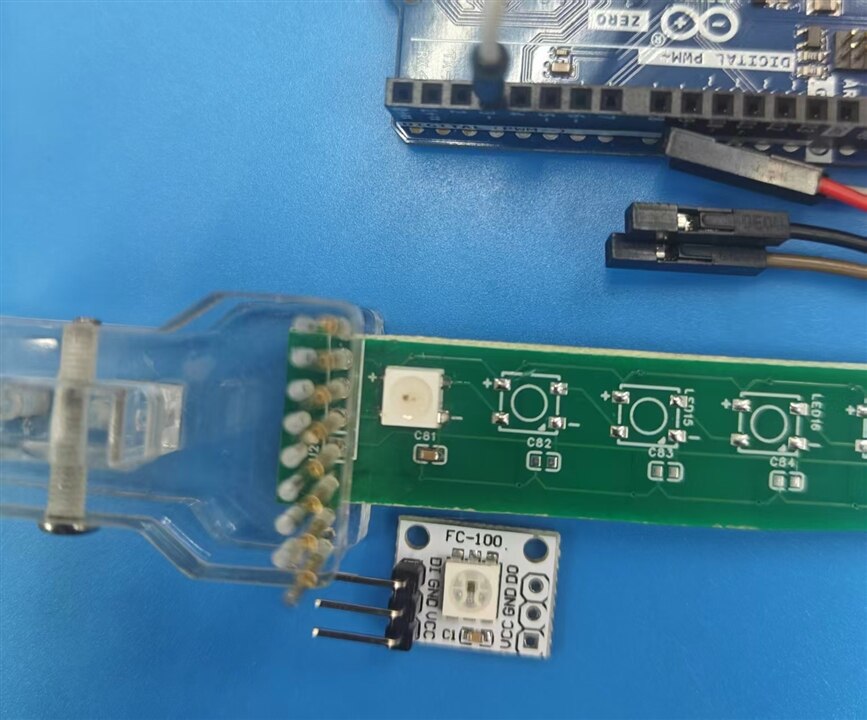
For start-up, start from 1312020030000, the 4-pins LED size of 50x50 , with only one welding on board, wiring with test clips
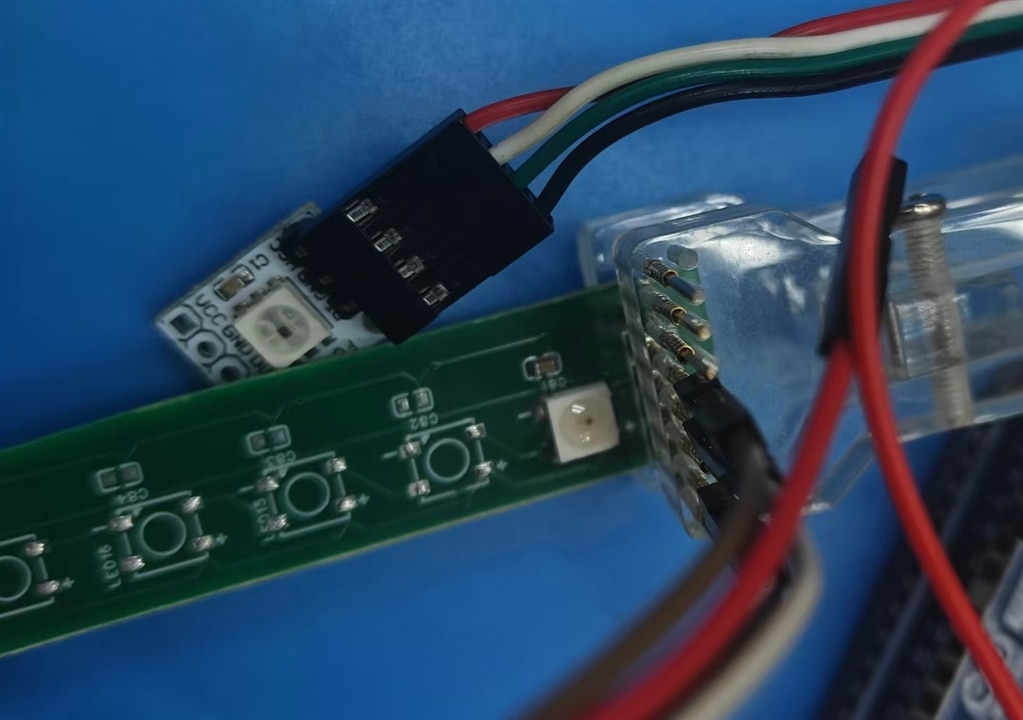

Other types of WL-ICLED shall be tested after welding on boards.
5 The control pin matters a lot
At first, the WL-ICLED is welded with this simple welding plate, good for LED removal, But some pin is not fixed in good position, the WL-ICLED light up without blinking.
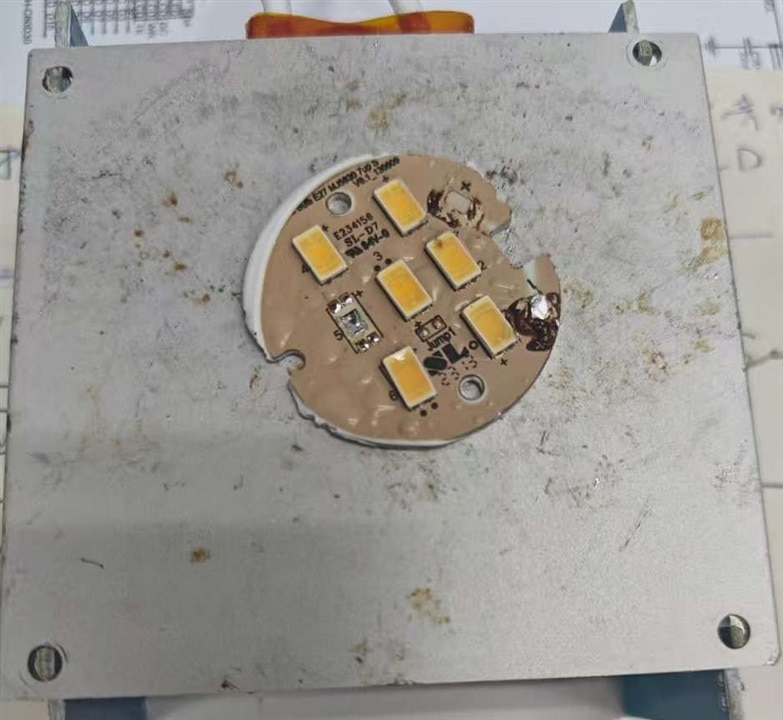

Then I hand weld again, it works fine.
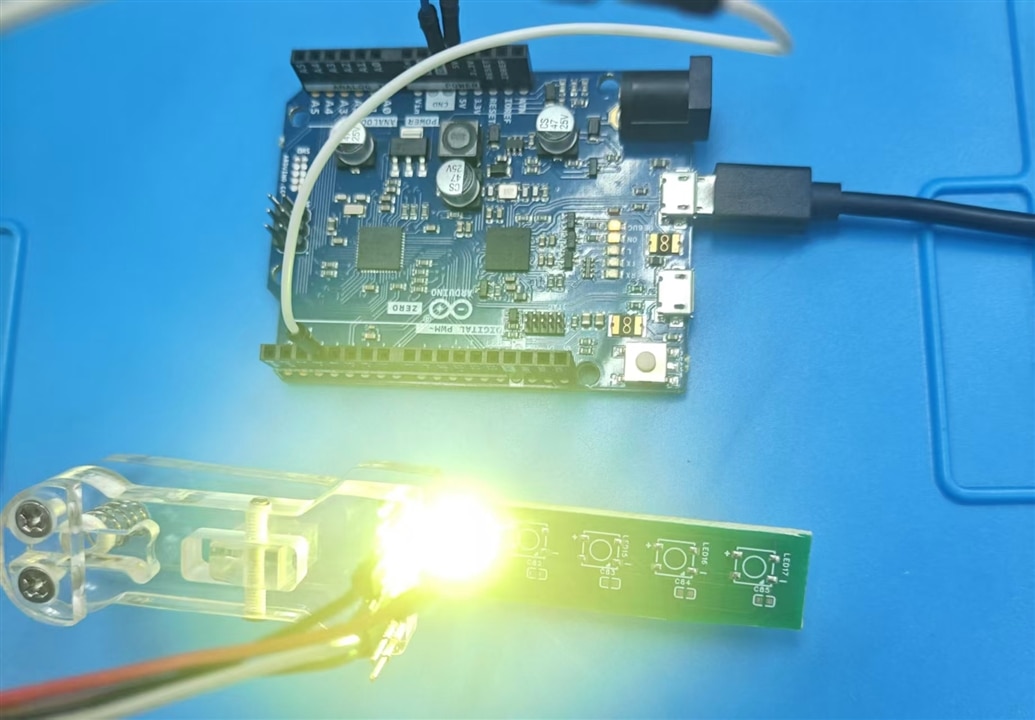

The data in pin is important, it outputs command for LED illumination control. If it is removed, the state of led is not changed again, it stale in on state of off state only.
6 Control two led strips
If two led strips to be controlled , only two pins from MCU is needed. It can be controlled easily just as this blink example.
7 Next post
Put all the LED on PCB boards is what in next post. Use different technique as comparation.
