Table of Contents
- Project Introduction
- Testing the OHD1-50B Thermal Sensor
- Testing the OHD1-50B and M-TRS5-60B Thermal Sensors
- Detecting Transition From ON to OFF on Thermal Sensors
- Activation of a Fan with a OHD1-30B Thermal Sensor
- Cutting Power to the 3D Printer when Thermal Sensor Detects Thermal Runaway
- Project Report Updated
**********************************************************************************************************************
Cutting Power to the 3D Printer when Thermal Sensor Detects Thermal Runaway
In this post I want to use a simple circuit without a programming board to demonstrate that when the thermal sensor detects the thermal runaway, then it interrupts the AC power supply to the 3D printer.
The control circuit can be made with discrete logic components or with microcontrollers. TTL, CMOS, LVTTL and LVCMOS logic circuit technologies can be used, below I indicate their working voltages.
- TTL: 5V
- CMOS: between 5V and 15V
- LVTTL: 3.3V
- LVCMOS: 3.3V, 2.5V or 1.8V
Schematic Diagram
Below you can see the electrical connections to test this project:
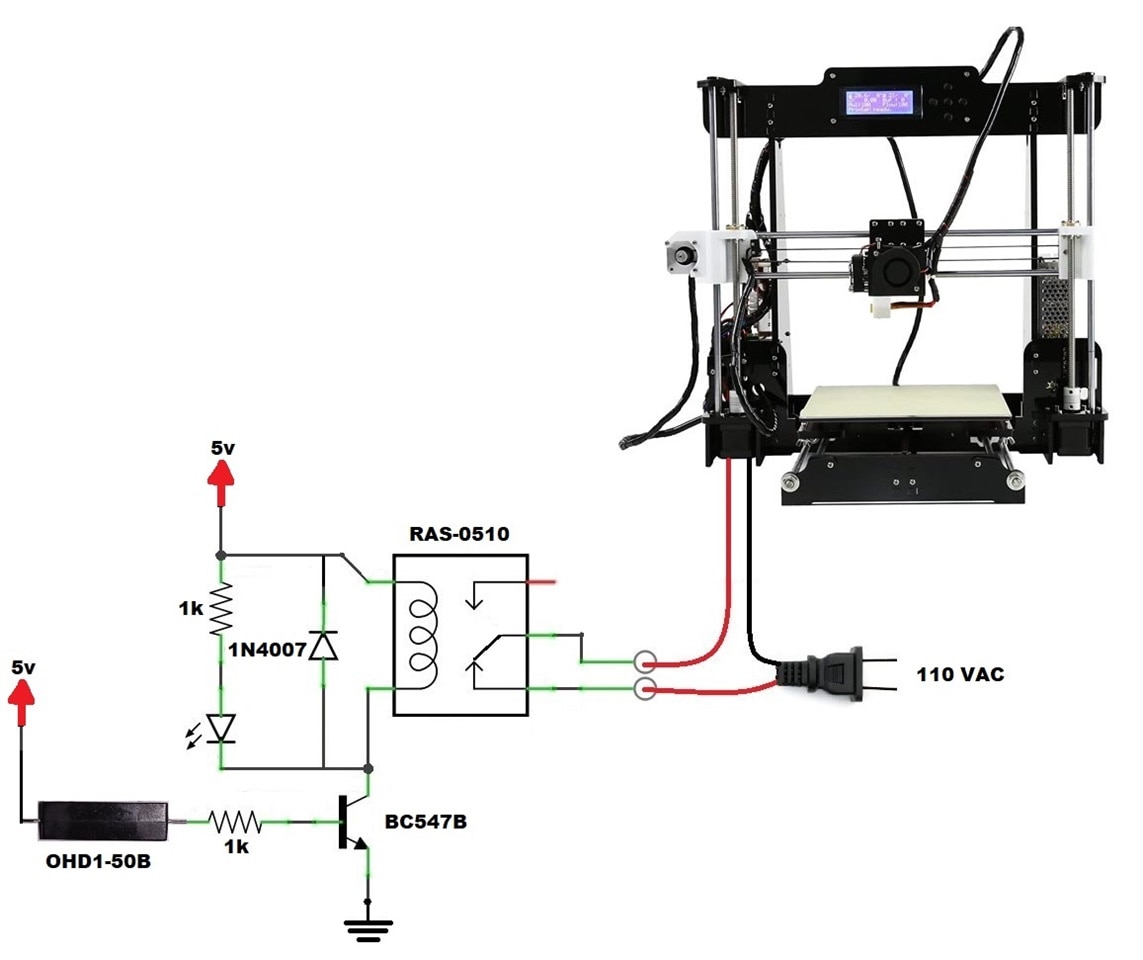
How does it work?
- The OHD1-50B thermal sensor is normally closed at low temperature;
- When the output of the control circuit is high (5V), the threshold voltage of the transistor base (0.6V) is exceeded and therefore a current begins to flow between base and ground. This current brings the transistor to the conduction state (between collector and emitter) closing the circuit of the relay coil and therefore activating it;
- Under these conditions, the 3D printer turns on and can works;
- The OHD1-50B thermal sensor is open at 50 degrees Celsius;
- When the output of the control circuit is low (0V) the base of the transistor will also be low and therefore it will not allow current to pass between the emitter and the collector to activate the relay coil;
- Under these conditions, the 3D printer turns off; and
- When we deactivate the relay through the transistor, interrupting the current passing through the coil, the magnetic field present in it induces in it, for a brief moment, a very high voltage of opposite polarity at its terminals. This voltage spike known as "extra opening voltage" can damage the control transistor. To solve this problem, the simplest solution is to connect a reverse biased rectifier diode (1N4007) in parallel with the coil in such a way that it absorbs these voltage peaks of opposite polarity.
Experiment:
- When the thermal sensor detects the 50 degree Celsius thermal runaway, the 3D Printer AC power supply turns OFF.
Assembling the Test Module
In the figure below you can see the test module once it has been assembled.
And now it's ready for thermal runaway testing.
I have used a 5v portable charger to power the DC circuit, since this device automatically turns off when it stops powering the circuit for more than 15 seconds. This way we guarantee a permanent power outage on our 3D printer until we arrive and find out that our 3D printer had a thermal runaway.

Test
In the video below I show you the tests carried out with the OHD1-50B thermal sensor with the 3D printer working in Preheat PLA mode.
Conclusion:
- Using the OHD1-50B thermal sensor as a thermal switch to detects a thermal runaway on power module of the heated bed is a good idea. This experiment shows me that the 3D printer turs off on time when it's power module reaches 51 degree Celsius.
- Please, I recommend you take precautions when working with alternating current, if you don't have experience, ask for the help of someone who does.

Top Comments