Welcome to the Panasonic Industry page on element14. Here you can find things such as our latest news, training videos, and product details. Additionally, you can engage with us in our forums.
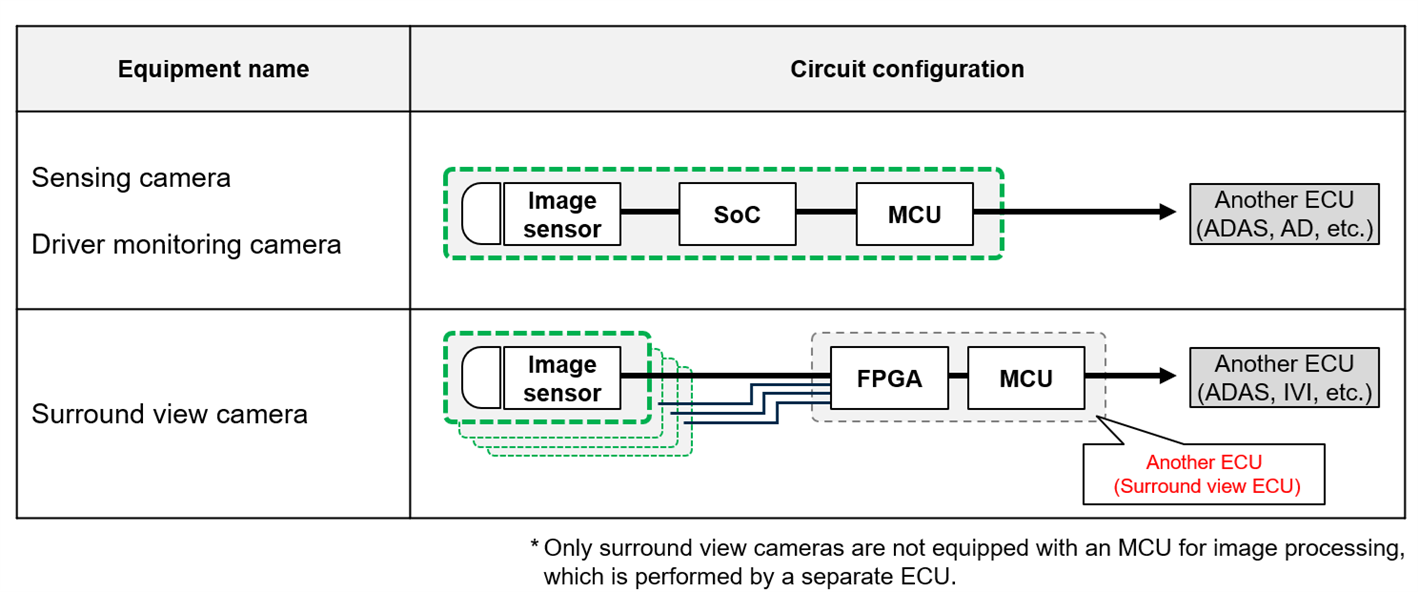
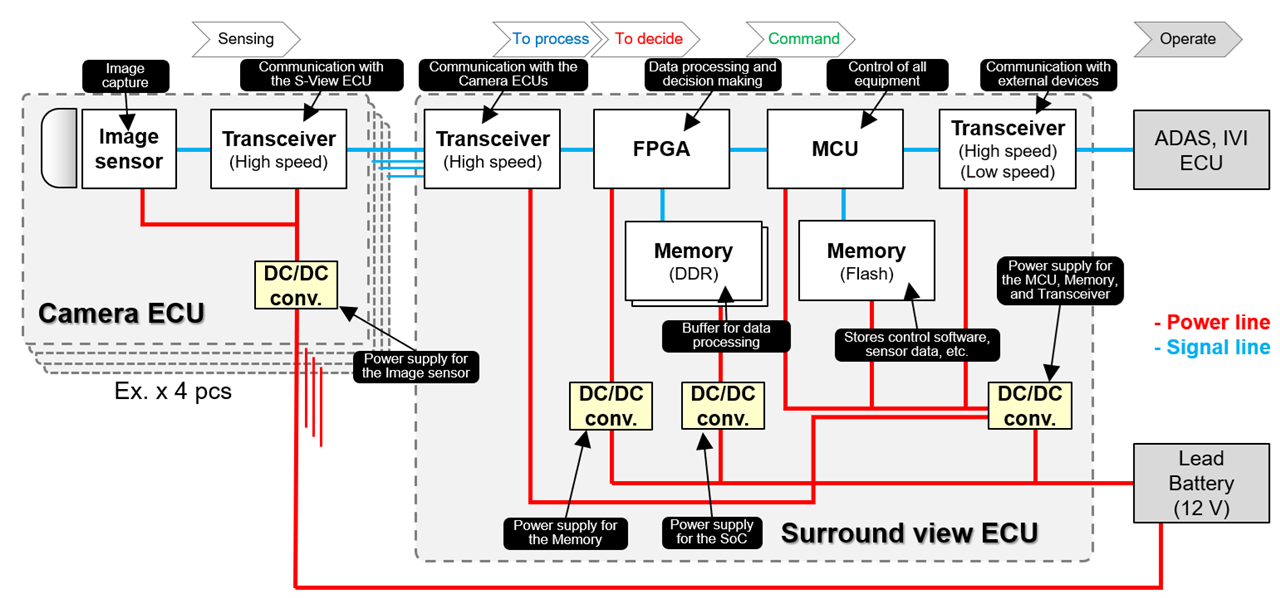
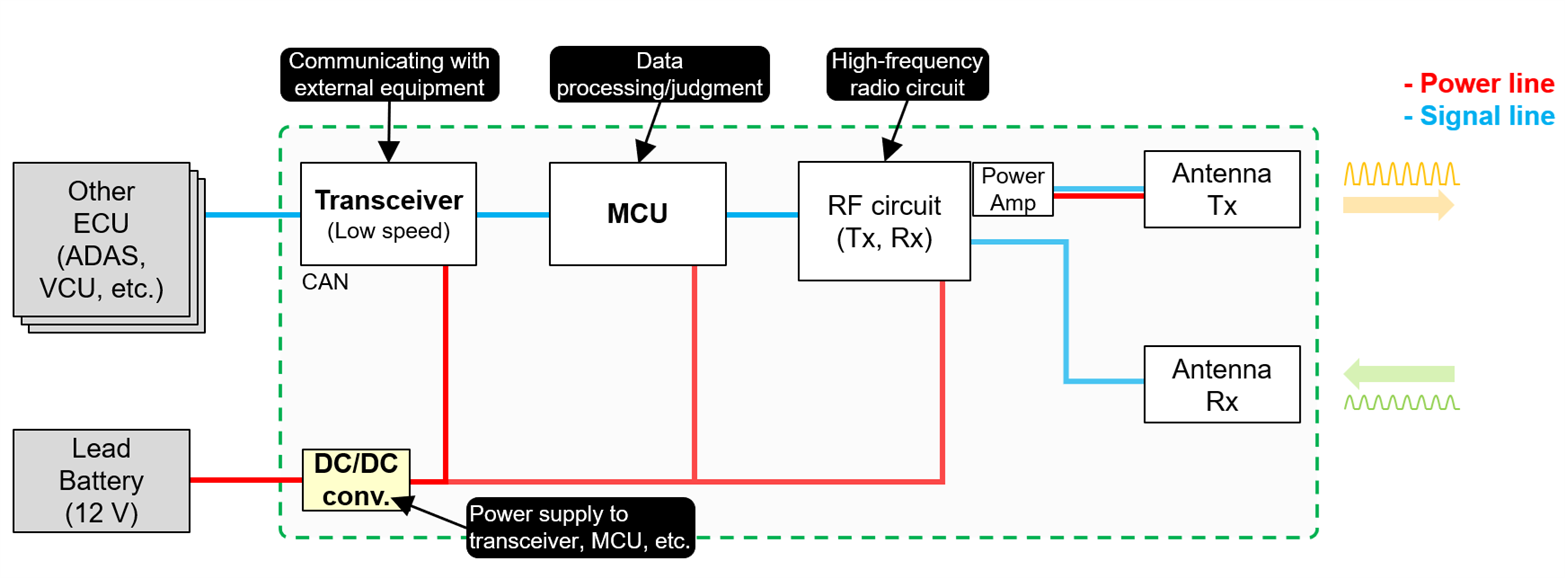
A camera ECU and surround view ECU are used to make up a surround view camera. Unlike other types of camera modules, multiple camera units are mounted on a vehicle to make up the surround view camera. Therefore, transceiver circuits must communicate larger amounts of data. An FPGA is used to integrate the acquired image data into one, where image processing is performed at high speed.
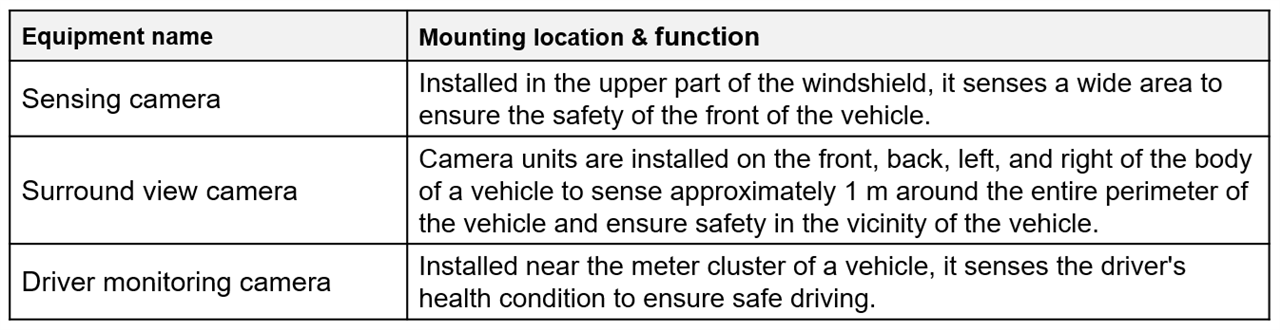
Other configurations are the same as those of sensing cameras and driver monitoring cameras.
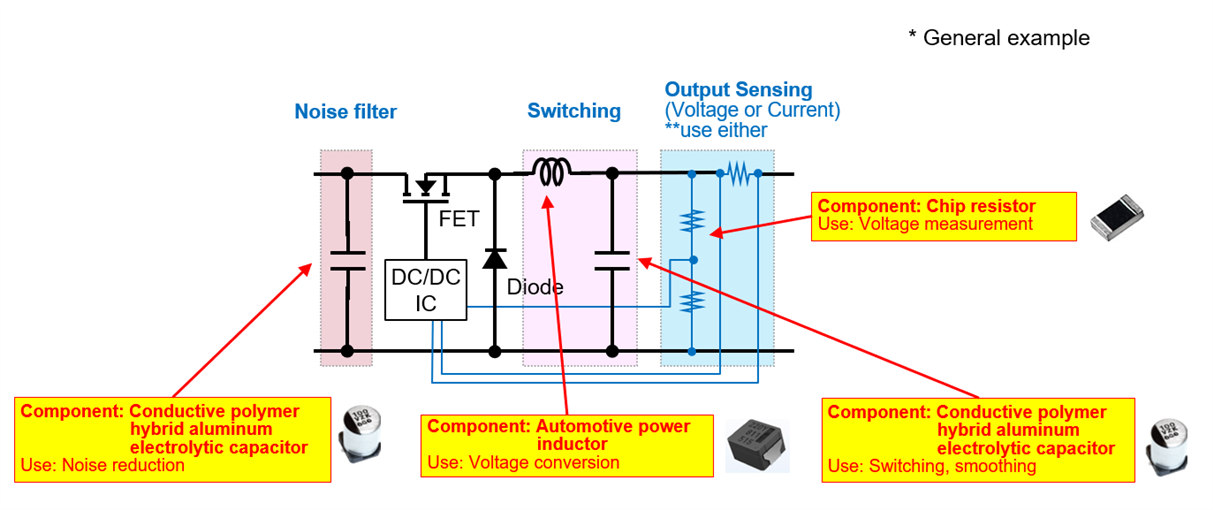
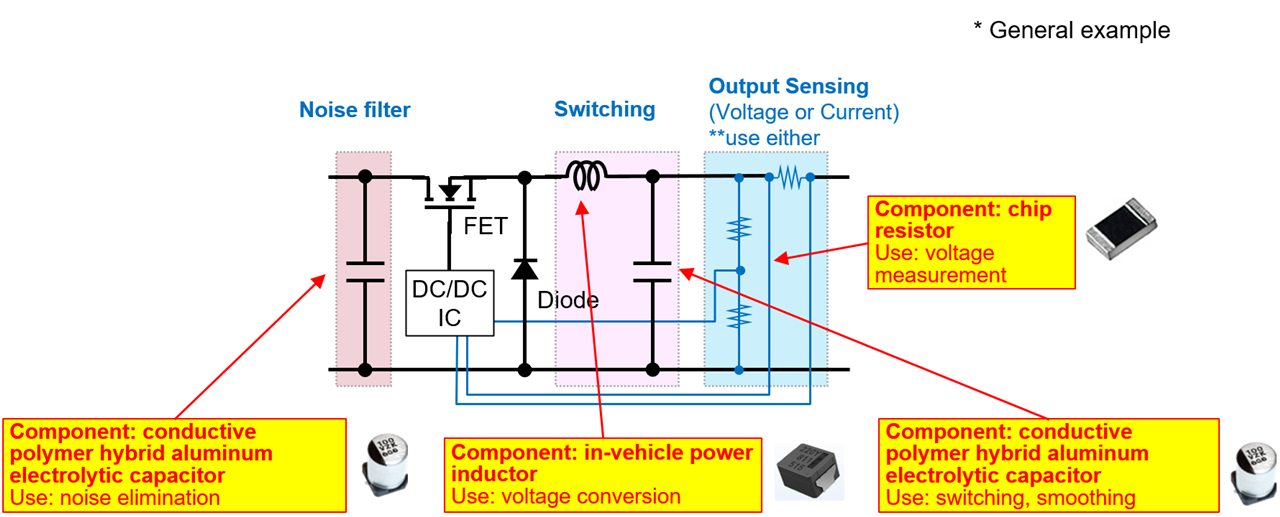
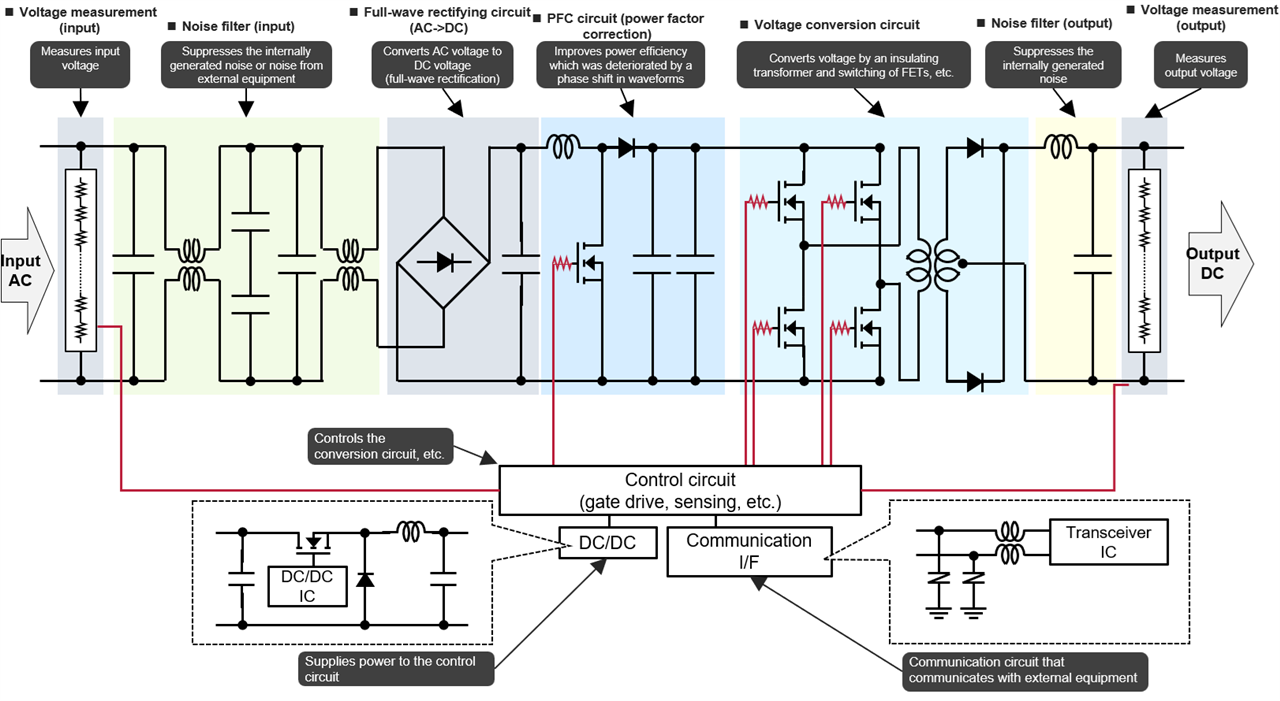
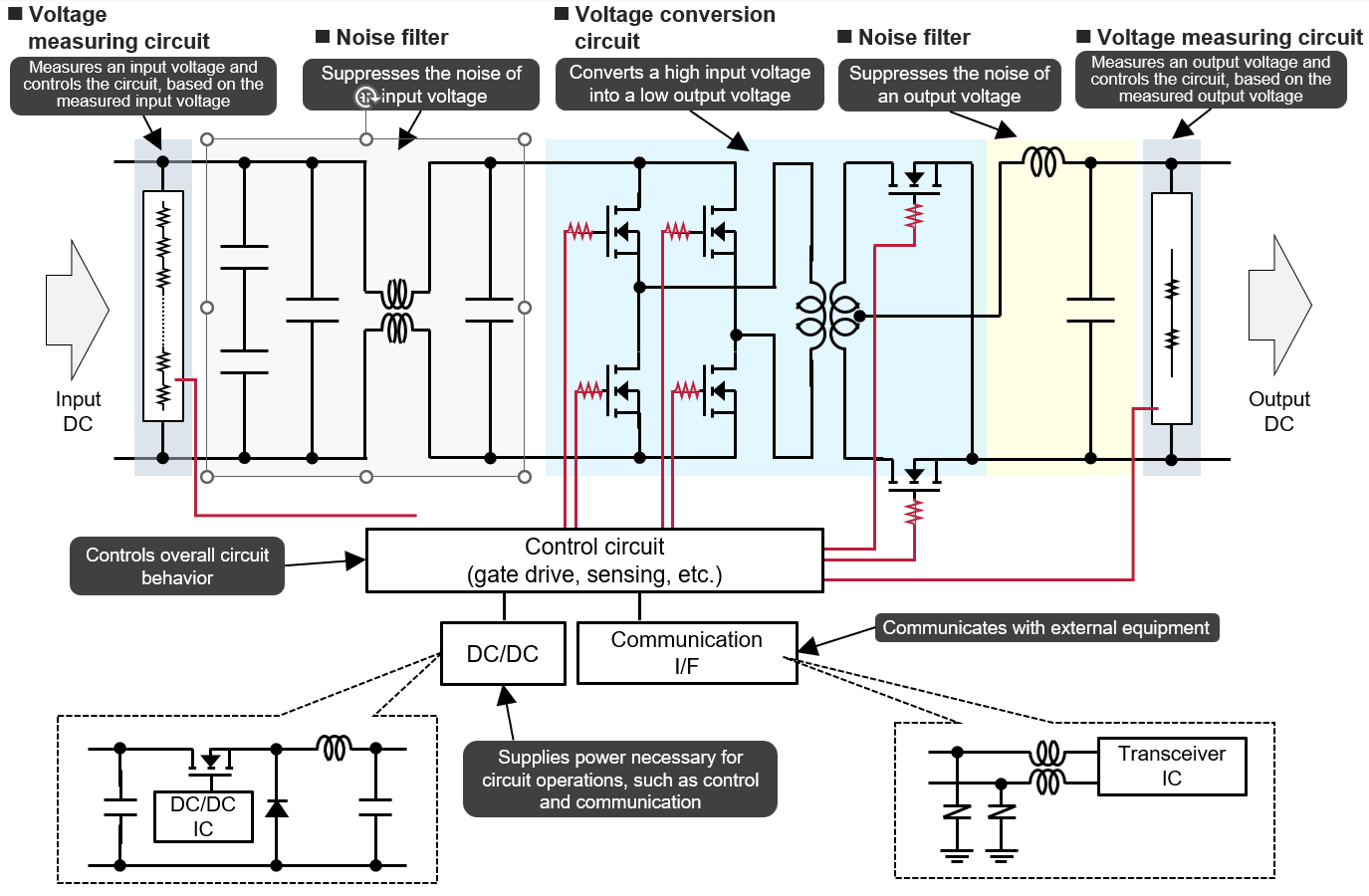
Components used in a DC/DC converter

LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a sensing technology that measures the distance to objects by emitting laser pulses and capturing the reflected light. The combination of emission direction and time‑of‑flight enables the generation of a high‑resolution 3D point cloud, which is widely used in ADAS and autonomous driving systems. As vehicle automation advances, the adoption of LiDAR is expected to grow steadily.
| Optical element | Optical axis varying method | Type | Scanning |
|---|---|---|---|
| LD, PD | Mechanical method | Rotation by a motor | A number of LDs and PDs are rotated by a motor to scan the whole area. |
| Polygon mirror | Respective optical axes of a single LD and a single PD are varied by a polygon mirror in scanning. | ||
| Non-mechanical method (solid-state) | MEMS mirror | Respective optical axes of a single LD and a single PD are varied by a MEMS mirror in scanning. | |
| Phased array | Respective optical axes of a single LD and a single PD are varied by a waveguide in scanning. | ||
| Flash | Light from a light source, such as an LED, is emitted over a wide area, and reflected light is collectively scanned by an array of PDs. |
By repeatedly scanning in multiple directions, LiDAR creates a point cloud.
This data is used to:
As autonomous driving levels increase, LiDAR systems must meet three key requirements:
| Requirement | Reason |
|---|---|
| Higher power | Higher‑resolution sensing increases CPU load and power demands. |
| Faster communication | High‑frequency and high‑speed data transfer is essential to process large point clouds. |
| Smaller size & lighter weight | Vehicles incorporate more sensors, requiring miniaturized components. |
A LiDAR unit typically consists of:
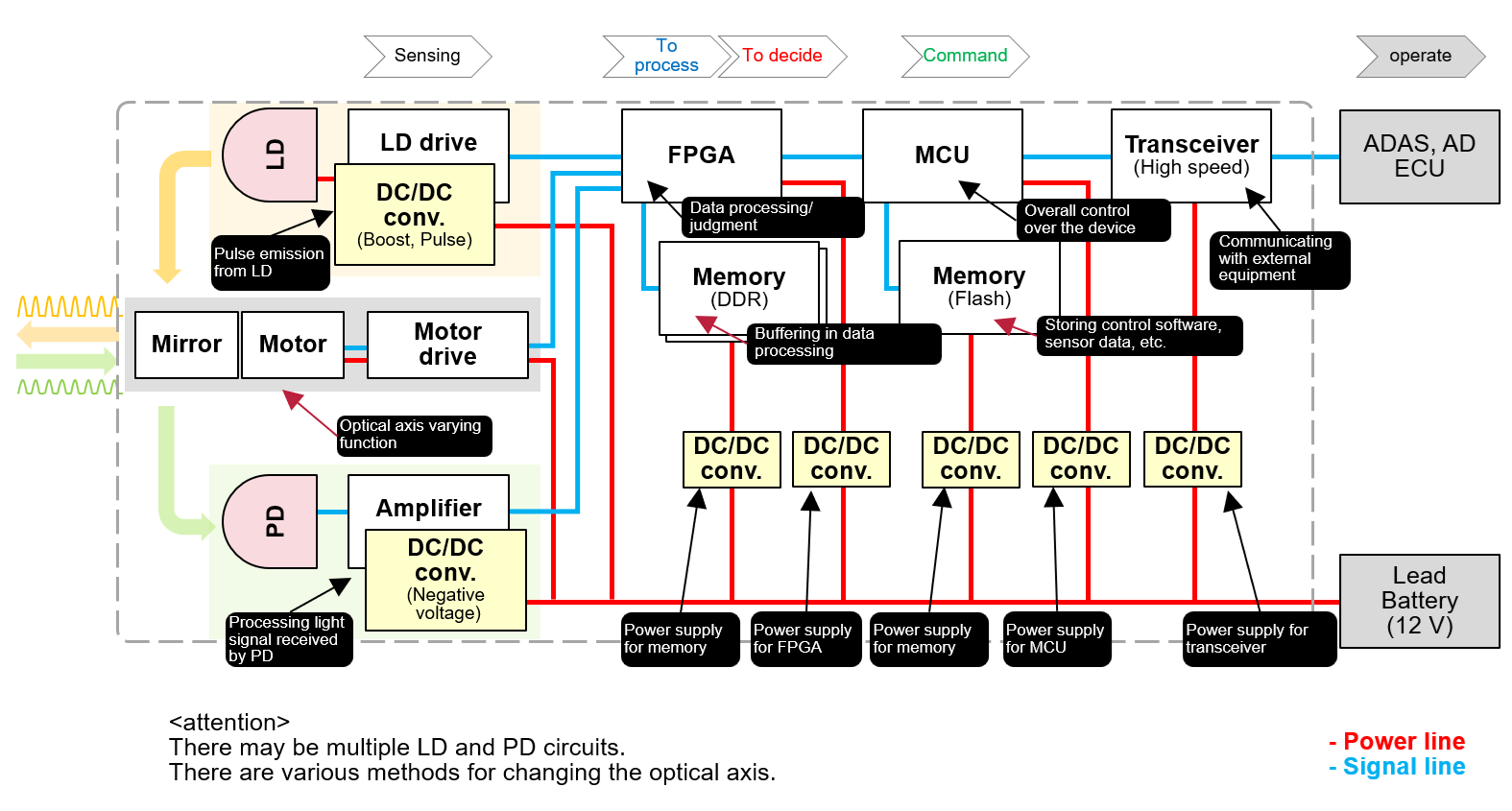
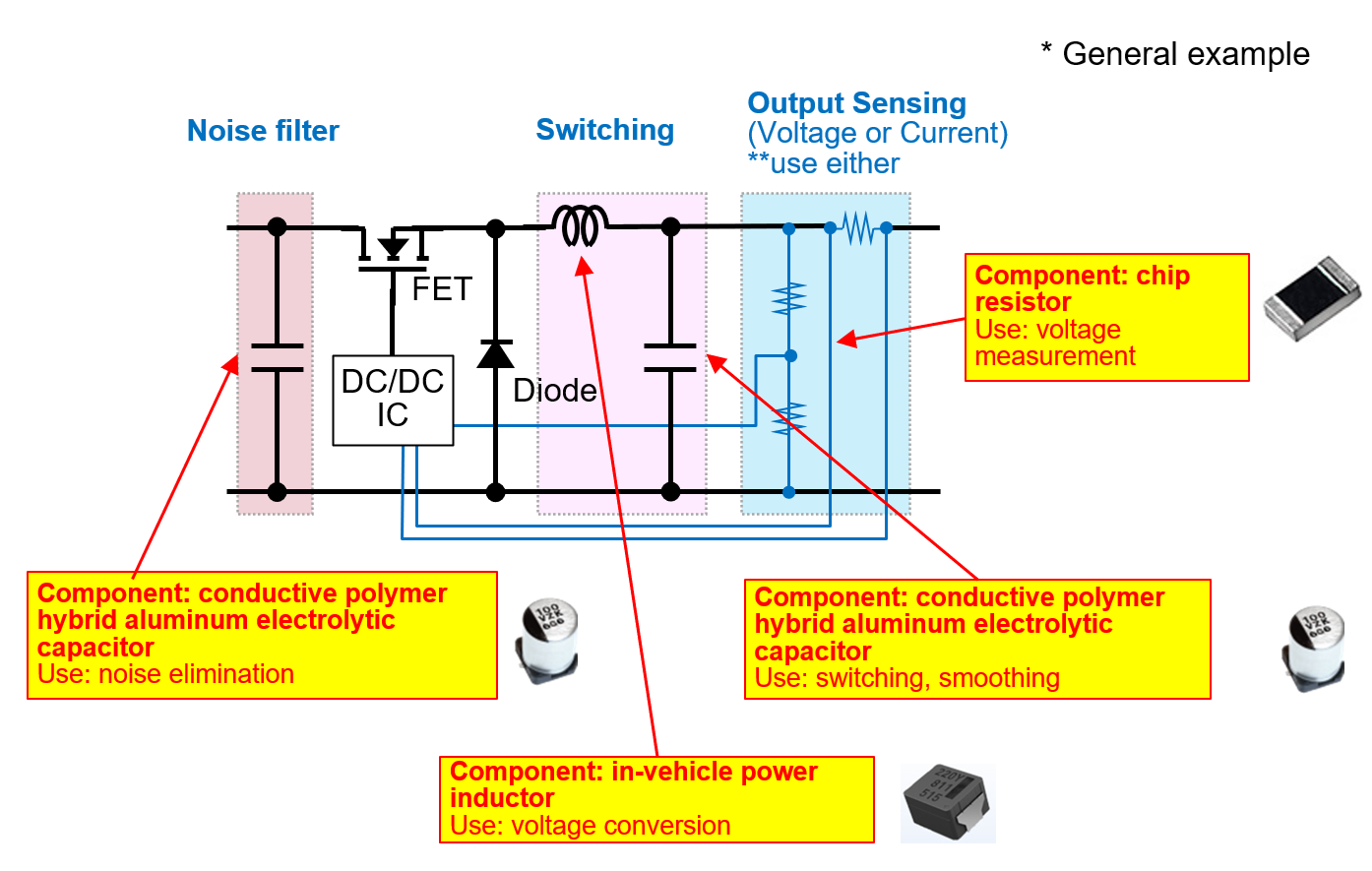
High‑performance LiDAR requires stable, low‑noise power.
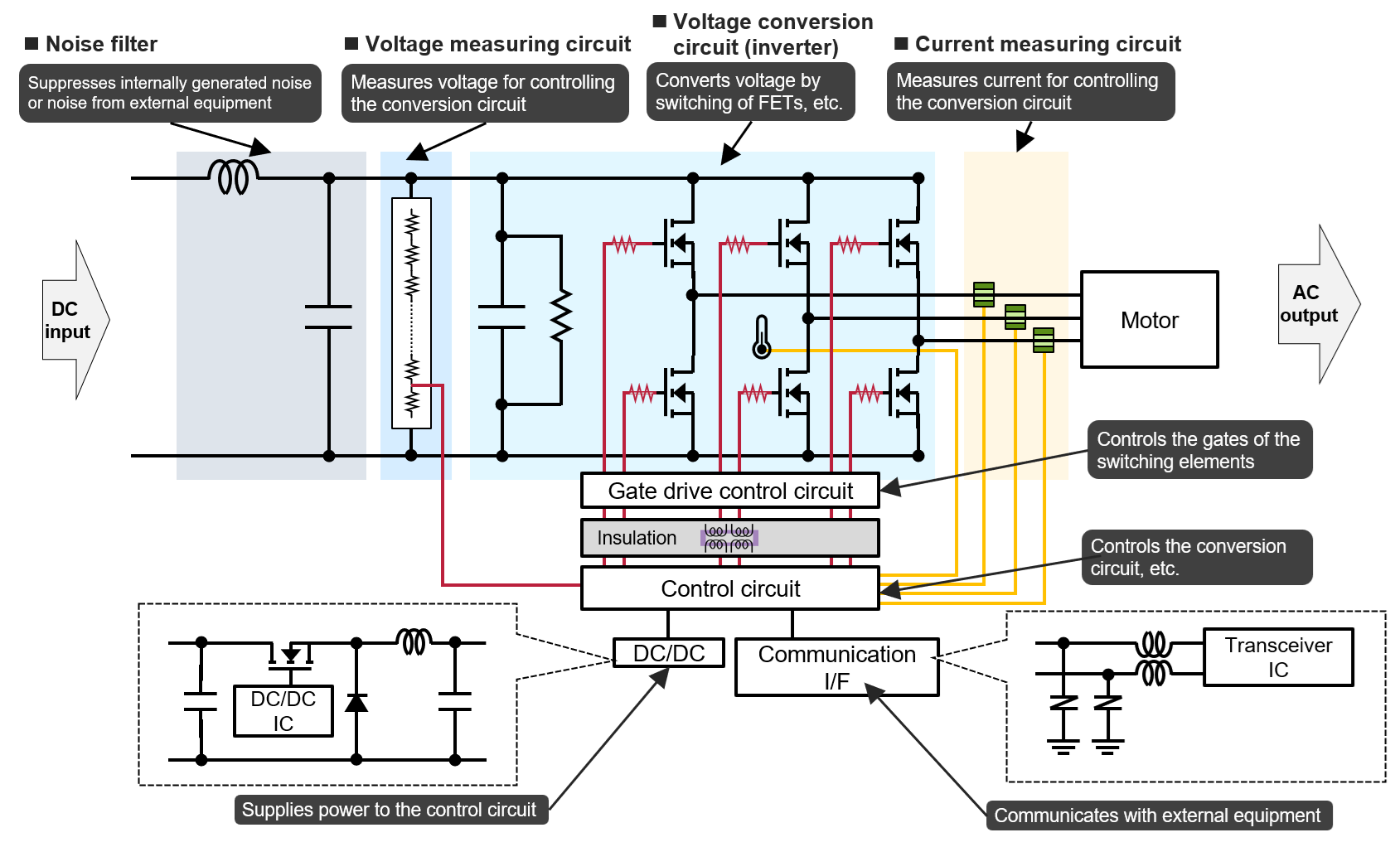
| Function | Component | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Noise filtering & smoothing | Conductive polymer hybrid aluminum electrolytic capacitor | Low ESR, high ripple tolerance, excellent high‑frequency behavior |
| Voltage conversion | Automotive power inductor | High current capability, low loss, low ACR |
| Voltage measurement | High‑precision chip resistor | Low resistance tolerance, low TCR for accurate control |
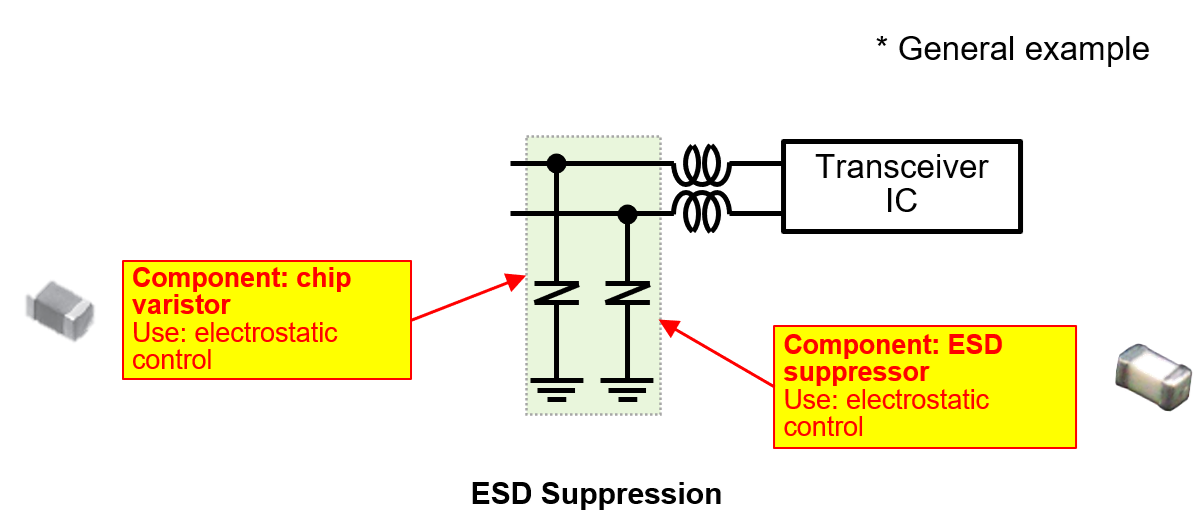
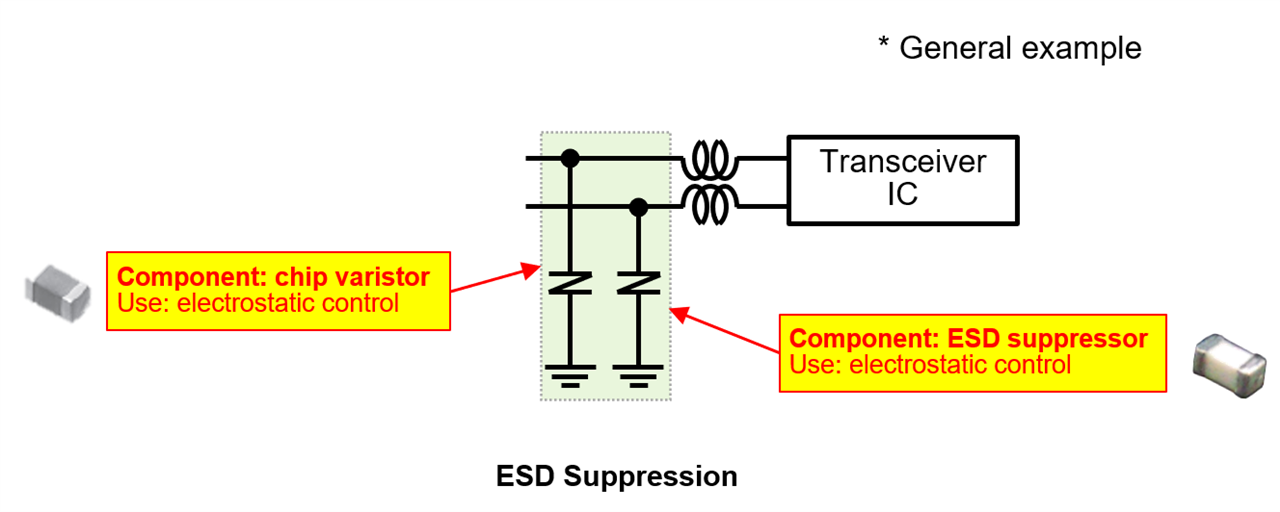
Because communication lines are exposed to ESD, protection devices are critical.
Key points:
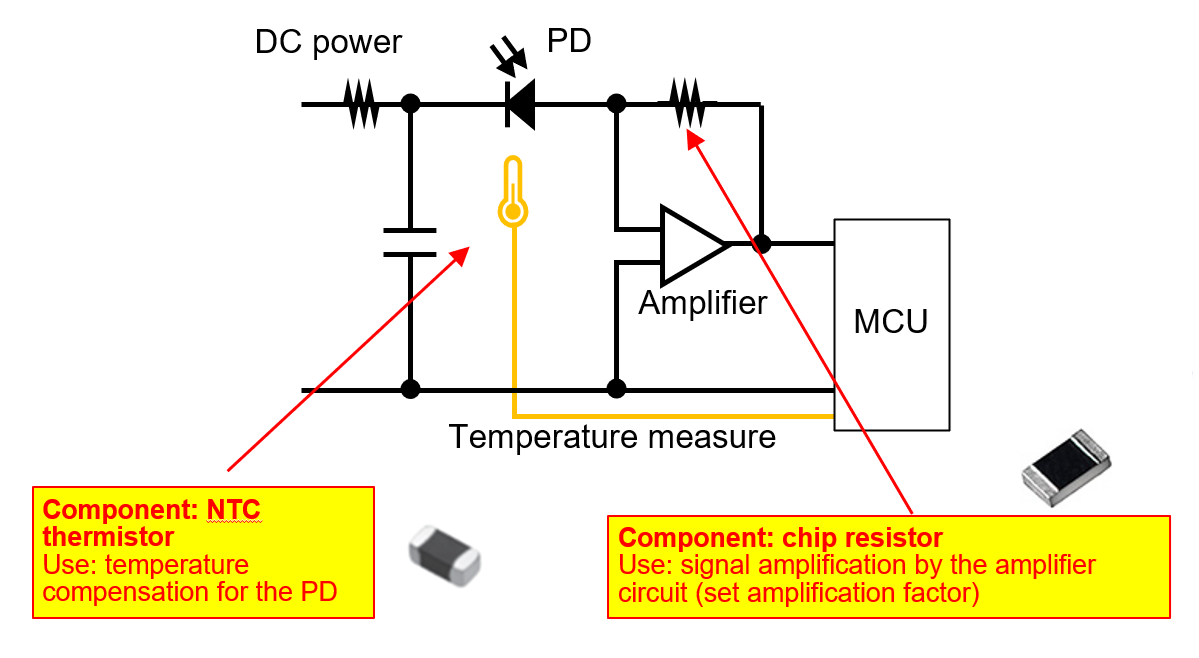
Reflected laser light is weak and must be amplified with high precision.
Why they matter:
A GaN FET is typically used to deliver high‑speed, high‑power pulses.
Key advantage:
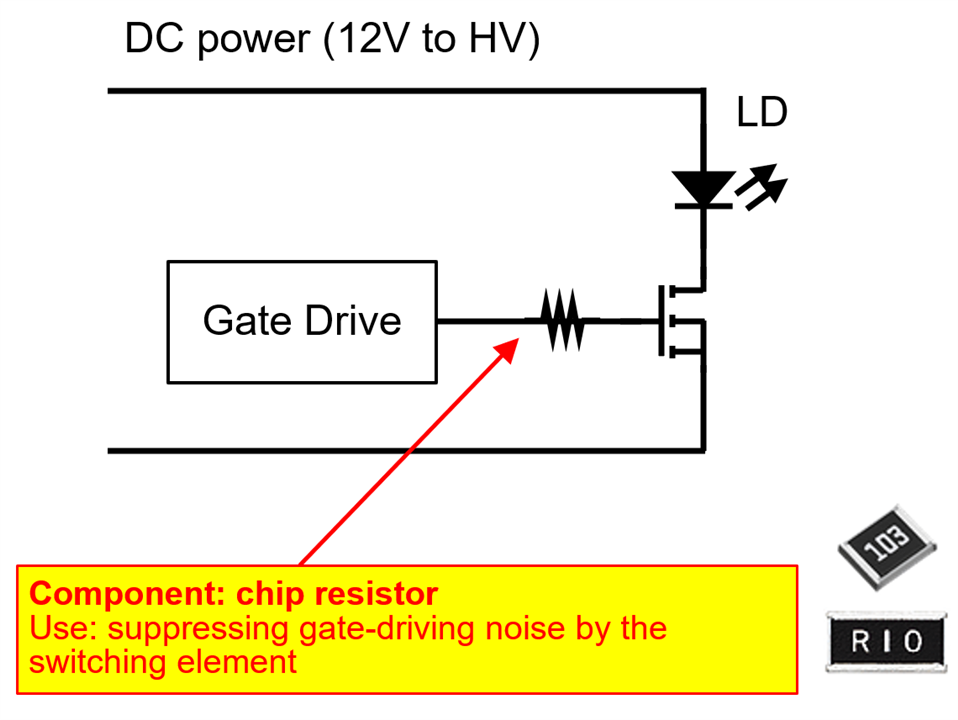
As autonomous vehicles adopt more LiDAR units, the demand for electronic components offering:
will continue to grow. Panasonic Industry offers a broad portfolio—including hybrid capacitors, automotive inductors, high‑precision resistors, varistors, ESD suppressors, and thermistors—that aligns well with these requirements.
| Component | Feature | Large current | Low loss | High frequency | Small size | High precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductive polymer hybrid aluminum electrolytic capacitor | Low ESR High reliability |
|||||
| Automotive power inductor | Large current, low loss High reliability |
|||||
| High precision, high resistance to heat | ||||||
| Chip varistor | Small and light | |||||
| ESD suppressor | Low capacitance Ultrafast data I/F |
|||||
| NTC thermistor (chip type) | Small, high resistance to heat |
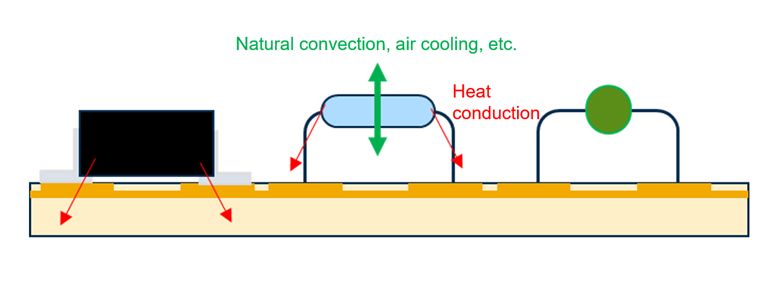
Heat effect image of resistor with leads

| Method | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
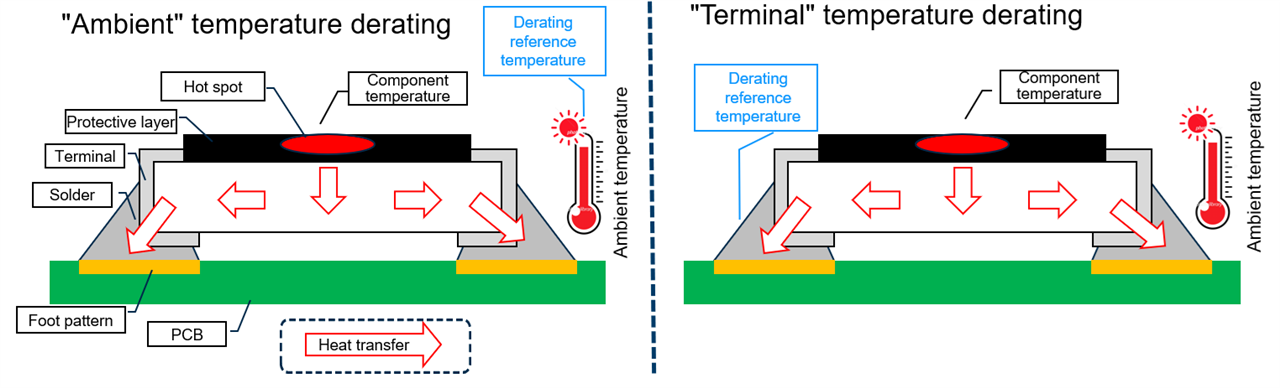
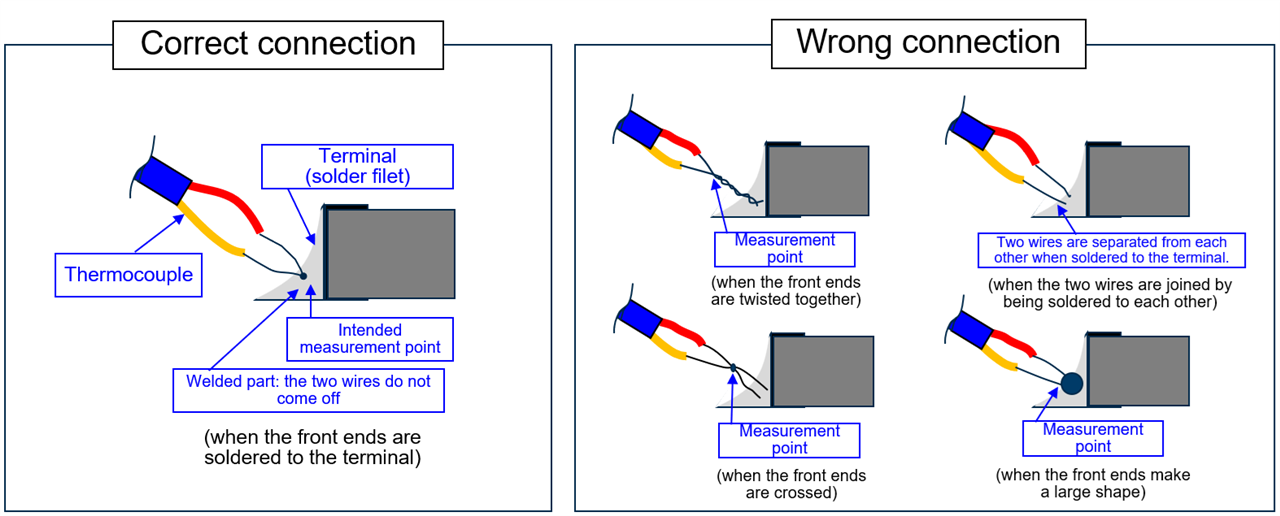
| Thermocouple | High accuracy, direct measurement | Requires physical contact; heat conduction through wires may distort readings |
| Infrared thermography | Contactless, easy to use, wide temperature range | Cannot measure through glass; requires high surface emissivity (may need black coating) |
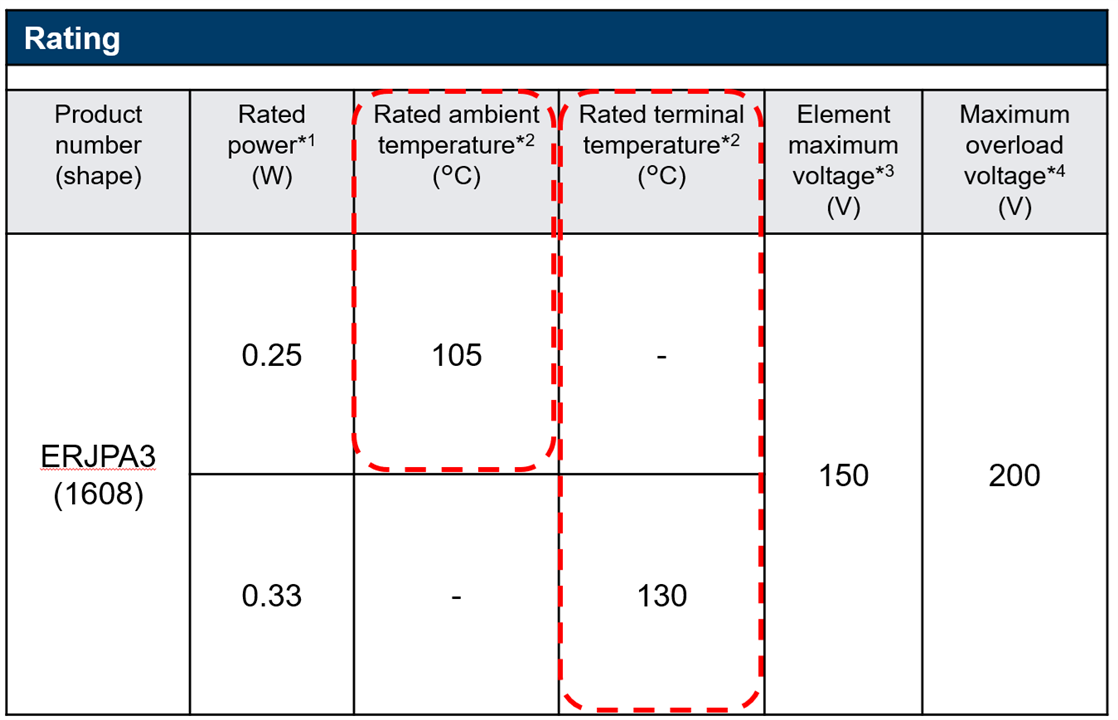
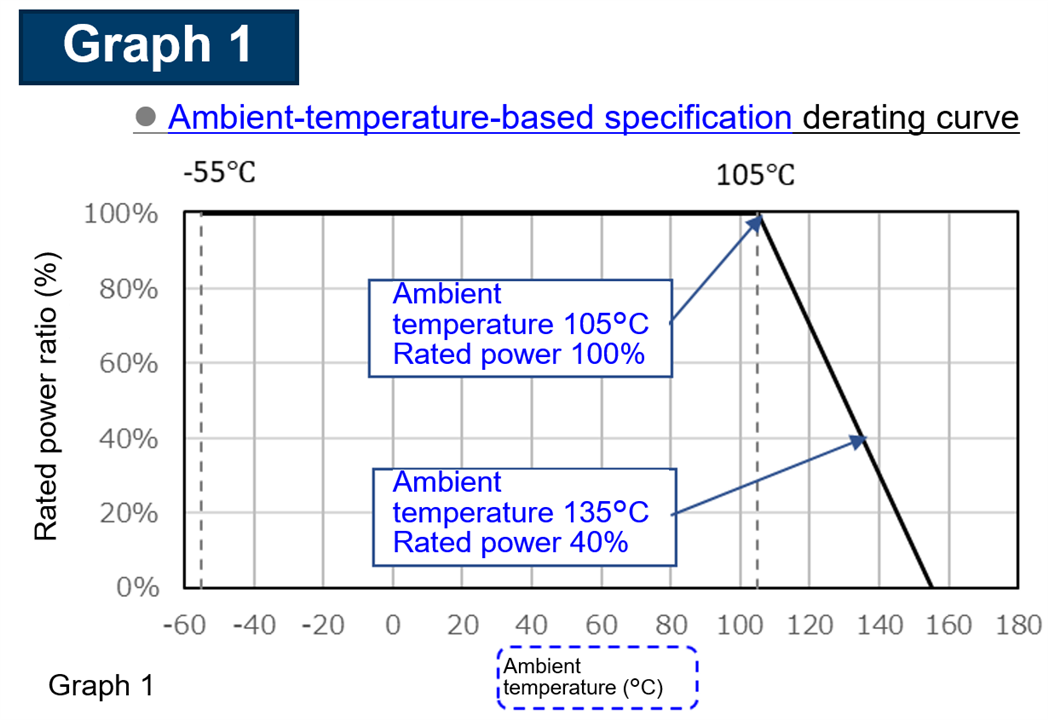
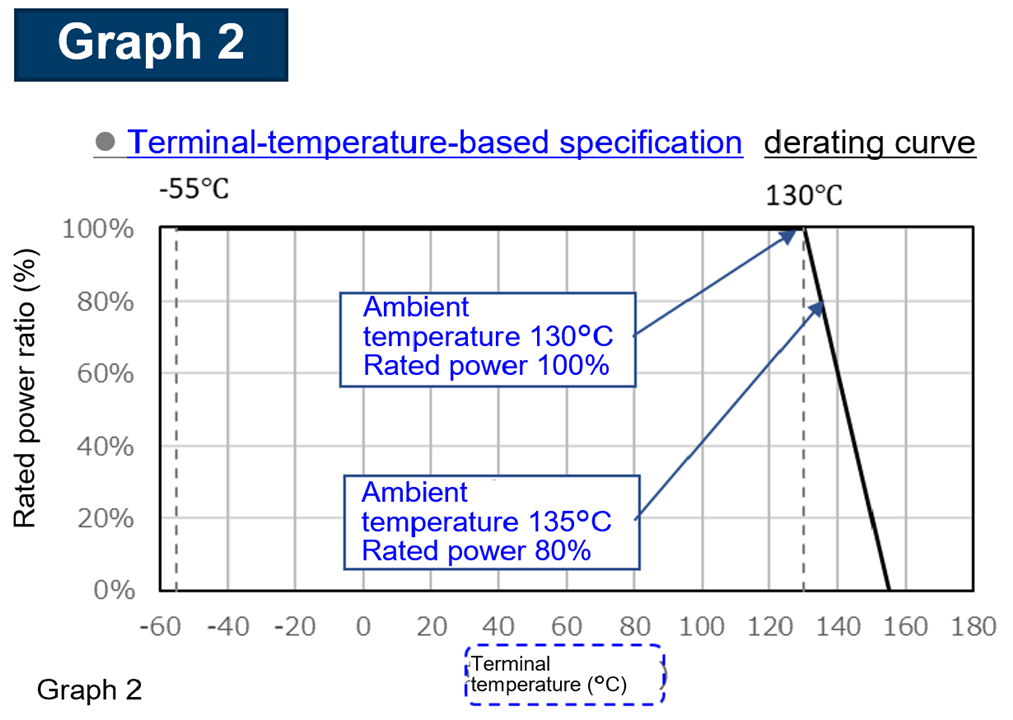
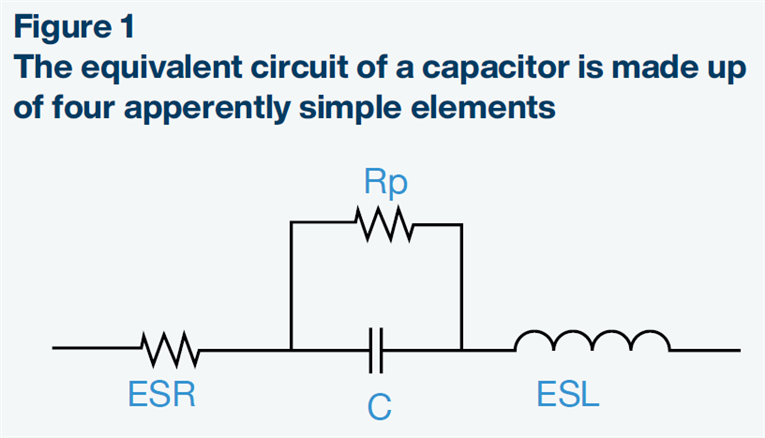
ESR represents the resistive component within a capacitor’s equivalent circuit. It influences:
Panasonic offers one of the industry’s most comprehensive portfolios of low ESR electrolytic capacitors, available in THT (Through-Hole) and SMD (Surface-Mount) configurations.
| Component | Features | Large Current | Low Loss | Compact |
Small Size |
High Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors | Low ESR, High Reliability | |||||
| Automotive Power Inductors | High Current, Low Loss | |||||
| High-Precision & High-Power Chip Resistors | High Accuracy, Heat Resistance | |||||
| Chip Varistors | Compact, Lightweight |
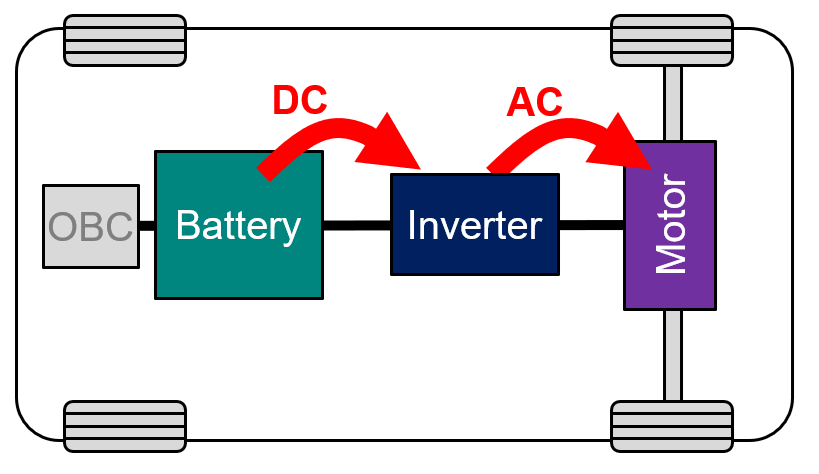
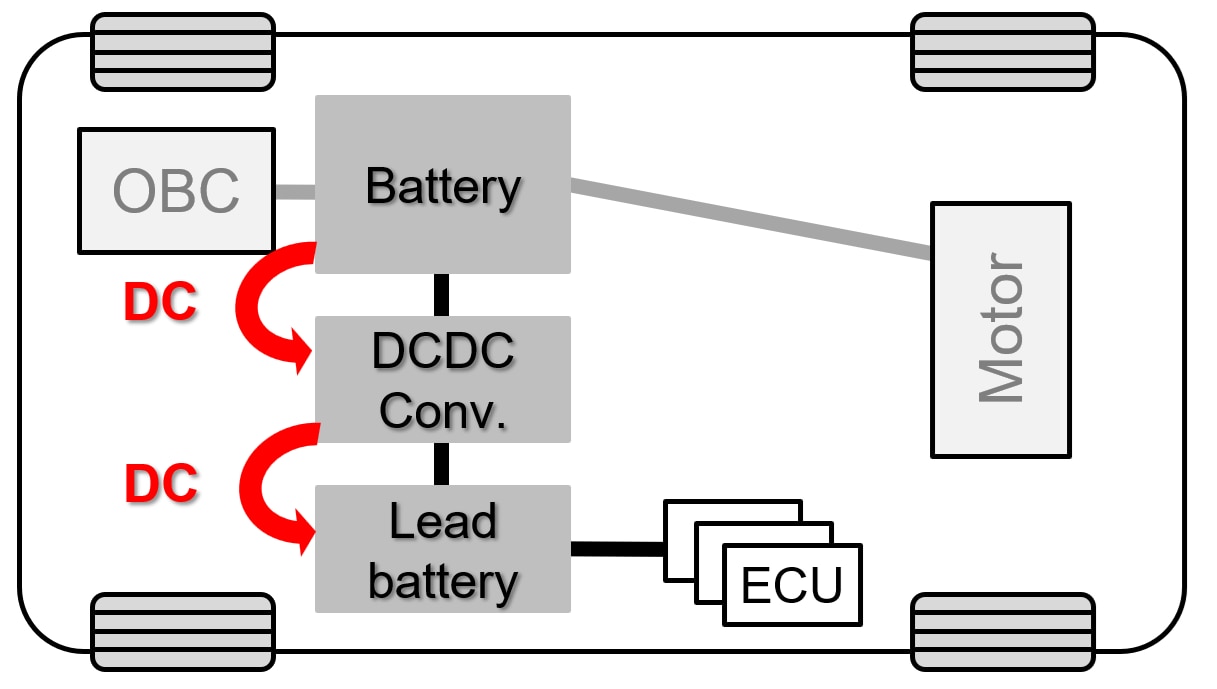
・Normal charging
In normal charging, the battery is charged to full. The battery of an EV is charged with AC voltage from a private residents' charging equipment or a public charging station. Generally, charging the battery fully takes about eight hours. In the case of normal charging, the OBC incorporated in the vehicle converts AC voltage into DC voltage applicable to the vehicle battery.
・Quick charging
Quick charging is charging to refill the battery in a short time. In quick charging, the charging station supplies DC voltage corresponding to the battery voltage, charging up the vehicle battery in a short time by quickly feeding the battery with large power. Quick charging, in general, takes about 30 minutes to 1 hour to finish, depending on the battery capacity. You will find those chargers for EVs in a lot of expressway rest areas, commercial establishments, etc.
| Charging Type | Power Source | Location | OBC Usage | Charging Time | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Charging | AC (200V/400V) | Home, Office | Converts AC to DC | ~8 hours | Full battery charge |
| Fast Charging | DC (direct output) | Highways, Commercial Facilities | Not used | ~30–60 minutes | Quick top-up |
| Component | Features | High Voltage | High Current | Low Loss | Compact | Heat Resistant | High Precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors | Low ESR, High Reliability | ||||||
| Automotive Power Inductors | High Current, Low Loss | ||||||
| High-Precision & High-Power Chip Resistors | High Accuracy, Heat Resistance | ||||||
| Chip Varistors | Compact, Lightweight | ||||||
| Automotive Film Capacitors | High Reliability |
| Component | Feature | High Voltage | Large Current | Low Loss | Miniaturization | High Heat Resistance | High Precision |
| Film Capacitors | High reliability |  |
 |
||||
| Conductive Polymer Hybrid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor | Low ESR High reliability |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Power Inductor for Automotive Application | Large current, low loss High reliability |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Chip Resistor | High precision, high resistance to heat |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Chip Varistor | Small and light |  |
|||||
| NTC thermistor | Small, high resistance to heat |  |
 |
 |
| Component | Feature | High voltage | Large current | Low loss | Miniaturization | High heat resistance | High precision |
| Film Capacitors (Automotive, Industrial and Infrastructure Use) | High reliability |  |
 |
||||
| Conductive Polymer Hybrid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors | Low ESR High reliability |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Power Inductors for Automotive application | Large current, low loss High reliability |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| High Precision Chip Resistors Small & High Power Chip Resistors |
High precision, high resistance to heat |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Chip Varistor | Small and light |  |
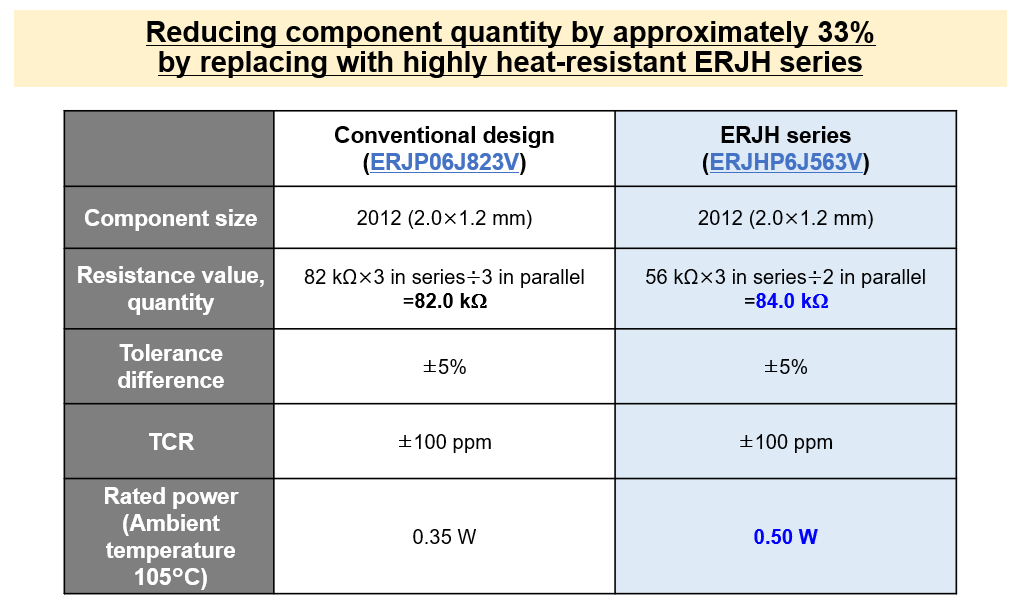
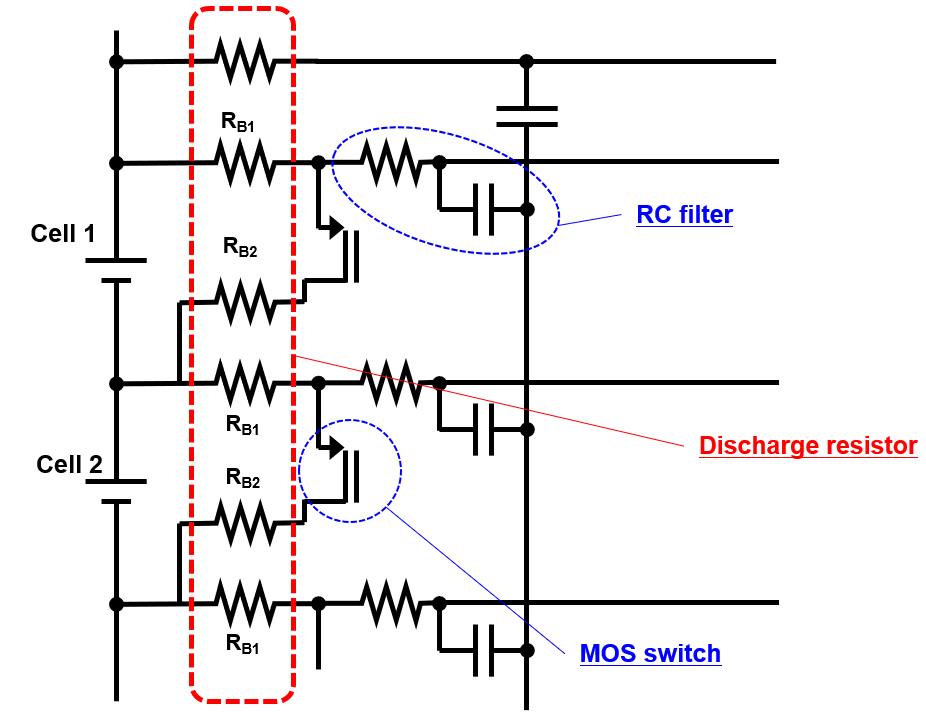
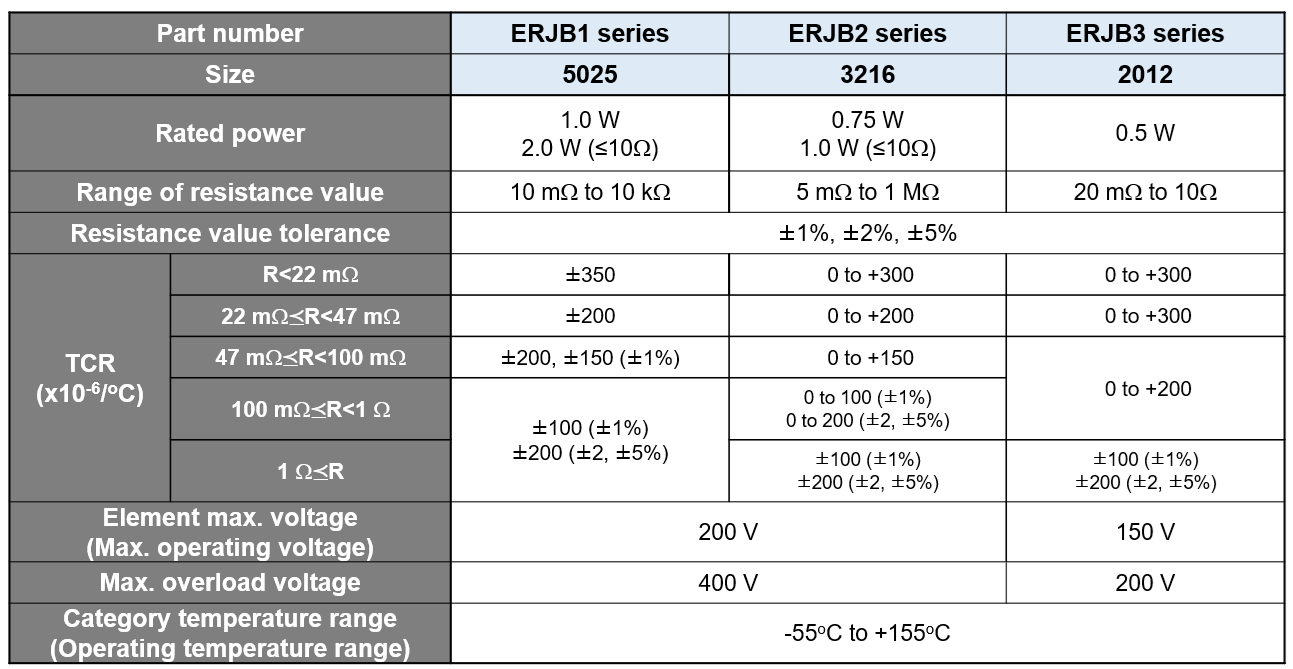
Explore our lineup on PANASONIC Chip SMD Resistors | Farnell® UK