Differences Between Spartan 6 and 7 Series FPGAs
Spartan 6 series of FPGAs were launched in 2009 consisting of LX and LXT series. Now due to various reasons, Spartan 6 FPGAs are getting outdated and designers are moving towards 7 series and higher-end FPGAs. This is a short summary of the differences between Spartan 6 and 7 series FPGAs. For further details about migrating the design check [1].
Now let us see the reasons why one should migrate towards 7 series of FPGAs.
- Newer technology node, Spartan 6 FPGAs use 45nm technology which is getting older, and difficult to meet supply chain requirements. Whereas Spartan 7 and other 7 series of FPGAs are manufactured using 28nm technology and are 30% faster compared to Spartan 6 FPGAs.
- Power Consumption, compared to the Spartan 6 series of FPGAs which operate at 1.2V (1.0V Low Power Mode) core voltage, Spartan 7 FPGAs operating at 1.0V (0.95V Low Power Mode) core voltage consumes 50% less power.
- Better development tool, Spartan 6 FPGAs are only supported by Xilinx ISE tool which has limited options and is which achieved. 7 series FPGAs are supported by Xilinx Vivado tool along with Vitis for software development, Vivado Webpack edition is a free version which supports most of 7 series FPGAs. Vivado has the best GUI and offers features like block design, it has got many IP cores, a very good simulator, and helps in reducing the design development cycle. Migration of RTL from ISE to Vivado is direct, but coming to constraints ISE used UCF while Vivado uses XDC constraints, check [2] for details.
- Wide range of selection with more logic resources, 7 series offer a wide range of FPGAs. Spartan 7 is a low-end cost-optimized FPGA up to Virtex 7 at the high end. Artix 7 and Kintex 7 fall in low to mid-range along with transceivers. Whereas Zynq 7000 is an All-Programmable SOC with ARM Cortex A9 hard processor. 7 series also offer a wide range of evaluation kits which are very helpful during the initial development stages. Refer to [3].
Now let us have a look at the architectural differences between Spartan 6 and 7 Series FPGAs one by one.
Logic Blocks
Logic blocks are like the heart of FPGAs which will be utilized to implement the required functionality along with other blocks. 7 series Configurable Logic Blocks (CLB) are not very different from Spartan 6 CLBs. Both of them contain 2 slices where each slice consists of four 6 input Look Up Tables (LUT) and 8 Flip Flops, Multiplexers, and an arithmetic carry chain. LUTs can also be used as two 5 input LUTs with two outputs.
Both Spartan 6 and 7 series FPGAs consist of SLICEL and SLICEM, where SLICEM can also be configured as 64-bit RAM or 32-bit Shift Register. SLICEX which was present in Spartan 6 is not present in 7 series FPGAs but this was a very basic structure similar to SLICEL without arithmetic carry chains, hence it is automatically retargeted to SLICEL. Additionally, 7 series FPGAs contain more routing logic between CLBs.
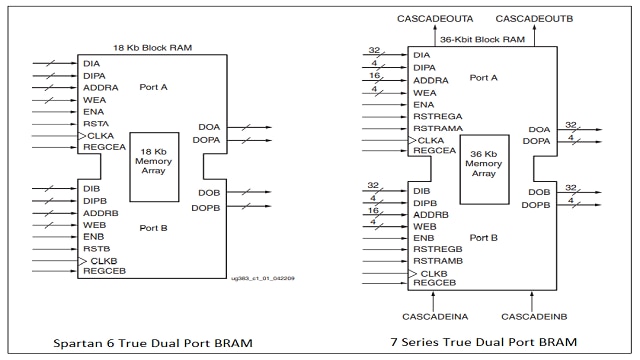
Block RAM
Spartan 6 FPGAs contain BRAM cells of 18 Kb in size, each block can also be used as two independent 9 Kb blocks. Whereas 7 series FPGAs offer 36 Kb BRAM cells which can be broken into two 18 Kb blocks. Additionally, the 7 series also offer some features like built-in ECC, dedicated integrated FIFO, and cascading of BRAMs to form a larger block.
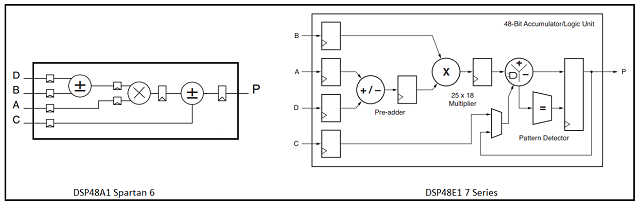
DSP
FPGAs are efficient in implementing DSP algorithms parallel to digital logic with the help of dedicated DSP blocks. Spartan 6 DSP blocks are very simple and composed of an 18 x 18 multiplier along with a pre adder and post adder. 7 series FPGAs DSP48E1 consists of a 25 x 18 multiplier, 48-bit accumulator, pre adder, optional logic block capable of implementing up to 10 different functions (ALU) along with a Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) block, and a pattern detector.
SDRAM Memory Controllers
Spartan 6 includes hardened Memory Controller Blocks (MCB) supporting DDR, DDR2, DDR3, and LPDDR with data rates up to 800 Mb/s (12.8 Gb/s peak bandwidth). Whereas 7 series FPGAs does not include hardened memory controller hence soft memory controller needs to be implemented, this offers more flexibility. PHY is hardened to support the highest throughput up to 1866 Mb/s in Virtex 7 devices.
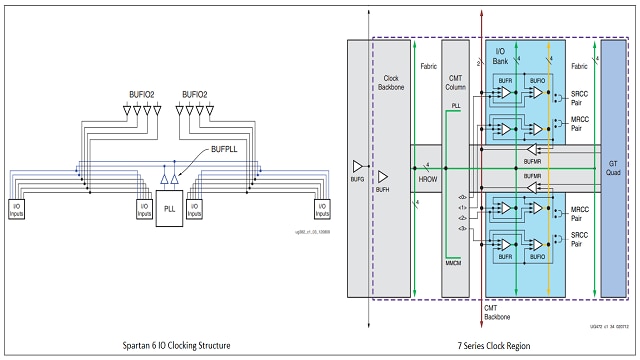
Clock Management Blocks
The clock is very important in digital circuit designs; Spartan 6 FPGA contains up to 6 Clock Management tiles each CMT contains 2 Digital Clock Managers (DCM) and 1 Phase Locked Loop (PLL). There are different clock buffers like BUFG, BUFGMUX, BUFIO2, BUFIO2_CLK, BUFPLL, and BUFH to provide jitter-free low skew clock routing.
Compared to Spartan 6, 7s series clocking structure is simple, flexible along with improved performance which contains up to 24 CMTs, each CMT consists of 1 MMCM and 1 PLL. MMCM is a new functional block with fractional divide and fine phase shifting capabilities. 7 series BUFIOs are similar to Spartan 6 but only span a single bank, each bank has BUFIOs. Many of the Buffers in Spartan 6 are not present in the 7 series and are replaced by new buffers.
IO Features
Spartan 7 FPGAs have up to 576 IOs with a maximum supported data rate of 1080 Mbps. All the features like I/O DDR, I/O DELAY, I/O SERDES, and voltage support up to 3.3v are present even in 7 series FPGAs. While 7 series offer up to 500 IOs with a maximum supported data rate of 1866 Mbps. the 7 series contains two different types of IO banks HPIO and HRIO, HR IOs support a wide range of voltage standards while HP IOs are optimized for the highest performance operation, from 1.2 to 1.8 V.
High-Speed Serial Transceivers
Spartan 6 LXT series of FPGAs contain up to 8 serial transceivers with a maximum supported line rate of 3.2 Gbps, while 7 series FPGAs contain up to 16 transceivers supporting 6.25 Gbps of line rate.
XADC
7 series FPGAs integrate XADC block supporting additional Analog Signal Processing along with system monitoring. XADC can directly replace the requirement of external ADC hence reducing power consumption and BOM cost.
Summary
Major differences between Spartan 6 and 7 series FPGA architecture are BRAM, DSP blocks, and Clocking resources. Additionally, the 7 series also offer built-in XADC. The development tool has also changed from ISE to Vivado over a span of time.
References
[1] Migrating from Spartan 6 to 7 series white paper by Adam Taylor
[2] Xilinx ISE to Vivado Design Suite Migration Guide
[3] Xilinx 7 series FPGAs Product Selection Guide

