This learning module discuess remote monitoring including basic concepts, challenges, applications and the IoTConnect platform.
1. Introduction | 2. Objectives | 3. Basic Concepts | 4. Analysis/Applications | 5. Glossary | Related Components | Test Your Knowledge
Manufacturers and plant operators are compelled to efficiently monitor their assets, extract maximum asset performance, and respond swiftly to breakdowns. Remote monitoring (RM) eliminates on-scene presence. It takes several forms, including using cloud data storage to keep your data ready on deck, combining sensors, transmitters, receivers, data storage, processing, and analytics. IIoT-enabled remote monitoring frameworks achieve substantial improvements in asset management, operational efficiency, and cost. This learning module discuess remote monitoring including basic concepts, challenges, applications and the IoTConnect platform.
This element14 ESSENTIALS learning module explores the mindset, approach, and tools sets that can be used to help us discover issues in our designs and ensure a successful delivery.
2. Objectives
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
 Describe the role of remote monitoring in the Industrial IoT market
Describe the role of remote monitoring in the Industrial IoT market
 Understand the basics concept of Remote Monitoring
Understand the basics concept of Remote Monitoring
 Discuss the importance of IoTConnect and its application scenarios
Discuss the importance of IoTConnect and its application scenarios
 Explain the challenges and benefits of adopting remote monitoring
Explain the challenges and benefits of adopting remote monitoring
Remote monitoring (RM) is the ability to visualize, track, follow, and control assets and facilities by staying informed about the performance of applications without having to be on-site. It offers a connected environment for businesses to gain complete visibility into their assets and facilities being physically absent at the location. This capability is made possible through multiple technologies such as wireless networks, sensors, transmitters, receivers, data processing, cloud storage, and analytics.
- 3.1 Challenges faced while adopting RM
A successful project or transition must anticipate and consequently mitigate risks. Adopting RM can be a challenge. Any successful project requires measurable solutions with well-defined goals. Work management should not involve a radical change in the existing process. The initial process must lend itself to monitoring, then slowly expand capabilities to automate the response.
A team may be required, depending on the solution specified, to get it operational. Some systems offer plug-and-play capabilities that reduce installation time. IT department should approve the new technology and protocols, helping to identify and implement changes to the wired and/or wireless networks.
- 3.2 Benefits of RM
Some direct benefits include improved team efficiency, swifter incident response, real-time anomaly detection, and the provision of predictive maintenance. Remote monitoring with IIoT enables you to access asset information anywhere, anytime, and on any device. A smart sensor accurately monitors by digitally collecting and storing data, thereby reducing the probability of errors, and ensures accuracy in collecting repetitive data over manual methods. It also optimizes operations and gains maximum asset productivity, which translates to cost savings and improved profitability. A remote monitoring system ensures a steady stream of data flowing into the easily accessible cloud storage. It also assists regulatory compliance.
- 3.3 Remote monitoring Wireless System
An RM system includes two components: a transmitter or end unit and a receiver or coordinator. The transmitter captures the raw data, flowing directly from a thermocouple or RTD (temperature), pressure transducer, flowmeter, or other sensors. After capturing the data, the transmitter wirelessly transmits the data. A receiver, contrarily, receives the wireless signal from transmitters and transfers that data to another component, which can be Ethernet, to a local display or controller, or an industrial controller.
Depending on the application, the receiver may be a simple conduit for moving the data from one location to another, a panel meter or other indicator, or a controller, providing either relay, SSR, or analog outputs for process management. It is vital during receiver selection to ensure that the receiver is compatible with the desired transmitter/end unit.
- 3.4 Technology used in remote monitoring
Ethernet/internet-based data monitoring offers new capabilities and unprecedented access to process measurement and control. Using standard process sensors, such as thermocouples or RTDs (temperature), pressure transducers, flowmeters, or other sensors that produce a standard analog or pulse output, one can monitor, control or log data in almost from any location. These Ethernet-based sensor networks are connected to the internet through iServer technology by supporting a total of nine standard internet and networking protocols, removing the need for setup and configuration.
The iServer configures quickly and easily using either a web browser from any computer on the network or the iConnect software. The iServer can manage any machine and any version of the operating system. You can use the terminal emulator to send simple text commands to the iServer. For example, to show current settings or to send simple text instructions. IServer technology adds new capabilities to signal conditioners, indicators, meters, and controllers that make an excellent adjunct to typical process measurement and control instrumentation. This internet-enabled instrumentation enables remote access from anywhere, 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, wherever you have internet access.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) consists of networked devices creating systems that monitor, collect, exchange, and analyze data to enable smarter, faster business decisions for industrial companies. The benefits of applying IIoT approaches to industrial business problems are substantial. It improves efficiency and safety, maintains longer uptime, and helps in Predictive Maintenance. The machines get repaired even before they fail.
RM takes several forms, including using cloud data storage to keep your data available at your fingertips, combining sensors, transmitters, receivers, data storage, processing, and analytics. It overcomes "resistance to change" which is a common observation in industries. IIoT can bring something new to the industrial landscape and justify the time and money spent incorporating the technology.
- 4.1 Edge computing using Omega smart sensors
Edge computing involves three fundamental layers: sensors or edge devices, edge gateway, and the cloud or central server. The embedded microprocessor within Smart sensors or edge devices collects vital measurements from connected sensors. Smart sensors or edge devices collect data measurements such as time-stamp, hours of operation, connectivity, calibration conformance, and a host of other micro-operations. An edge gateway, the central repository for edge devices data, sits between the edge devices and the cloud. The cloud receives only higher-order data processes for modeling and analytics. Cloud is an interconnected network of virtual servers and web services hosted on the internet. It is where the higher-order data from the edge gateways get stored, processed, and analyzed.
Omega’s Smart Probe (SP series) sensors are an excellent example of industrial edge computing devices. These sensors have the differentiated feature of onboard local control and closed-loop control at the point of sense, eliminating the need for multiple single-purpose devices that need separate configurations. Some of the smart sensors also feature real-time autonomous control through the alarm and control. The sensor can be set to transmit data only when there is a desired significant change in the value. Such a feature extends the device's battery life. This smart sensor can also trigger Digital I/O pins that can be connected to an alarm or relay information even when the network is down.
- 4.2 Avnet's IoT Connect platform
Avnet’s IoTConnect is a cloud platform that facilities device communication and management, data storage, app creation, and robust security protocols. The full-featured secure, flexible, scalable platform can develop and manage end-to-end IoT solutions. IoTConnect is a full-fledged platform as a Service (PaaS) built on Microsoft Azure services. It bundles IoT hardware, software, applications, data analytics, and artificial intelligence capabilities with an easy-to-use toolkit. It reduces complexity, cost, and time to market and thus helps OEMs access an ever-expanding set of sensor solutions. It’s a bridge between real things and the digital world that allows you to add, create, customize and manage your IoT devices.
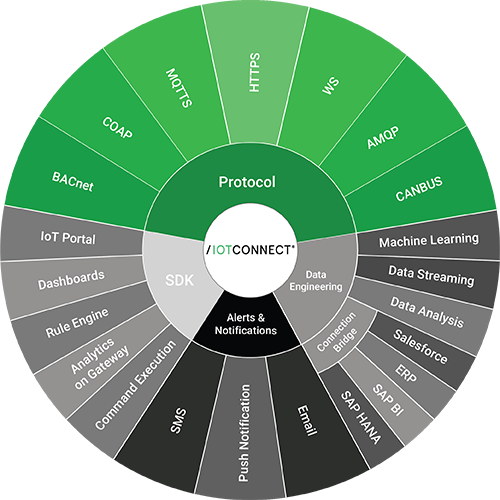
Figure 1: IoTConnect components
In the preceding figure, the IoTConnect platform consists of various components like tools, technologies, SDKs, APIs, and protocols that support multiple created IoT solutions. IoTConnect supports many standard protocols to connect your enterprise. It enables information extraction, connects existing systems, and supports several types of alerts and notifications. IoTConnect provides a matrix of devices, sensors, gateways, actuators, and other modules. These devices collect various data at different intervals that are then monitored, filtered, and processed in real-time to provide you with actionable insights.
The IoTConnect architecture consists of components like Compute, Storage, Integration tools, and AI & visualizations. Compute Creates powerful cloud apps for web and mobile and get real-time analytics and insights from apps, sensors, and other devices. Storage allows you to store both structured and unstructured data in its globally distributed database. Integration tools offer reliable and secure bidirectional communications for millions of IoT devices and implement scalable integrations and workflows in the cloud. AI & visualizations provide modern AI techniques to identify hidden patterns in your data and efficiently visualize the data.
As a member of the IoTConnect Partner Program, Omega offers a Smart Sensor Suite that’s fully compatible with all the hardware and software you need to build a complete sensor-to-cloud technology stack. The partnership will provide all the advisory, design and build, and support services you’ll require throughout your devices’ entire lifecycle.
One can combine Avnet’s IoTConnect Platform with Omega’s IoTConnect-certified sensors, monitors, and transmitters to build an end-to-end IIoT solution that’s both complete and secure. This Solutions Hub has an extensive library of supported devices, sensors, and solution accelerators available in ExpressConnect. IoTConnect adds the highest levels of encryption in data transmission and explicitly ensures the authenticity of each device and gateway.
- 4.3 ExpressConnect Overview
Avnet ExpressConnect tool provides developers and non-programmers with the ability to deploy combinations of connected IoT solutions. It solves the challenges faced during IoT implementation so that one can focus on what's important. It provides a dramatic reduction in development effort and resources, quickening time to market.
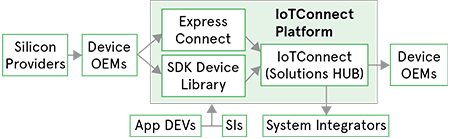
Figure 2: Block diagram of ExpressConnect offering portfolio
The preceding figure shows how ExpressConnect provides services to OEMs, system integrators, and solution providers to accelerate IoT implementation from POC to production. Avnet manages and secures the IoT-based designs created in Express Connect through the IoTConnect platform built on Microsoft Azure. Solution developers and OEMs create cloud-based applications that easily communicate with the Avnet IoTConnect API, avoiding the complexity of sensor interfaces, protocols, security, and device management.
ExpressConnect allows you to create and design the entire data flow, which when published, gets reflected as a template in IoTConnect. The template is essential in the IoT platform to define device properties like device type, connectivity, type of data, and actions to take when particular data is received. Manual template creation can be a little tedious. It depends on the number of devices you want to connect. ExpressConnect reduces the steps with an easy drag and drop interface that enables the efficient design of data flow. A template creates in IoTConnect with identical properties.
- 4.4 Application
1. Smart Energy Monitoring Solution
Avnet’s Smart Energy Monitoring Solution offers an all-inclusive software service that enables organizations and institutions to enjoy substantial enhancements on efficient energy usage while reducing conservation effects, energy consumption, and functioning expenses. With IoT sensors gathering data in real-time, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence, the solution can enable enormous energy-saving prospects.
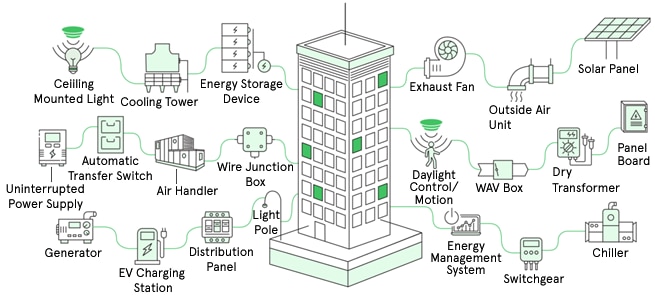
Figure 3: Smart Energy Monitoring Solution
As shown in the preceding figure, the smart sensor detects anomalies and abnormal patterns that can indicate potential failures and help with risk mitigation. It manages energy consumption conferring to economic and commercial standards, leading to smaller energy costs and increased occupant comfort. Avnet’s IoTConnect provides centralized monitoring with the ability to control in real-time and simplifies energy conservation efforts. It helps organizations to reduce expenditure on energy by optimizing energy use and preventing wastage. The system amalgamation reduces maintenance and operations costs, which results in continued savings.
2. Smart Asset Monitoring Solution
Avnet’s Smart Asset Monitoring solution enables industries to locate their assets and monitor their performance. This solution helps machines and equipment to infer information from collected data, measure the KPIs, and detect deviations. Avnet’s IoTConnect helps to monitor the combination of all processes, assets, workflows, and analytics in a single solution, to offer a centrally consolidated tracking, monitoring, and analytics system for asset-intensive sectors like manufacturing, industrial machinery, power & utilities, mining, oil & gas, healthcare, etc.
As IoT-based solutions are decisive to gain competitive advantage, IoTConnect enabled asset monitoring and management solutions help you to gain better control over your equipment and machinery. They also make a positive impact on various aspects like increasing efficiency and productivity. These solutions reduce operational costs and increase customer satisfaction.
Application Programming Interface (API): An application programming interface (API) is an interface that allows the user to access information from another service and integrate this service into their own application.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): A field of computer science dedicated to the study of computer software making intelligent decisions, reasoning, and problem solving.
Cloud: Refers to software and services that run on the Internet, instead of locally on your computer.
Cloud Storage: A model of computer storage in which data is stored in facilities (often multiple facilities) managed by a hosting company (cloud service provider) and is accessed remotely by the user via a network.
Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP): A specialized Internet Application Protocol for constrained devices, as defined in RFC 7252. It enables those constrained devices called "nodes" to communicate with the wider Internet using similar protocols.
Database: An organized collection of data.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): A term synonymous to Industry 4.0. It describes smart factories which contain intelligent machines using wireless connectivity, sensors, automation controllers, and AI to manufacture products with independent decision making.
Internet of Things (IoT): Refers to the ever-growing network of physical objects that feature an IP address for internet connectivity, and the communication that occurs between these objects and other Internet-enabled devices and systems.
Internet of Things (IoT): Refers to the ever-growing network of physical objects that feature an IP address for internet connectivity, and the communication that occurs between these objects and other Internet-enabled devices and systems.
Machine learning (ML): A field of AI focused on getting machines to act without being programmed to do so. Machines “learn” from patterns they recognize and adjust their behavior accordingly.
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT): A lightweight messaging protocol for use in cases where clients need a small code footprint and are connected to unreliable networks or with limited bandwidth resources. It is primarily used for machine-to-machine (M2M) communication or Internet of Things types of connections.
Modbus: An open, non-proprietary communication protocol that lets industrial systems to communicate with each other, gather data, and transmit results to a computer.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): A model of cloud computing in which a vendor provides the hardware and software tools necessary to create, deploy and manage applications at scale to the user via the internet, as a service.
Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD): A device with a significant temperature coefficient (that is, its resistance varies with temperature). It is used as a temperature measurement device, usually by passing a low-level current through it and measuring the voltage drop.
Software development Kit (SDK): Set of development tools that aids or allows the creation of applications for a certain platform. SDKs typically include APIs, sample code, documentation, debuggers and other utilities.
Solid State Relay (SSR): A relay that does not have a moving contact as compared to mechanical relays that have moving contacts. It employs semiconductor switching elements, such as thyristors, triacs, diodes, and transistors.
*Trademark. Omega Engineering is a trademark of Omega Engineering Corp. Other logos, product and/or company names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Related ComponentsBack to Top

This element14 ESSENTIALS of Remote Monitoring learning module explores the mindset, approach, and toolsets that can be used to help us find issues in our design and ensure a successful delivery. To extend the knowledge covered in the main module, this supplementary guide discusses the types of related components used for debugging or product development.
Remote Monitors

4-20 mA – Modbus Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
The 4-20 mA – Modbus Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit is a Sensor interface with integrated MEMS sensor technology. It contains SP-014-1 Smart Sensor, M12.5-S-M-FM/M12.5-B-S-M-FM Connectors, IF-002 Interface, PSU-93 Power Supply. It provides uniform multi-sensor interface across all sensor types. The IF-002 provides seamless integration of your Layer N Smart Probe to Modbus network, it does Smart Sensor to Modbus conversion. The PSU-93 is an unregulated power supply providing 16 to 23 Vdc with a maximum output of 300mA. It provide power for signal conditioners, temperature and pressure transmitters and other electronic equipment. SP-014 is a Layer N M12 Modular Smart Probe Analog Process interface with I/O. The SP-014 accepts standard process signals through its M12 5-pin connector and Layer N Smart Interfaces through its M12 8-pin connector. M12.5-S-M-FM / M12.5-B-S-M-FM is an 5-pin screw terminal Compensated M12 Field Mount Thermocouple Connectors, These connectors can be used with M8 RTD, M12 RTD or M8 & M12 Thermocouple extension cables.

USB Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
This is a Sensor interface with integrated MEMS sensor technology. It contains SP-013-1 Smart Sensor, M12.5-S-M-FM/M12.5-B-S-M-FM Connectors, IF-001 Interface, PSU-93 Power Supply. M12.5-S-M-FM provides 5 pin Screw Terminal connector, SP-013-1 processes and converts digital pulses to Smart Sensor digital interface. The Omega IF-001 Smart Interface cable provides an easy way to configure and monitor Omega Smart Probes. The USB 2.0 compliant device appears as a serial port and is compatible with Windows, iOS, and Linux. The IF-001 provides a Modbus RTU or Modbus ASCII interface to the entire smart sensor register set.

RTD/TC – Wireless Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
The smart RTD/TC wireless connectivity kit consist of M12-S-M-FM Sensor Connector, XW-EDA Interface, ZW-REC Wireless Receiver. M12-S-M-FM provides 4 pin Screw Terminal connector (Not required for M12 based probes). ZW-REC receiver provides Ethernet connection to SmartEdge gateway, it supports up to 128 XW-EDA transmitters. XW-EDA converts TC or RTD signals to Smart Sensor digital interface and transmits wirelessly to ZW-REC receiver, it supports up to 2 Thermocouple Sensors or 1 RTD Sensor.

Load Cell – Wireless Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
This smart load cell wireless connectivity kit provides Bridge Interface. It consists of SP-010-1 Smart Analog interface sensor, M12-S-M-FM Conn, DM12CAB-8-1 Cable, XW-ED Interface, ZW-REC Wireless Receiver. SP-010-1 converts Load Cell Bridge input to Smart Sensor digital interface, DM12CAB-8-1 provides M12 8-pin Interface cable used for smart sensors, transmitters, and dual RTD sensors. XW-ED connects Smart Probe digital interface and transmits wirelessly to ZW-REC receiver. The ZW-REC connects to up to 255 wireless transmitters and helps to View the data on the built in webpage.

Load Cell – USB Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
This smart load cell USB connectivity kit provides Bridge Interface which is a common means to detect small changes in resistance. It consists of M12-S-M-FM which provides 4 pin Screw Terminal connector, SP-010-1 converts Load Cell Bridge input to Smart Sensor digital interface, IF-001 provides Smart Sensor to USB conversion.

Digital – Modbus Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
This is a Sensor interface with integrated MEMS sensor technology. It contains SP-013-1 Smart Sensor, M12.5-S-M-FM/M12.5-B-S-M-FM Connectors, IF-002 Interface, PSU-93 Power Supply. SP-013-1 Digital Interface Smart Probe processes and converts digital pulses to Smart Sensor digital interface, it integrates to Layer N Ecosystem. M12.5-S-M-FM provides 5 pin Screw Terminal connector, IF-002 provides seamless integration of your Layer N Smart Probe to Modbus network, it provides RS485 serial interface supporting Modbus RTU and command line interpreter.

SmartProbe – Modbus Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
This kit consist of DM12CAB-8-1 Sensor Cable, XW-ED Interface, ZW-REC Wireless Receiver. DM12CAB-8-1 provides M12 8-pin Interface cable used for smart sensors, transmitters, and dual RTD sensors, XW-ED connects SmartProbe digital interface and transmits wirelessly to ZW-REC receiver, ZW-REC supports up to 128 XW-ED transmitters.

4-20 mA – Wireless Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
This kit consist of M12.8-S-M-FM Sensor Connector, XW-ED Interface, PSU-93 Power Supply, ZW-REC Wireless Receiver. 4-20 mA is a very common means to connect ‘field devices’ (Sensors) to control and monitoring equipment. PSU-93 Provides Excitation current, M12.5-S-M-FM provides 8 pin Screw Terminal connector, XW-ED converts 4-20 mA to Smart Sensor digital interface and transmits wirelessly to ZW-REC receiver, it supports up to 2 external 4-20 Process Signals. ZW-REC receiver provides Ethernet connection to SmartEdge gateway, it supports up to 128 XW-EDA transmitters.

Wireless Smart Sensor Connectivity Kit
This smart digital wireless connectivity kit consists of: M12.8-S-M-FM Sensor Connector, XW-ED Interface, PSU-93 Power Supply, ZW-REC Wireless Receiver. The XW-ED is a rugged wireless transmitter which connects to any Layer-N Smart Probe and transmits to a ZW-REC receiver. The ZW-REC connects to up to 255 wireless transmitters. It helps in viewing the data on the built in webpage. No PC required. It is OEG Compatible and supports all XW, ZW and most UW transmitters.
Test Your KnowledgeBack to Top

Are you ready to demonstrate your Remote Monitoring knowledge? Then take this 10-question quiz. To earn the IoT V Badge, read through the module attain 100% in the quiz, leave us some feedback in the comments section, and give the module a rating.


